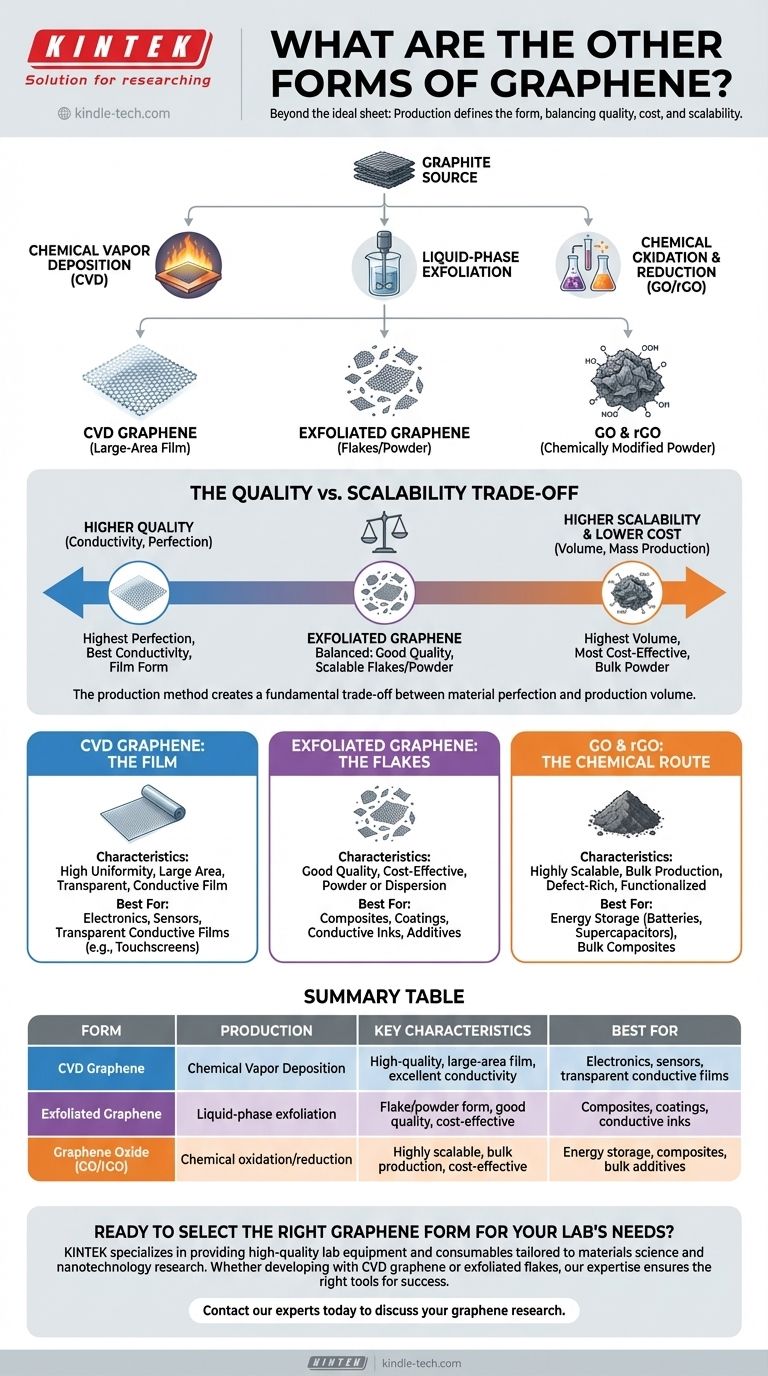
Beyond the ideal sheet, graphene is not a single material but a family of materials whose "form" is defined by its production method. The most common forms are CVD graphene, grown as a large sheet on a substrate; exfoliated graphene, which consists of tiny flakes derived from graphite; and graphene oxide (and its reduced form), which is produced through a bulk chemical process. Each form possesses a different balance of quality, cost, and scalability.
The "form" of graphene is a direct consequence of its manufacturing process. This creates a fundamental trade-off between the material's quality (like perfect conductivity and strength) and its scalability for real-world applications. There is no single "best" form—only the most appropriate form for a specific goal.

The Graphene Family: Production Defines the Form
The theoretical concept of graphene is a perfect, single-atom-thick layer of carbon. However, producing this ideal structure in useful quantities is the central challenge. The different production methods give rise to distinct forms of graphene, each with its own characteristics.
CVD Graphene: The Large-Area Film
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process that "grows" a continuous, high-quality sheet of single-layer graphene on a metal catalyst substrate, typically copper.
This method produces graphene that is highly uniform and can cover large areas, making it exceptionally well-suited for applications requiring a transparent, conductive film. It is the closest commercially available form to the theoretical ideal of a perfect graphene sheet.
Exfoliated Graphene: The High-Volume Flakes
This form is produced by breaking apart bulk graphite into tiny flakes, often consisting of one to a few layers of graphene. This process, known as liquid-phase exfoliation, typically involves high-energy mixing of graphite in a liquid.
The result is not a continuous sheet but a powder or a dispersion of graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs). Because it can be produced in large quantities at a lower cost, it is ideal for mixing into other materials to create composites.
Graphene Oxide (GO) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO): The Chemical Route
This is a multi-step chemical process for mass production. First, graphite is aggressively oxidized to create graphene oxide (GO), a material rich in oxygen-containing groups that is easily dispersed in water.
In a second step, the GO is "reduced" to remove most of the oxygen and restore graphene-like properties, creating reduced graphene oxide (rGO). While highly scalable, this process introduces structural defects that compromise some of the material's pristine properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Quality vs. Scalability
Choosing the right form of graphene requires understanding the compromises inherent in each production method. The primary trade-off is between the structural perfection of the material and the cost and volume of its production.
The Quality Spectrum
The production method directly impacts the defect density and, therefore, the properties of the final material.
- CVD graphene offers the highest quality, with large, uniform crystal domains and minimal defects. This preserves its exceptional electrical conductivity and transparency.
- Exfoliated graphene has higher quality than rGO but consists of small, individual flakes. Its properties depend heavily on the size and thickness of these flakes.
- Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) has the most structural defects due to the harsh chemical processing. These defects disrupt the honeycomb lattice, reducing its electrical and thermal conductivity compared to other forms.
The Scalability and Cost Spectrum
Scalability is often inversely proportional to quality. The methods that produce the highest quality material are typically the most difficult and expensive to scale.
- GO and rGO are by far the most scalable, with production capacity reaching tons per year. This makes them the most cost-effective option for bulk applications.
- Exfoliated graphene also offers good scalability and is becoming increasingly cost-competitive for use in composites, inks, and coatings.
- CVD graphene is the least scalable and most expensive, as it involves slow, high-vacuum deposition processes. Its use is limited to high-value applications where its unique film properties are essential.
The Form Factor Divide
A critical distinction is whether you need a continuous sheet or a bulk additive.
- CVD graphene is a film. It exists only as a large, continuous, atom-thin layer on a substrate (which can later be transferred). It's used for surfaces.
- Exfoliated graphene and rGO are powders or dispersions. They are meant to be mixed into liquids, polymers, or cements to enhance their properties from within.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision depends entirely on your specific engineering or research goal. There is no universally superior form of graphene.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or sensors: You need the large, uniform, and highly conductive film provided by CVD graphene.
- If your primary focus is creating stronger composites or conductive inks: You need the cost-effective bulk volume of exfoliated graphene nanoplatelets or rGO.
- If your primary focus is energy storage (e.g., batteries or supercapacitors): You need a scalable material with a high surface area, making rGO a common and practical choice.
Ultimately, navigating the world of graphene means matching the form of the material to the function it must perform.
Summary Table:
| Form of Graphene | Production Method | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVD Graphene | Chemical Vapor Deposition | High-quality, large-area film, excellent conductivity | Electronics, sensors, transparent conductive films |
| Exfoliated Graphene | Liquid-phase exfoliation | Flake/powder form, good quality, cost-effective | Composites, coatings, conductive inks |
| Graphene Oxide (GO/rGO) | Chemical oxidation/reduction | Highly scalable, bulk production, cost-effective | Energy storage, composites, bulk additives |
Ready to select the right graphene form for your lab's needs? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to materials science and nanotechnology research. Whether you're developing next-generation electronics with CVD graphene or enhancing composite materials with exfoliated flakes, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your graphene research and development projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How does a Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) reactor function? Expert Guide to Diamond Film Fabrication
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems



















