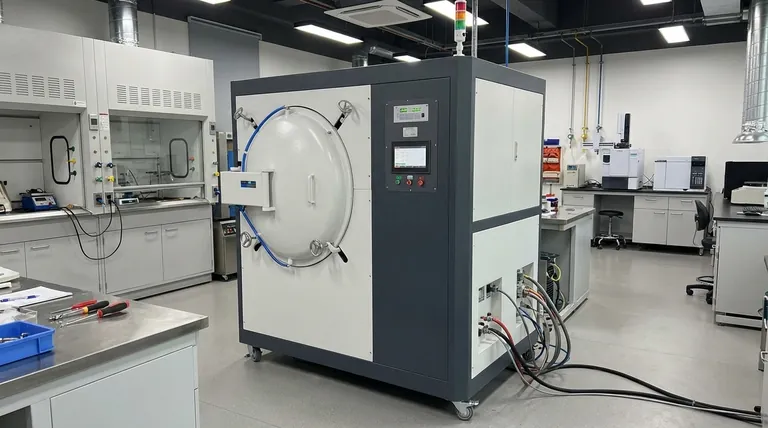
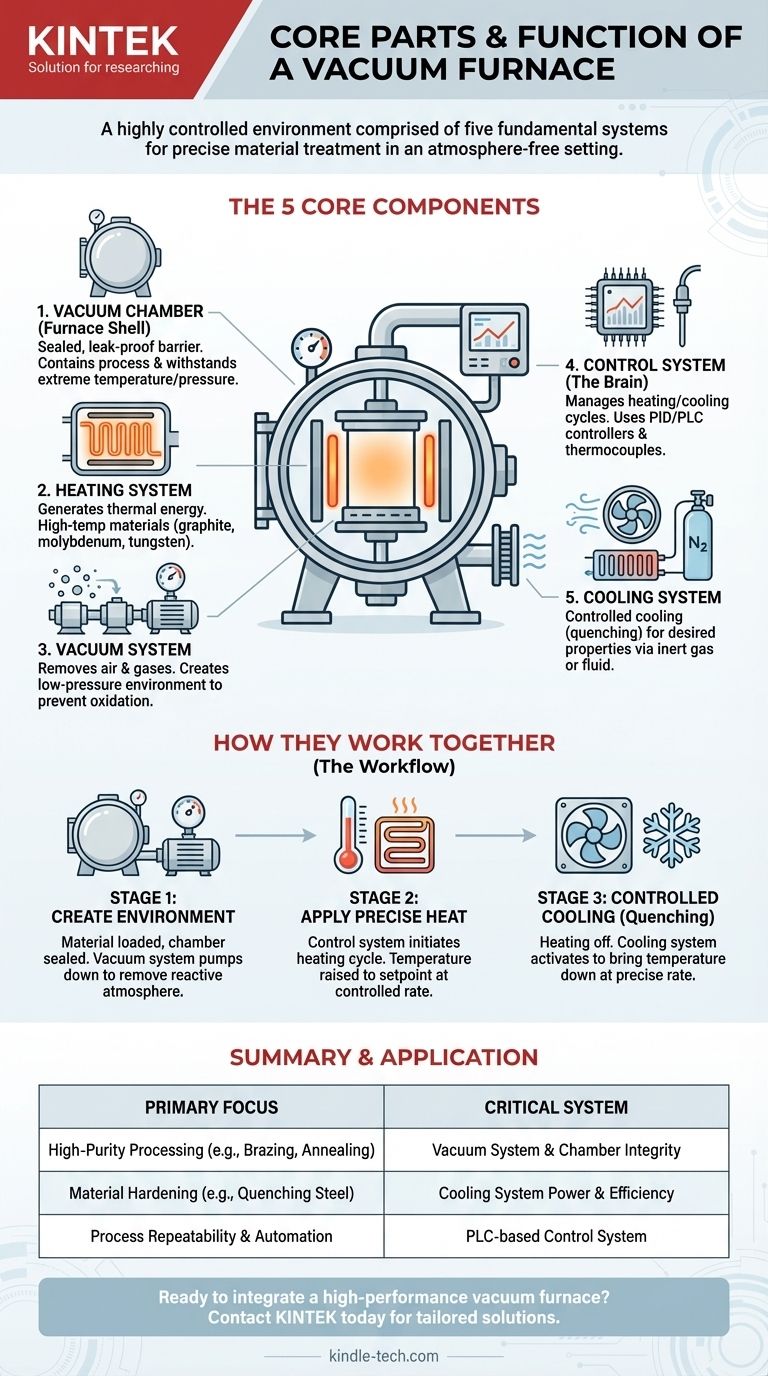
At its core, a vacuum furnace is a highly controlled environment. It is comprised of five fundamental systems that work in concert: the vacuum chamber, the heating system, the vacuum system, the cooling system, and the control system. These components allow for the precise heating and cooling of materials in an atmosphere-free environment, which prevents oxidation and contamination.
A vacuum furnace is not simply a box that gets hot. It is a sophisticated instrument where the removal of air (the vacuum) is just as critical as the application of heat, enabling material treatments that are impossible in a conventional oven.

The Core Components of a Vacuum Furnace
Each part of a vacuum furnace plays a distinct and critical role in the overall process. Understanding how they interrelate is key to understanding the furnace's capabilities.
The Vacuum Chamber (Furnace Shell)
This is the sealed, leak-proof vessel that contains the entire process. It is the physical barrier between the controlled interior environment and the outside atmosphere.
The chamber must be robust enough to withstand both extreme temperatures and the immense external pressure created when the inside is pumped down to a vacuum.
The Heating System
This system is responsible for generating the thermal energy required for the process. It is typically located inside the vacuum chamber.
Heating elements are often made from materials like graphite or specialized ceramics and metals (like molybdenum or tungsten) that can withstand very high temperatures without degrading in a vacuum.
The Vacuum System
The vacuum system is the heart of the furnace's unique capability. It consists of a series of pumps and measurement gauges designed to remove air and other gases from the chamber.
This system creates the low-pressure environment that prevents oxidation and removes impurities, which is the primary reason for using a vacuum furnace in the first place.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the operation. It precisely manages the heating and cooling cycles according to a predefined program.
It uses sensors, such as thermocouples, to measure the temperature and sophisticated controllers (PID or PLC systems) to regulate the power sent to the heating elements, ensuring the material follows an exact thermal profile.
The Cooling System
After the heating cycle is complete, the material must be cooled in a controlled manner. This is the job of the cooling system, which is critical for achieving the desired material properties (e.g., hardness).
This is often accomplished by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon, which is then circulated by a fan over the hot parts to remove heat rapidly. Some systems may also use fluid-carrying pipes for liquid quenching.
How These Components Work Together
The operation of a vacuum furnace is a sequential process where each system hands off to the next. This precise interplay is what allows for advanced material processing.
Stage 1: Creating the Environment
First, the material is loaded and the vacuum chamber is sealed. The vacuum system then activates, pumping down the chamber to the required vacuum level, removing the reactive atmosphere.
Stage 2: Applying Precise Heat
Once the target vacuum is reached, the control system initiates the heating cycle. It sends power to the heating system, raising the temperature at a controlled rate until it reaches the setpoint for the process (e.g., brazing, annealing, hardening).
Stage 3: Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
After the material has "soaked" at the target temperature for the required time, the heating elements are turned off. The control system then activates the cooling system to bring the temperature down at the precise rate needed to lock in the desired metallurgical structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific design and capability of these components determine what a furnace can be used for. Understanding your goal helps clarify which system is most important.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing (e.g., brazing, annealing): The integrity of the vacuum system and the leak-proof quality of the chamber are your most critical factors to prevent contamination.
- If your primary focus is material hardening (e.g., quenching steel): The power and efficiency of the cooling system are paramount for achieving the rapid cooling rates necessary for creating hardness.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and automation: A sophisticated PLC-based control system is essential for ensuring every cycle runs exactly the same way without manual intervention.
By understanding how these core systems function together, you can better diagnose issues, plan processes, and appreciate the furnace as a complete and integrated tool.
Summary Table:
| System | Primary Function | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed vessel to contain the process | Robust, leak-proof shell |
| Heating System | Generates thermal energy | Graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten elements |
| Vacuum System | Removes air and gases | Pumps and measurement gauges |
| Control System | Manages heating/cooling cycles | PLC/PID controllers, thermocouples |
| Cooling System | Cools material at a controlled rate | Gas quench (N2, Argon), fans, heat exchangers |
Ready to integrate a high-performance vacuum furnace into your lab?
Understanding the components is the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces, tailored to your specific application—whether it's high-purity annealing, precise brazing, or rapid quenching for material hardening.
Our experts will help you select a system where the vacuum chamber, heating elements, and control systems work in perfect harmony to ensure process repeatability and superior results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory's thermal processing needs and discover the right solution for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- Can I vacuum the inside of my furnace? A Guide to Safe DIY Cleaning vs. Professional Service



















