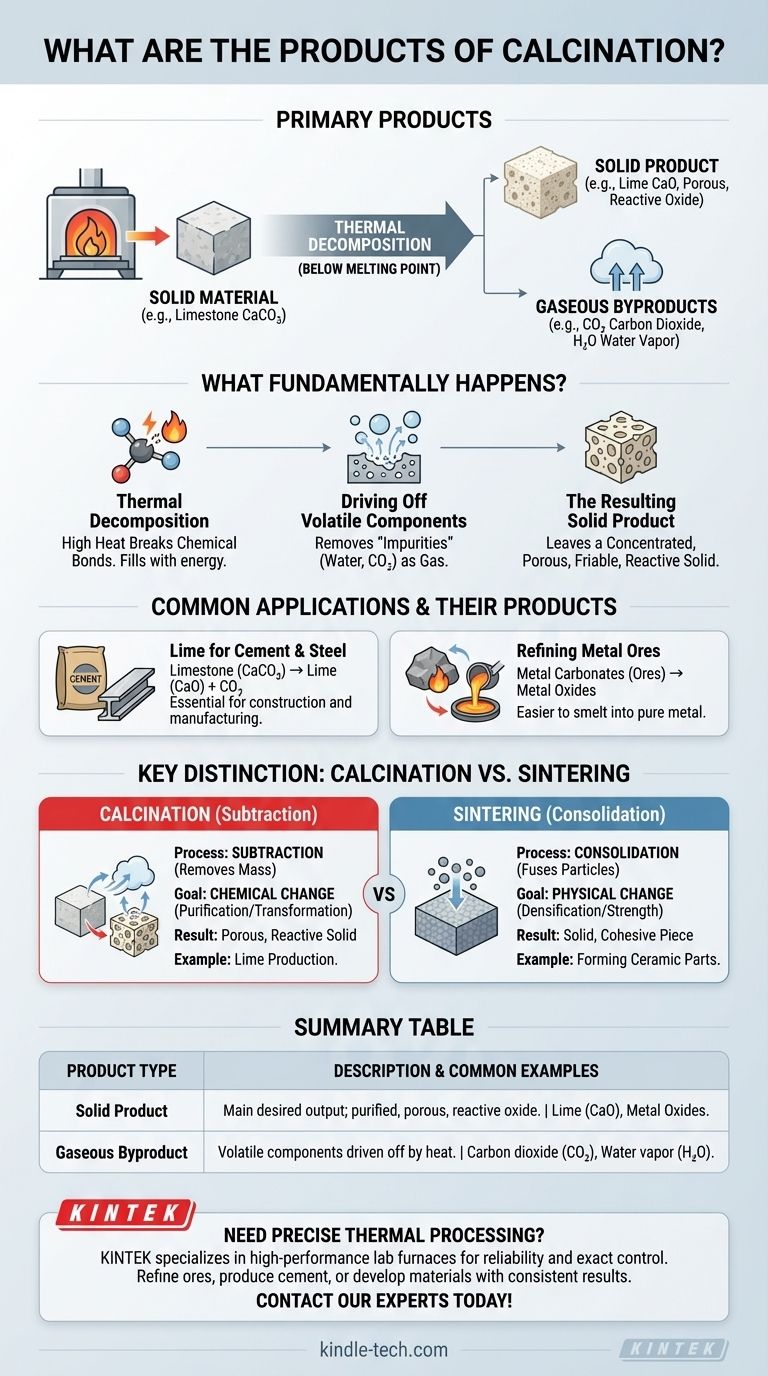
In short, the primary products of calcination are a solid material that has undergone thermal decomposition and one or more gaseous byproducts. For instance, when limestone (calcium carbonate) is calcined, it decomposes into solid lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide gas, which is driven off by the heat. The resulting solid is the main desired product.
Calcination is fundamentally a purification and transformation process. Its purpose is to heat a solid material to break it down chemically, driving off volatile components like water or carbon dioxide to produce a more concentrated, porous, or reactive solid.
What Fundamentally Happens During Calcination?
The Principle of Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a process of thermal decomposition, meaning it uses high heat to break down a compound into simpler substances. Critically, this occurs at a temperature below the material's melting point.
The process forces a chemical change by breaking bonds. The most common example is the decomposition of a carbonate into its oxide and carbon dioxide gas.
Driving Off Volatile Components
The core goal of calcination is to remove "volatile" substances that are chemically bound within the solid. The reference notes this as the "removal of impurities."
These substances are typically water (from hydrated minerals), carbon dioxide (from carbonates like limestone), or other decomposable compounds. Heating provides the energy needed for these components to escape as gas.
The Resulting Solid Product
The solid that remains is the principal product. It is often an oxide of the original material, such as lime (CaO) from limestone (CaCO₃).
As the gas escapes, it leaves behind a porous, friable structure. This is why the reference describes the resulting lime as being in an "easily powdered condition," which increases its surface area and chemical reactivity.
Common Applications and Their Products
Production of Lime for Cement
The most iconic example is producing lime from limestone. The solid product, lime (calcium oxide), is a fundamental component of cement and is also used in steel manufacturing and chemical production.
Refining Metal Ores
Calcination is a vital step in metallurgy. Ores like zinc carbonate (smithsonite) or lead carbonate (cerussite) are heated to convert them into their respective oxides.
These metal oxides are the desired product because they are much easier to reduce (smelt) into pure metal in a subsequent step.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Calcination vs. Sintering
Calcination: A Process of Subtraction
Calcination is a subtractive process. It removes mass from the material in the form of gas.
Its primary goal is chemical change: to purify a material or convert it into a more useful chemical intermediate. The resulting solid is often more porous and physically weaker.
Sintering: A Process of Consolidation
Sintering, in contrast, is a process of consolidation. It uses heat to fuse or weld small particles together, increasing the material's density and strength.
No significant chemical change occurs, and no mass is lost. The goal is to turn a powder into a solid, cohesive piece, as noted in the reference.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The process you choose depends entirely on what you need the final material to do.
- If your primary focus is to purify an ore or create a chemical intermediate like lime: You are looking at calcination, where the key product is the solid oxide left after volatile gases are removed.
- If your primary focus is to create a strong, dense final part from a powder: You are looking at sintering, where the product is a solid mass formed by fusing particles without chemical change.
Ultimately, understanding whether you need to decompose a material or consolidate it is the key to selecting the correct thermal process.

Summary Table:
| Product Type | Description | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Product | The main desired output; a purified, porous, and reactive oxide. | Lime (CaO) from limestone (CaCO₃), metal oxides from ores. |
| Gaseous Byproduct | Volatile components driven off by heat during decomposition. | Carbon dioxide (CO₂), water vapor (H₂O). |
Need precise thermal processing equipment for your calcination or sintering projects? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing systems designed for reliability and exact temperature control. Whether you are refining ores, producing cement, or developing new materials, our equipment ensures consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the results of calcination? A Guide to Purification and Material Transformation
- What is a biomass pyrolysis plant? Turn Waste into Renewable Energy & Biochar
- What is the high temperature of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniform Heating for Powders & Granules
- What are the raw materials for pyrolysis? From Waste to Energy with Versatile Feedstocks
- Is plastic pyrolysis energy efficient? Achieve a Positive Net Energy Balance with Smart Design
- What can pyrolysis oil be used for? A Guide to Fuel, Chemicals, and Waste Valorization
- What is the purpose of calciner? Boost Cement Production Efficiency & Clinker Formation
- How is torrefaction different from pyrolysis biochar? A Guide to Biomass Thermal Conversion



















