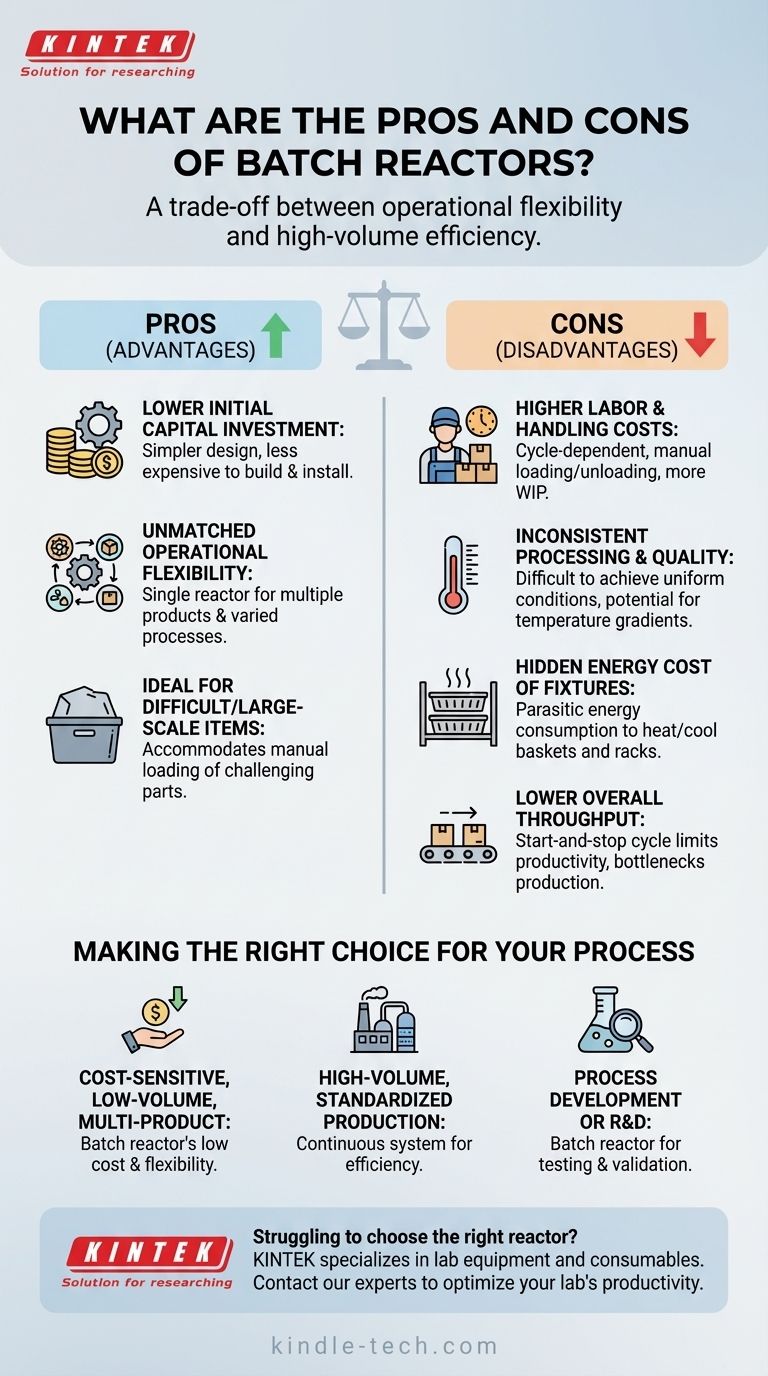
At its core, a batch reactor is a trade-off between operational flexibility and high-volume efficiency. It offers a lower initial investment and the versatility to handle varied processes, making it ideal for specific applications. However, these benefits come at the cost of higher labor requirements, potential inconsistencies in product quality, and lower overall throughput compared to continuous systems.
The decision to use a batch reactor is not about finding a universally superior option, but about matching the reactor's inherent characteristics—flexibility and low initial cost—to specific operational needs like low-volume production, process development, or handling difficult materials.

The Primary Advantages of Batch Operation
The appeal of a batch reactor lies in its simplicity and adaptability, which translates into several key business and operational advantages.
Lower Initial Capital Investment
Batch reactors are fundamentally simpler in design. They often consist of little more than a sealed vessel, which makes them significantly less expensive to build, purchase, and install than complex, integrated continuous systems.
This lower barrier to entry makes them an excellent choice for startups, smaller-scale operations, or for adding capacity without a massive capital outlay.
Unmatched Operational Flexibility
A single batch reactor can be used for multiple products, different process recipes, or varied heat treatment cycles with minimal changeover.
This versatility is invaluable in environments where production needs fluctuate, such as in contract manufacturing or facilities that produce a wide range of low-volume products. It is also ideal for research and development, where processes are constantly being tested and refined.
Ideal for Difficult or Large-Scale Items
Some materials or parts are simply too large, bulky, or difficult to handle for an automated continuous-feed system.
A batch reactor allows for the manual loading of these challenging items, providing a practical solution that continuous systems cannot easily accommodate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Inefficiencies
The flexibility of a batch reactor comes with inherent inefficiencies that must be carefully considered. These drawbacks are the primary reason continuous systems are preferred for mass production.
Higher Labor and Handling Costs
The batch process is cycle-dependent, requiring operators to manually load raw materials and unload finished products for every single run.
This also means more work-in-process (WIP) inventory is needed as parts must be gathered and staged to form a complete batch, adding to logistical complexity and labor cost.
Inconsistent Processing and Quality
Achieving uniform conditions within a batch is a major challenge. In a heat treatment furnace, for example, parts closest to the heat source will heat up much faster than those in the center of the load.
This temperature gradient can lead to inconsistent product quality, with variations from one part to another within the same batch.
The Hidden Energy Cost of Fixtures
Parts are typically loaded into a batch reactor using baskets, racks, or carts. This thermal mass must also be heated and cooled along with the product during every cycle.
This parasitic energy consumption significantly increases the overall heat load and drives up energy costs, an inefficiency that is largely absent in continuous systems where fixtures remain at a constant operating temperature.
Lower Overall Throughput
The total cycle time for a batch includes loading, heating, processing, cooling, and unloading. This start-and-stop nature inherently limits its productivity.
For high-volume needs, the downtime between batches creates a bottleneck that makes it impossible to compete with the non-stop output of a continuous reactor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The choice between a batch reactor and an alternative is a strategic one that depends entirely on your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive, low-volume, or multi-product manufacturing: A batch reactor's low initial cost and high flexibility are its greatest assets.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: The inherent inefficiencies in labor, energy, and throughput make a continuous system the clear choice.
- If your primary focus is process development or R&D: The ability to run small, varied, and isolated experiments makes a batch reactor the ideal tool for testing and validation.
By understanding these fundamental trade-offs, you can confidently select the right tool for your specific operational goal.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pros (Advantages) | Cons (Disadvantages) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower initial capital investment | Higher labor and handling costs |
| Flexibility | Unmatched versatility for multi-product use | Lower overall throughput |
| Operation | Ideal for difficult or large-scale items | Inconsistent processing and quality |
| Efficiency | Excellent for R&D and process development | Hidden energy cost from heating fixtures |
Struggling to choose the right reactor for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and solutions tailored to your specific processes—whether you need the flexibility of a batch reactor or the efficiency of a continuous system. Contact our experts today to optimize your lab's productivity and achieve consistent, high-quality results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is high pressure generated in an autoclave? Unlock the Science of Sterilization & Synthesis
- Does pressure affect melting and boiling? Master Phase Changes with Pressure Control
- What is a high pressure autoclave? A Complete Guide to High-Temp, High-Pressure Reactors
- How is the temperature in the reactors controlled under normal conditions? Master Thermal Stability for Efficient Metallurgy
- What is a high pressure high temperature autoclave reactor? Unlock Extreme Chemical Synthesis



















