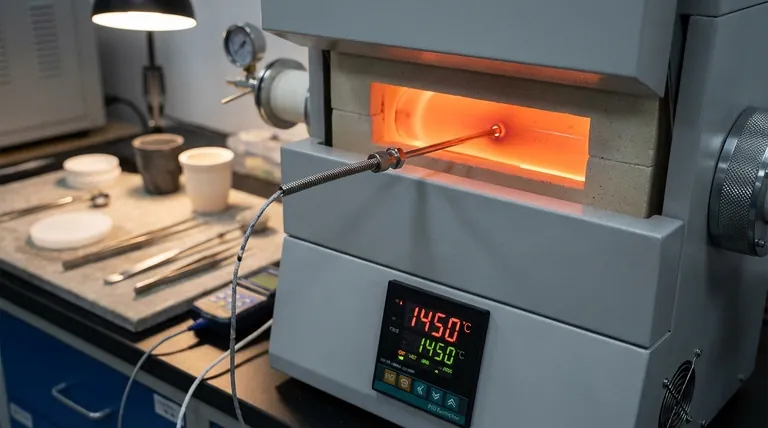
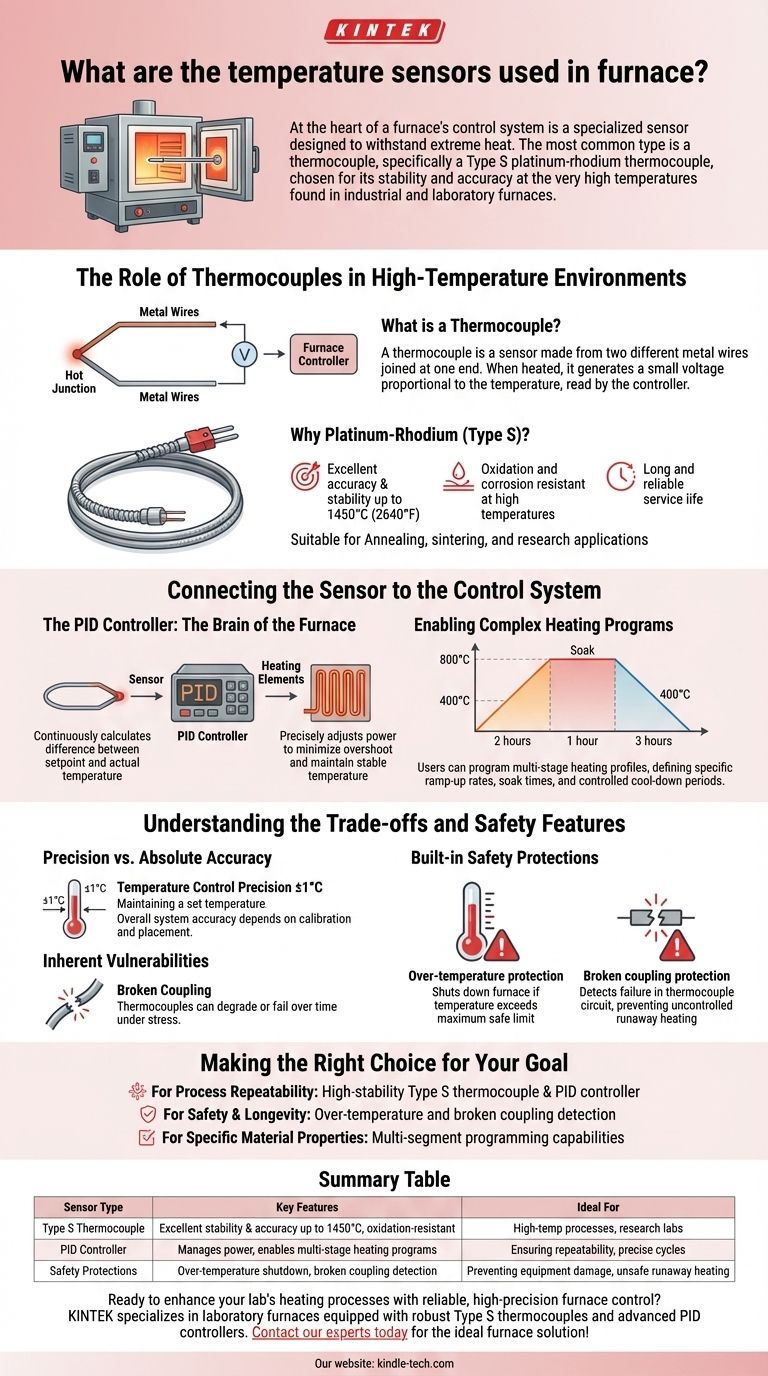
At the heart of a furnace's control system is a specialized sensor designed to withstand extreme heat. The most common type is a thermocouple, specifically a Type S platinum-rhodium thermocouple, chosen for its stability and accuracy at the very high temperatures found in industrial and laboratory furnaces.
The choice of a temperature sensor is not just about measuring heat; it's about enabling the precise control, safety, and repeatability required for sophisticated heating processes. The sensor is the critical link between the furnace's physical state and its digital control system.

The Role of Thermocouples in High-Temperature Environments
A furnace's ability to execute a complex heating program depends entirely on the quality of its temperature feedback. This feedback comes from a sensor that can survive and remain accurate in punishing conditions.
What is a Thermocouple?
A thermocouple is a sensor made from two different metal wires joined at one end, known as the "hot junction." When this junction is heated, it generates a small voltage that is proportional to the temperature.
This voltage is then read by the furnace's controller, which translates it back into a temperature reading.
Why Platinum-Rhodium (Type S)?
While many types of thermocouples exist, Type S (platinum-rhodium) is standard for high-temperature furnaces for several key reasons.
It offers excellent accuracy and stability at temperatures up to 1450°C (approx. 2640°F) and can be used intermittently at even higher temperatures. This makes it ideal for processes like annealing, sintering, and research applications.
Furthermore, its resistance to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures contributes to a long and reliable service life, often in a protective "armored" sheath.
Connecting the Sensor to the Control System
The sensor itself is only one part of a larger system. Its data is fed into a controller that makes intelligent decisions to manage the heating process.
The PID Controller: The Brain of the Furnace
Modern furnaces use a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This is a sophisticated algorithm that continuously calculates the difference between the desired temperature (setpoint) and the actual temperature measured by the thermocouple.
Based on this error, the PID controller precisely adjusts the power sent to the heating elements, minimizing overshoot and maintaining a stable temperature.
Enabling Complex Heating Programs
The synergy between a reliable thermocouple and a PID controller allows for advanced functionality. Users can program multi-stage heating profiles, defining specific ramp-up rates, soak times at set temperatures, and controlled cool-down periods.
For example, a process might require heating to 800°C over 2 hours, holding for 1 hour, then cooling to 400°C over 3 hours. This is only possible with accurate, real-time temperature data.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Features
While highly effective, the thermocouple-based system has inherent characteristics and requires safety mechanisms to function reliably.
Precision vs. Absolute Accuracy
A key specification is temperature control precision, often cited as ±1°C. It's crucial to understand this refers to the controller's ability to maintain a set temperature, not the absolute accuracy of the temperature itself. The overall system accuracy depends on the thermocouple's calibration and placement.
Inherent Vulnerabilities
Thermocouples can degrade or fail over time, especially under thermal or mechanical stress. This is known as broken coupling.
Built-in Safety Protections
To mitigate these risks, furnace controllers have essential safety features. Over-temperature protection will shut down the furnace if the temperature exceeds a maximum safe limit, preventing damage to the furnace and its contents.
Broken coupling protection detects a failure in the thermocouple circuit. Without this, a broken sensor could read as a low temperature, causing the controller to apply full power in a dangerous, uncontrolled runaway.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection and understanding of the temperature sensing system should align with your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Ensure your furnace uses a high-stability Type S thermocouple paired with a PID controller to execute identical heating profiles every time.
- If your primary focus is safety and equipment longevity: Verify the furnace includes critical protections like over-temperature and broken coupling detection to prevent catastrophic failures.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Leverage the multi-segment programming capabilities enabled by the PID system to design the precise thermal treatment your application requires.
Ultimately, the temperature sensor is the trusted informant that makes intelligent furnace control possible.
Summary Table:
| Sensor Type | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Type S Thermocouple (Platinum-Rhodium) | Excellent stability & accuracy up to 1450°C, oxidation-resistant | High-temp processes (annealing, sintering), research labs |
| PID Controller | Manages power to heating elements, enables multi-stage heating programs | Ensuring repeatability, precise ramp/soak/cool cycles |
| Safety Protections | Over-temperature shutdown, broken coupling detection | Preventing equipment damage and unsafe runaway heating |
Ready to enhance your lab's heating processes with reliable, high-precision furnace control? KINTEK specializes in laboratory furnaces equipped with robust Type S thermocouples and advanced PID controllers, ensuring the safety, repeatability, and accuracy your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the ideal furnace solution for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature Uniformity and Control
- What are the advantages of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Purity



















