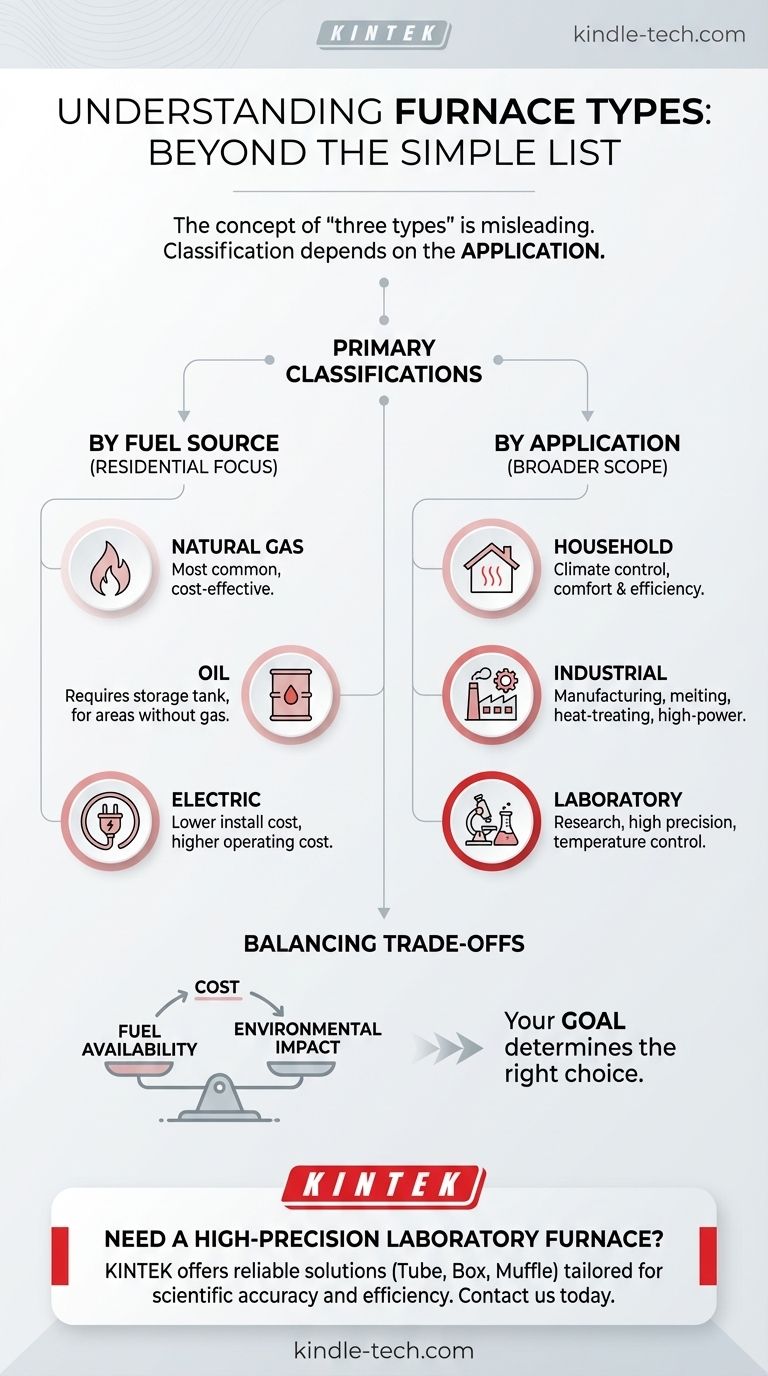
The answer is not as simple as a single list of three. The way furnaces are categorized depends entirely on their intended use. For residential heating, the three types are defined by their fuel source: natural gas, oil, and electric. However, on a broader scale, furnaces are classified by their application: household, industrial, and laboratory.
The concept of "three types of furnaces" is a misleading oversimplification. The most useful way to understand them is to first ask: "What is the furnace being used for?" This clarifies whether you should be thinking about fuel sources for your home or specialized equipment for industrial and scientific applications.

The Two Primary Ways to Classify Furnaces
To make sense of the dozens of furnace types that exist, experts group them in two fundamental ways. One looks at the energy they consume, and the other looks at the job they are designed to do.
Classification by Fuel Source (For Your Home)
When discussing furnaces for residential heating, the classification is almost always based on the type of fuel used.
- Natural Gas Furnaces: These are the most common type in areas with access to a municipal gas line. They are typically the most cost-effective to operate.
- Oil Furnaces: These are more common in regions without widespread natural gas infrastructure. They require a dedicated oil storage tank on the property.
- Electric Furnaces: These units use electric resistance heating elements. While they are often cheaper to install, their operating costs can be significantly higher depending on local electricity rates.
Classification by Application (The Bigger Picture)
A more fundamental way to classify all furnaces is by their primary function. This gives a clearer picture of the vast differences in scale, power, and precision.
- Household Furnaces: These are the units designed for residential climate control, as described above. Their main goal is comfort and energy efficiency.
- Industrial Furnaces: This is a massive category of high-power systems used in manufacturing. They perform tasks like melting metals (e.g., electric arc furnaces), heat-treating parts (e.g., vacuum furnaces), or heating process fluids in refineries.
- Laboratory Furnaces: These are smaller, highly precise units designed for scientific research and testing. They offer exceptional temperature control for specific experiments (e.g., tube, box, and muffle furnaces).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace, whether for a home or an industrial plant, involves balancing cost, efficiency, and environmental impact. The right choice in one context is often wrong in another.
Operating Costs vs. Installation Costs
For homeowners, natural gas furnaces often have the lowest operating costs but can be expensive to install if gas lines aren't present. Electric furnaces are simple and cheap to install but can lead to high monthly bills.
Fuel Availability
Your geographic location is a primary constraint. A natural gas furnace is not an option in a rural area without gas lines, making oil or electricity the default choices.
Environmental Impact
This is a major consideration in industrial settings. Fired process furnaces, which burn fuel, are common in refineries but produce pollutants. In contrast, electric process furnaces produce no direct emissions, but they are more expensive to operate and their environmental impact depends on how the electricity is generated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your goal determines which classification of "three types" matters to you.
- If you are a homeowner choosing a heating system: Your decision will center on the three fuel types—natural gas, oil, and electric—based on local availability and cost.
- If you are trying to understand industrial processes: Focus on the furnace's function, such as melting (arc), heat treating (vacuum), or fluid heating (process).
- If you are working in a research or lab setting: Your choice will be among specialized, high-precision units like tube, box, or muffle furnaces.
Ultimately, understanding a furnace begins with understanding its purpose.
Summary Table:
| Classification Method | The Three Primary Types | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| By Fuel Source (Residential) | Natural Gas, Oil, Electric | Based on energy source; impacts cost, availability, and efficiency for home heating. |
| By Application (General) | Household, Industrial, Laboratory | Based on purpose; defines scale, power, and precision, from comfort to manufacturing to R&D. |
Need a High-Precision Laboratory Furnace?
Whether your research requires the exact temperature control of a tube furnace, the uniform heating of a box furnace, or the contamination-free environment of a muffle furnace, KINTEK has the solution. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable, high-performance furnaces tailored to your scientific needs.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory and enhance the accuracy and efficiency of your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the range of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Temperature for Your Lab
- What is the most common form of heat treatment? Mastering Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is a furnace classified as? Understand the Two Main Types for Your Application
- What precautions should be taken during muffle furnace? Essential Safety & Operational Guidelines
- How hot is a muffle furnace in Celsius? A Guide to Temperature Ranges from 800°C to 1800°C



















