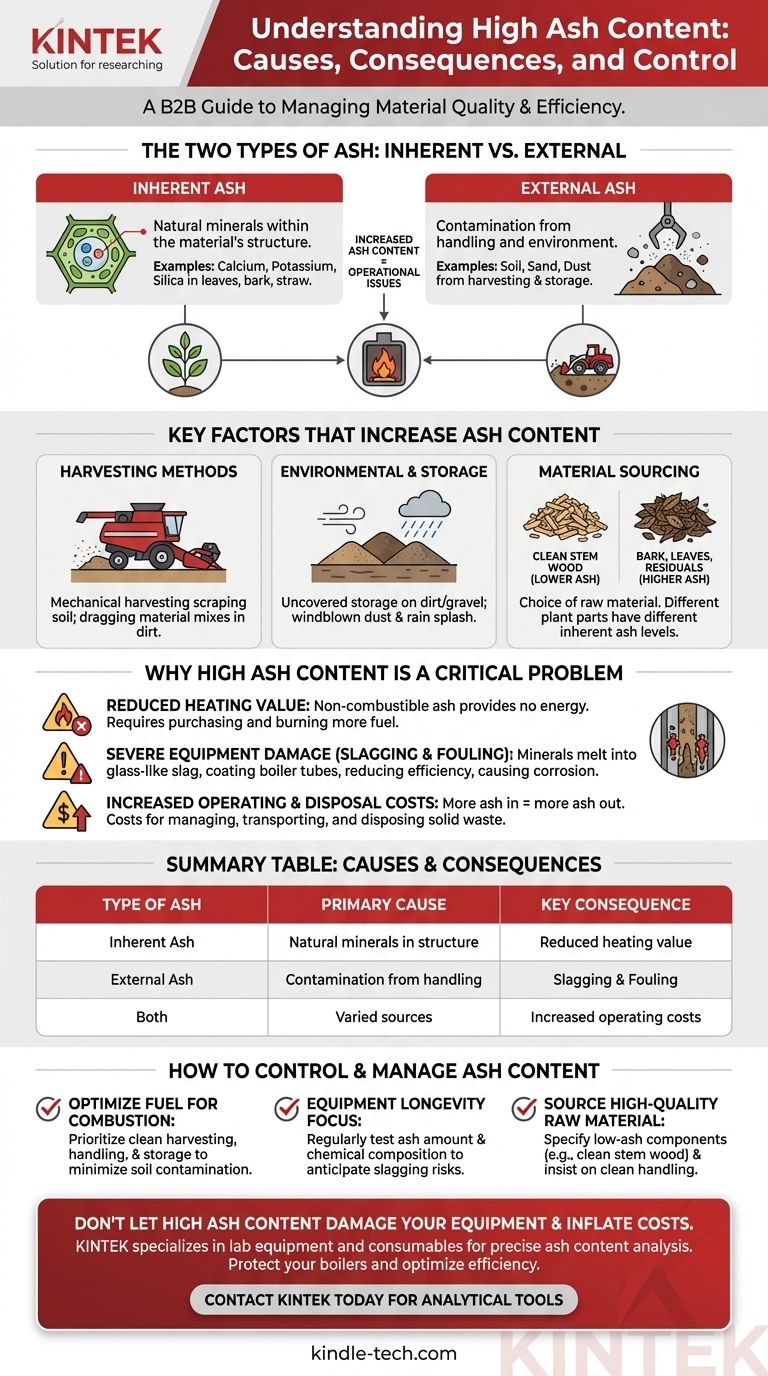
An increase in ash content is driven by two main sources: the naturally occurring, non-combustible minerals within the material itself (inherent ash) and external contamination from substances like soil, sand, and dust introduced during harvesting, handling, and storage (external ash).
The core issue is that ash is not a single substance but a combination of a material's intrinsic mineral makeup and any foreign contaminants it has accumulated. Effectively controlling high ash content requires understanding and managing both the source of the material and every step of its subsequent supply chain.

The Two Types of Ash: Inherent vs. External
To properly diagnose and control high ash content, you must first distinguish between its two fundamental origins. Each type has different causes and requires a different management strategy.
Inherent Ash: The Material's Natural Blueprint
Inherent ash consists of the minerals that are a natural, structural part of the material. This includes elements like calcium, potassium, silica, magnesium, and phosphorus.
The level of inherent ash is determined primarily by the material's biology and growing conditions. For example, in biomass, leaves, bark, and straw naturally contain significantly more minerals than the clean, woody part of a tree's stem.
External Ash: The Contamination Factor
External ash is essentially dirt and grit. It is not part of the material's original structure but is introduced from the outside environment.
This type of ash is the most variable and often the largest contributor to excessively high ash levels. It is also the factor you have the most direct control over.
Key Factors That Increase Ash Content
Several specific actions and conditions can significantly elevate ash levels, primarily by introducing external contaminants.
Harvesting and Collection Methods
This is one of the most common sources of contamination. Mechanical harvesters that scrape the ground, or processes where material is dragged or raked, will inevitably mix in soil, rocks, and sand.
For agricultural residues like corn stover or wheat straw, how low the crop is cut and the collection method used are critical variables.
Environmental and Storage Conditions
Materials stored uncovered on dirt or gravel surfaces will become contaminated. Wind can blow dust and soil onto stockpiles, and rain can splash mud onto the lower layers.
The local soil type also plays a role. Operations in sandy or dusty regions face a much higher risk of wind-blown contamination than those in areas with heavy clay soils.
Material Sourcing and Anatomy
The choice of raw material is a fundamental factor. As noted, different parts of a plant have vastly different levels of inherent ash.
Opting for bark, leaves, or agricultural grasses over clean, debarked wood chips will always result in a higher baseline ash content before any external contamination is even considered.
Why High Ash Content Is a Critical Problem
Understanding the causes of high ash is important because its presence has severe technical and financial consequences. It is not merely an inert filler; it actively creates operational problems.
Reduced Heating Value
For any combustion process, ash is non-combustible material. It provides no energy value. Higher ash content directly translates to a lower energy density (BTU/lb or MJ/kg), meaning you must purchase and burn more fuel to generate the same amount of heat.
Severe Equipment Damage: Slagging and Fouling
This is the most critical operational issue. Certain minerals in ash (especially alkali metals like potassium and sodium combined with silica) have low melting points.
Inside a boiler, these minerals can melt into a molten, glass-like substance called slag. Slag coats boiler tubes and heat-exchange surfaces, drastically reducing efficiency and often requiring costly, unscheduled shutdowns for cleaning. It can also cause severe corrosion, shortening the life of expensive equipment.
Increased Operating and Disposal Costs
The ash that doesn't melt and slag must be removed from the system as bottom ash or fly ash. Managing, transporting, and disposing of this solid waste represents a significant and direct operational cost. More ash in, more ash out.
How to Control and Manage Ash Content
Effectively managing ash requires a targeted approach based on your specific operational goals and where you have influence in the supply chain.
- If your primary focus is optimizing fuel for combustion: Prioritize clean harvesting, handling, and storage protocols to minimize soil contamination, as this is the most controllable variable.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Regularly test not just the amount of ash but also its chemical composition to anticipate and mitigate slagging and fouling risks before they cause major damage.
- If your primary focus is sourcing high-quality raw material: Specify low-ash components, such as clean stem wood over forest residuals, and insist on suppliers who can demonstrate clean handling practices.
Ultimately, controlling ash is a matter of controlling both your raw material selection and the integrity of your entire handling process from source to use.
Summary Table:
| Type of Ash | Primary Cause | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Inherent Ash | Natural minerals within the material's structure. | Calcium, potassium, silica in leaves, bark, and straw. |
| External Ash | Contamination from handling and environment. | Soil, sand, and dust from harvesting and storage. |
| Key Consequence | Impact on Operations | Financial Effect |
| Slagging & Fouling | Molten ash coats boiler tubes, reducing efficiency. | Costly shutdowns, repairs, and equipment damage. |
| Reduced Heating Value | Less energy per unit of fuel due to inert material. | Higher fuel costs to achieve the same heat output. |
Don't let high ash content damage your equipment and inflate your costs. KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables for precise ash content analysis. Our solutions help you monitor and control ash levels, protecting your boilers from slagging and fouling while optimizing your fuel efficiency. Contact us today to find the right analytical tools for your laboratory needs and ensure the quality of your materials. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you calibrate a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Lab
- What is the melting temperature of ceramics? Understanding High-Temperature Material Performance
- Will brazing stick to cast iron? A Low-Heat Joining Solution for Crack-Free Repairs
- Why ceramics can withstand high temperature? Unlock the Secrets of Atomic Structure
- What is the most common form of heat treatment? Mastering Annealing, Hardening, and Tempering



















