Fundamentally, a hydraulic press is a machine that uses pressurized fluid to generate immense, controlled force. It applies this force to compress, mold, bend, or assemble materials. Its applications range from large-scale industrial fabrication and maintenance to precise sample preparation in a laboratory setting.
The true value of a hydraulic press lies not just in its raw power, but in its ability to multiply a small initial effort into a massive, consistent, and easily controlled output force. This principle makes it one of the most versatile and efficient tools for tasks requiring significant pressure.

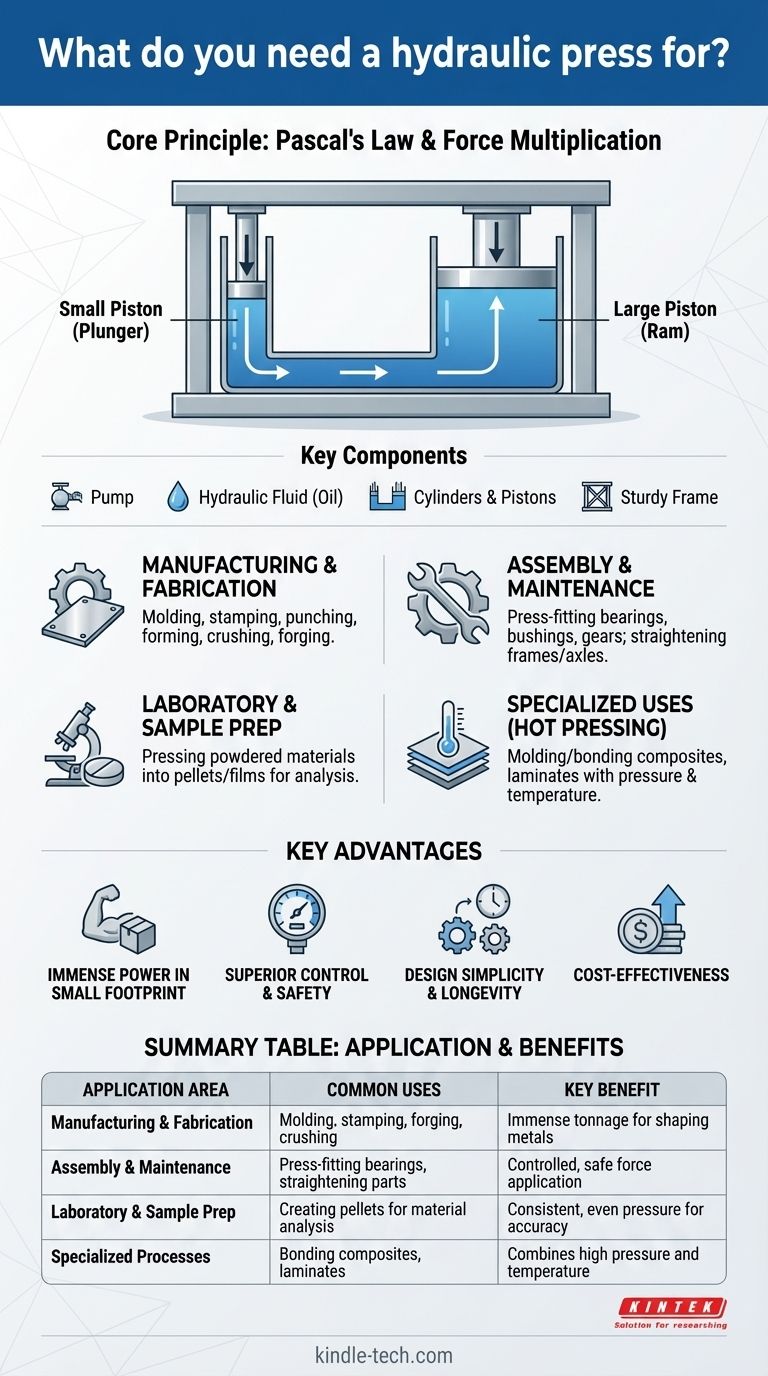
How a Hydraulic Press Generates Force
To understand what a hydraulic press is used for, you must first understand how it works. Its operation is based on a simple but powerful physics principle.
The Core Principle: Pascal's Law
A hydraulic press operates on Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
The press uses two interconnected cylinders of different sizes filled with hydraulic fluid. A small force is applied to a small piston (the plunger), creating pressure in the fluid. This same pressure then acts on a much larger piston (the ram), generating a proportionally larger output force.
Key Components
A typical hydraulic press consists of a few core parts:
- A pump to move the hydraulic fluid.
- Hydraulic fluid (usually oil) to transfer the pressure.
- Two cylinders and pistons (a small plunger and a large ram).
- A sturdy frame or bed that holds the material and withstands the immense force.
The Result: Force Multiplication
This design is a force multiplier. A small motor or even a manual hand pump can generate pressure capable of producing many tons of force at the ram, making it an incredibly efficient way to perform heavy work.
Primary Applications Across Industries
The ability to generate controlled, high tonnage in a compact machine makes the hydraulic press essential in numerous fields.
Manufacturing and Fabrication
This is the most common area of use. A press equipped with dies can be used for molding, stamping, punching, and forming metal sheets into parts like car body panels or kitchen sinks. It is also used for crushing scrap metal or forging raw metal billets into shape.
Assembly and Maintenance
In workshops, hydraulic presses are indispensable for assembly and repair. They are used to press-fit bearings, bushings, or gears onto shafts. They can also be used to straighten bent frames, axles, or other structural components.
Laboratory and Sample Preparation
On a smaller scale, hydraulic presses are a staple in scientific laboratories. They are used to press powdered materials into solid pellets or thin films for analysis, such as in spectroscopy. This requires the consistent and even pressure that a hydraulic system provides.
Specialized Uses (e.g., Hot Pressing)
Some hydraulic presses are also equipped with heated platens. These "hot presses" use a combination of immense pressure and high temperature to mold or bond materials, which is crucial for producing composites, laminates, and certain types of plastics.
Understanding the Key Advantages
Compared to purely mechanical presses, hydraulic systems offer several distinct benefits that drive their widespread adoption.
Immense Power in a Small Footprint
A hydraulic press can generate extremely high tonnage (force) from a relatively small machine, requiring less floor space than a mechanical press of equivalent power.
Superior Control and Safety
The output force is directly related to the fluid pressure, which can be precisely controlled. Furthermore, hydraulic systems have built-in overload protection; pressure relief valves prevent the machine from exceeding its force limit, protecting both the tool and the workpiece.
Design Simplicity and Longevity
With fewer moving parts than complex mechanical presses, hydraulic systems experience less wear and tear. This leads to a longer tool lifespan, lower maintenance costs, and significantly quieter operation.
Cost-Effectiveness
The simpler design often results in lower initial investment and reduced production costs, especially for applications that don't require extremely high cycle speeds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice to use a hydraulic press depends entirely on your operational priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum force and precise control: A hydraulic press is the ideal choice for jobs requiring high tonnage and a steady application of pressure, like deep drawing, forging, or pressing large assemblies.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repeatable production: A mechanical press may be more suitable for applications like stamping small, simple parts where cycle time is the most critical factor.
- If your primary focus is precision laboratory work: A small-tonnage manual or automated hydraulic press is essential for creating consistent pellets and films for material analysis.
By understanding the principle of force multiplication through fluid, you can effectively leverage the unique capabilities of a hydraulic press for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Common Uses | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing & Fabrication | Molding, stamping, forging, crushing | Immense tonnage for shaping metals |
| Assembly & Maintenance | Press-fitting bearings, straightening parts | Controlled, safe force application |
| Laboratory & Sample Prep | Creating pellets for material analysis | Consistent, even pressure for accuracy |
| Specialized Processes (Hot Pressing) | Bonding composites, laminates | Combines high pressure and temperature |
Ready to harness the power of a hydraulic press for your projects?
Whether you are in manufacturing, maintenance, or a laboratory setting, KINTEK's hydraulic presses deliver the precise, high-tonnage force you need. Our robust and reliable equipment is designed for efficiency, safety, and long-term performance.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect press for your specific application and discover how we can support your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy



















