At its core, hot-pressing is a manufacturing process that uses high temperature and uniform, high-pressure gas to densify materials and eliminate internal defects. This simultaneous application of heat and pressure fundamentally improves a component's mechanical properties by removing microscopic voids created during initial fabrication.
The crucial insight is that hot-pressing transforms a part from the inside out. It addresses the root cause of many material failures—internal porosity—to create a dense, uniform component with superior strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance.
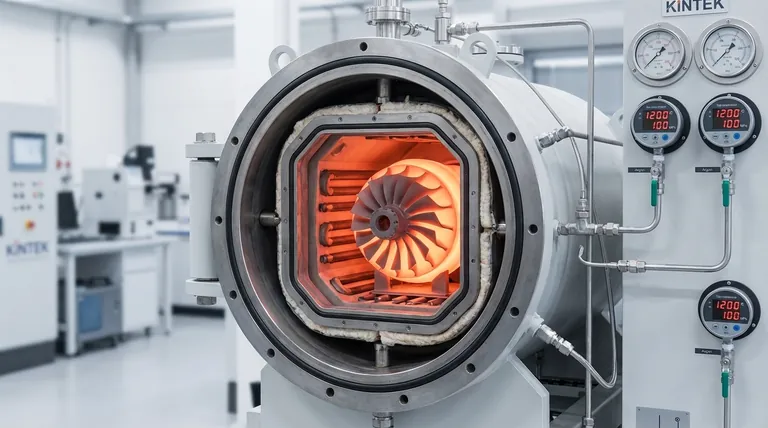
The Core Principle: Eliminating Internal Voids
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is a specific and common form of hot-pressing. The process targets the microscopic imperfections inherent in many manufacturing methods, particularly those involving powders or melting.
How It Works: Heat and Pressure
A component is placed inside a high-pressure vessel which is then heated to an elevated temperature, often just below the material's melting point. Simultaneously, an inert gas like argon is used to apply uniform, isostatic pressure from all directions.
The Target: Porosity
The heat softens the material, allowing the high pressure to physically close internal voids, gas pockets, and microscopic pores. These defects are common weak points in parts made by casting, sintering, or 3D printing.
The Result: A Uniform Microstructure
By eliminating these internal gaps, the process forces the material's atoms into intimate contact, creating strong metallic bonds. The outcome is a fully dense part with a consistent and uniform internal structure, which is the foundation for enhanced performance.
Key Improvements to Material Properties
Eliminating internal defects translates directly into measurable improvements in how a material behaves under stress. This is the primary reason for specifying the hot-pressing step.
Enhanced Density and Ductility
By closing voids, hot-pressing drives a part toward 100% theoretical density. This increase in density directly improves ductility, which is a material's ability to deform without fracturing.
Superior Fatigue Resistance
Internal pores act as stress concentrators, creating initiation sites for cracks under cyclic loading. By removing these defects, hot-pressing dramatically increases a part's resistance to fatigue failure, a critical factor for components in aerospace and medical applications.
Relief of Internal Stresses
The high temperatures involved in the process also serve as a heat treatment, relieving residual thermal stresses that may have been introduced during the initial casting or printing process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, hot-pressing is an additional manufacturing step that requires careful consideration. It is not a universal solution for every application.
Added Cost and Complexity
The process requires specialized, high-pressure equipment and adds time to the overall production cycle. This increases the final cost of the component, making it most suitable for high-performance or mission-critical parts where reliability is paramount.
Not a Cure for Surface Defects
Hot-pressing is designed to eliminate internal porosity. It cannot fix surface-connected defects or correct major dimensional inaccuracies from the initial manufacturing step.
Process Efficiency Gains
Conversely, the process can sometimes consolidate multiple steps. For certain alloys, hot-pressing can be combined with solution treatment, quenching, and aging, potentially streamlining the overall post-processing workflow and reducing total production time.
When to Specify Hot-Pressing
The decision to use hot-pressing hinges on the performance requirements of the final component.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
For metal 3D-printed parts, hot-pressing is often considered a mandatory step. It is the most effective way to heal the porosity between printed layers and achieve material properties comparable to traditional wrought or forged metals.
Cast and Sintered Components
In high-performance casting and powder metallurgy, hot-pressing is used to close shrinkage porosity and ensure that the final part meets demanding specifications for strength and fatigue life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and fatigue life: Hot-pressing is a critical step to ensure the component can withstand cyclic loads without premature failure.
- If your primary focus is elevating 3D-printed metal parts to their full potential: This process is the industry standard for achieving full density and optimal mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of non-critical parts: The added expense of hot-pressing may not be justified if the application does not demand maximum material performance.
Ultimately, hot-pressing is the definitive step to transform a promising component into a finished part with predictable, high-performance characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Impact on Material |
|---|---|
| Eliminates Internal Porosity | Removes microscopic voids and defects, achieving near 100% density. |
| Improves Fatigue Resistance | Significantly extends component life under cyclic loading. |
| Enhances Ductility | Increases the material's ability to deform without fracturing. |
| Creates Uniform Microstructure | Results in consistent, predictable mechanical properties. |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials? The hot-pressing process is essential for achieving maximum reliability in mission-critical components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to support your research and production needs. Whether you're working with additive manufacturing, castings, or sintered parts, our expertise can help you achieve superior material performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace over HIP? Optimize Fiber-Foil Composite Production
- Why must a high vacuum be maintained during Cu-CNT sintering? Ensure Optimal Bonding and Material Integrity
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- What is the function of a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve High Densification in Al-Ti-Zr Synthesis



















