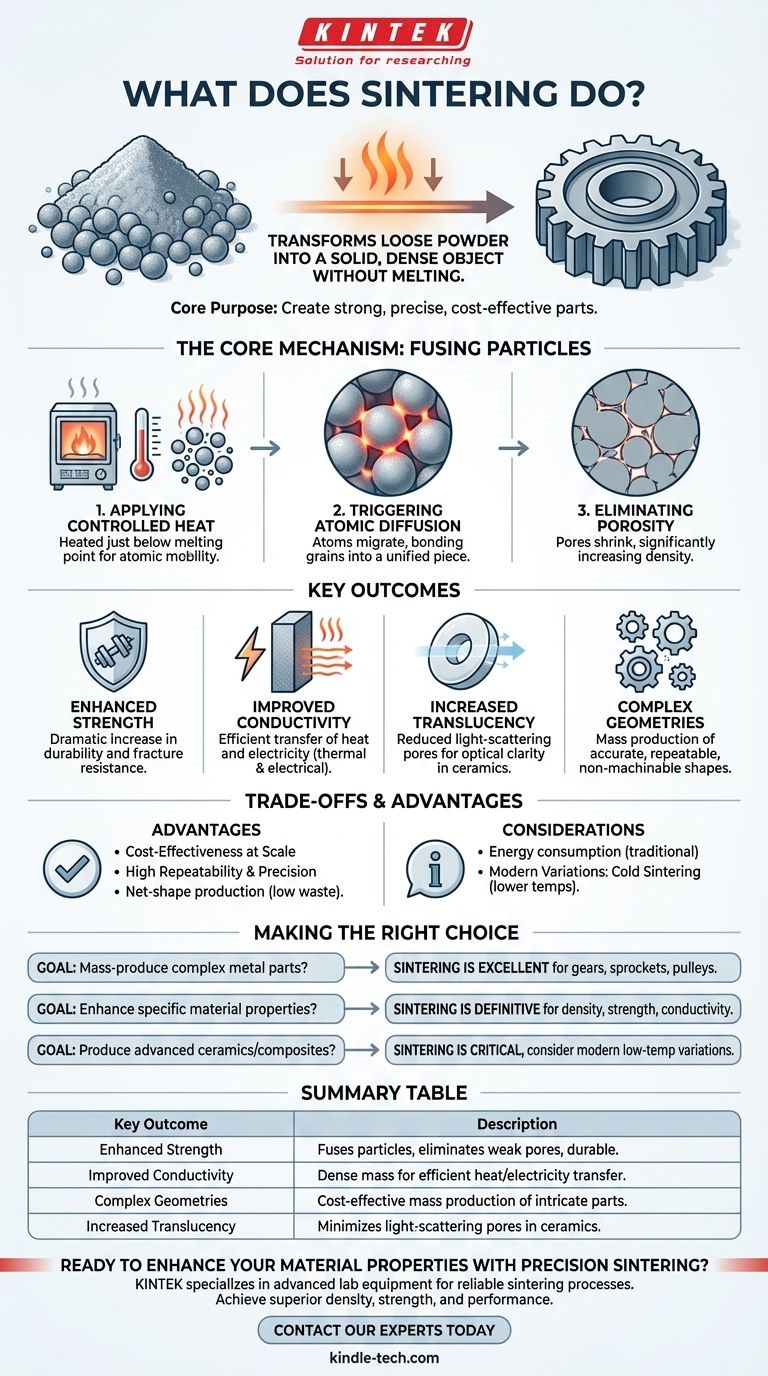
In essence, sintering transforms a collection of loose powder into a solid, dense object using heat and pressure without melting it. This process fuses the individual particles together at an atomic level, dramatically reducing the empty space between them and fundamentally changing the material's properties.
The core purpose of sintering is to create strong, precise, and dense parts from powders in a cost-effective way. It avoids the complexities of melting and casting while significantly enhancing a material's strength, conductivity, and other critical properties.

The Core Mechanism: Fusing Particles Without Melting
Sintering is fundamentally a process of consolidation. It takes a compacted powder, often called a "green part," and turns it into a coherent solid mass with useful mechanical or electrical properties.
Applying Controlled Heat
The process takes place inside a specialized furnace. The material is heated to a temperature just below its melting point, which provides the thermal energy necessary for the atoms to become mobile.
Triggering Atomic Diffusion
This heat allows atoms to migrate across the boundaries of the individual particles. The particles begin to fuse together where they touch, forming "necks" that grow until the individual grains are bonded into a single, unified piece.
Eliminating Porosity
As the particles fuse, the empty spaces, or pores, between them shrink and are gradually eliminated. This reduction in porosity is the primary driver behind the significant improvements in the material's final properties.
Key Outcomes of the Sintering Process
By consolidating loose powder into a dense solid, sintering imparts several valuable characteristics to the final product.
Enhanced Material Strength
The primary outcome is a dramatic increase in strength and integrity. By eliminating pores, which are natural weak points, the material becomes far more durable and resistant to fracture.
Improved Conductivity
A dense, unified mass allows for more efficient transfer of heat and electricity. Sintering is often used to improve the thermal and electrical conductivity of components used in electronics and high-temperature applications.
Increased Translucency
For certain materials, particularly ceramics, reducing porosity to a minimum can significantly increase optical translucency. This is because pores scatter light, making the material appear opaque.
Creating Complex Geometries
Sintering is highly effective for the mass production of parts with complex or non-machinable shapes. It can produce highly repeatable and accurate components like gears, bearings, and electrical contacts with great cosmetic results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Advantages
Like any manufacturing process, sintering has a specific set of benefits and considerations that make it ideal for certain applications.
Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
For large production volumes, sintering is an extremely cost-effective method. It minimizes material waste and can often produce a net-shape part that requires little to no finishing, reducing overall manufacturing time and cost.
High Repeatability and Precision
The process allows for tight dimensional control, making it possible to produce highly accurate and consistent parts in large quantities, which is crucial for components used in complex assemblies.
A Note on Modern Variations
To reduce the high energy consumption of traditional sintering, modern variations have been developed. Cold Sintering, for example, enables densification at much lower temperatures (120–300°C), opening up possibilities for new material combinations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on your material, desired quantity, and the final properties you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex metal parts: Sintering is an excellent choice for creating items like gears, sprockets, and pulleys repeatably and cost-effectively.
- If your primary focus is enhancing specific material properties: Sintering is the definitive process for increasing the density, strength, and thermal or electrical conductivity of a powdered material.
- If your primary focus is producing advanced ceramics or composites: Sintering is a critical step, and modern low-temperature variations may offer unique advantages for heat-sensitive materials.
Ultimately, sintering provides a powerful method for engineering materials at a microscopic level to achieve superior macroscopic performance.
Summary Table:
| Key Outcome | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Strength | Fuses particles to eliminate weak pores, creating a durable, fracture-resistant material. |
| Improved Conductivity | Creates a dense mass for efficient transfer of heat and electricity. |
| Complex Geometries | Enables cost-effective mass production of precise, intricate parts like gears and bearings. |
| Increased Translucency | For ceramics, minimizes light-scattering pores to enhance optical properties. |
Ready to enhance your material properties with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for reliable sintering processes. Whether you are developing new materials, mass-producing complex metal parts, or working with advanced ceramics, our solutions help you achieve superior density, strength, and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific sintering and materials development goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of calciners? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Processing Equipment
- What is a mixed hot zone and what is its primary disadvantage? Understanding Contamination Risks
- What is the technical value of using a high-vacuum heat treatment furnace for 800 °C annealing? Maximize Bond Strength
- What is a vacuum sintering furnace? Unlock Purity and Performance in Advanced Materials
- What is the primary function of a vacuum drying oven in chemical compatibility testing? Ensure Accurate Mass Measurements
- What is a pyrolysis plant? Converting Waste into Valuable Resources
- Why is a high vacuum furnace used for the homogenization of 3D-printed alloy libraries before corrosion testing? - FAQ
- How does a vacuum oven contribute to the quality of NIPU films? Achieve Superior Material Density and Strength



















