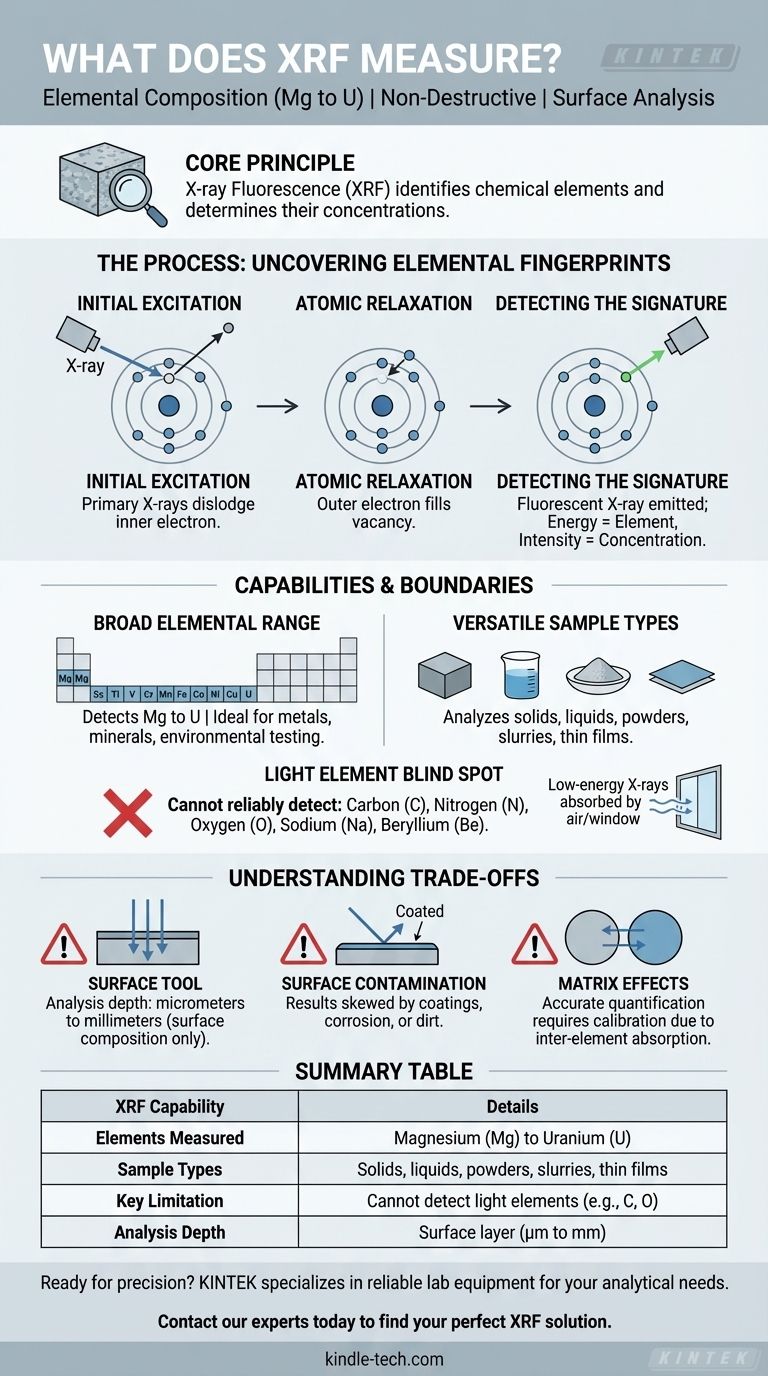
At its core, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) measures the elemental composition of a material. This powerful, non-destructive technique identifies which chemical elements are present in a sample and can determine the concentration of each, from Magnesium (Mg) to Uranium (U) on the periodic table.
XRF works by using X-rays to energize the atoms within a sample, causing them to emit unique energy signatures, like elemental fingerprints. While it is a fast and powerful tool for surface analysis, understanding its limitations with light elements and sample depth is critical for interpreting its results correctly.

How XRF Uncovers Elemental Fingerprints
To understand what XRF measures, we must first understand its fundamental process. The technique is a two-step sequence of atomic excitation and relaxation.
The Initial Excitation
An XRF analyzer directs a primary beam of high-energy X-rays onto the surface of a sample. This energy is absorbed by the atoms in the material and is powerful enough to dislodge an electron from one of the atom's inner orbital shells (e.g., the K-shell).
The Atomic Relaxation
The removal of an inner-shell electron creates a vacancy, leaving the atom in an unstable, high-energy state. To regain stability, an electron from a higher-energy outer shell immediately drops down to fill this vacancy.
Detecting the Signature
As the electron moves from a high-energy to a low-energy shell, it releases the excess energy in the form of a secondary X-ray. This emission is called "fluorescence."
The energy of this fluorescent X-ray is the key. It is a unique and precise signature characteristic of the specific element from which it was emitted. A detector within the XRF instrument measures both the energy and the number of these fluorescent X-rays.
The energy level identifies the element, while the intensity (the number of X-rays detected at that energy) corresponds to the element's concentration in the sample.
What XRF Can (and Cannot) Analyze
XRF is a highly versatile method, but its capabilities have clear boundaries that are essential to recognize.
Broad Elemental Range
XRF is excellent for detecting and quantifying most elements on the periodic table, specifically those from Magnesium (Mg) through Uranium (U). This makes it invaluable for applications like metal alloy identification, mineral exploration, and environmental testing.
Versatile Sample Types
One of the great strengths of XRF is its ability to analyze a wide variety of sample forms. It can effectively measure solids, liquids, powders, slurries, and even thin films with minimal to no sample preparation.
The Light Element Blind Spot
XRF technology cannot reliably detect very light elements. Elements lighter than Magnesium—such as Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Sodium, and Beryllium—produce fluorescent X-rays with such low energy that they are absorbed by the air or the detector window before they can be measured.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No analytical technique is perfect. Trusting XRF data requires an objective understanding of its inherent limitations.
A Powerful Surface Tool
XRF is fundamentally a surface analysis technique. The primary X-ray beam only penetrates a shallow depth into the material, typically from a few micrometers to several millimeters, depending on the material's density. The results only represent the composition of this near-surface layer.
The Risk of Surface Contamination
Because it analyzes the surface, the results can be skewed by coatings, platings, corrosion, or simple surface dirt. The composition of the surface may not accurately reflect the bulk composition of the entire object.
Matrix Effects and Quantitative Accuracy
The X-rays emitted by one element can be absorbed or enhanced by other elements present in the sample, an issue known as "matrix effects." Accurate quantitative analysis (determining "how much") requires sophisticated software corrections or careful calibration with standards of a similar composition to mitigate these effects.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing the right analytical method depends entirely on your goal. XRF is an outstanding tool when applied to the correct problem.
- If your primary focus is rapid quality control or alloy identification: XRF is an ideal choice due to its speed, portability, and accuracy for most metallic elements.
- If your primary focus is analyzing precious or irreplaceable artifacts: The non-destructive nature of XRF makes it one of the safest and most effective methods available for art and archeology.
- If your primary focus is measuring the bulk composition of a coated or corroded material: Be cautious, as XRF will only measure the surface layer and may not represent the underlying material without proper surface preparation.
- If your primary focus is determining the composition of plastics or organic materials: You will need to use a different technique, as XRF cannot detect the core elements of these materials (Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen).
By understanding both its capabilities and its boundaries, you can confidently leverage XRF to obtain precise and immediate elemental data.
Summary Table:
| XRF Capability | Details |
|---|---|
| Elements Measured | Magnesium (Mg) to Uranium (U) |
| Sample Types | Solids, liquids, powders, slurries, thin films |
| Key Limitation | Cannot detect light elements (e.g., Carbon, Oxygen) |
| Analysis Depth | Surface layer (micrometers to millimeters) |
Ready to identify the elemental composition of your materials with precision?
XRF analysis provides fast, non-destructive results for quality control, alloy verification, and material science. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific analytical needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect XRF solution for your laboratory and ensure accurate, immediate elemental data for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Head Tweezers with Pointed Elbow Zirconia Ceramic Tip
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- How does a three-electrode electrochemical workstation assess TA10 titanium corrosion? Expert Testing Insights
- How does an electrochemical workstation evaluate corrosion resistance of welded joints? Expert Testing Guide
- What are the core functions of a high-precision electrochemical workstation? Optimize 304L Passive Film Analysis
- Why is a potentiostat or galvanostat indispensable for assessing the corrosion resistance of high-entropy alloy coatings?
- What role does an electrochemical workstation play in TiNO coating evaluation? Quantify Biological Corrosion Protection












