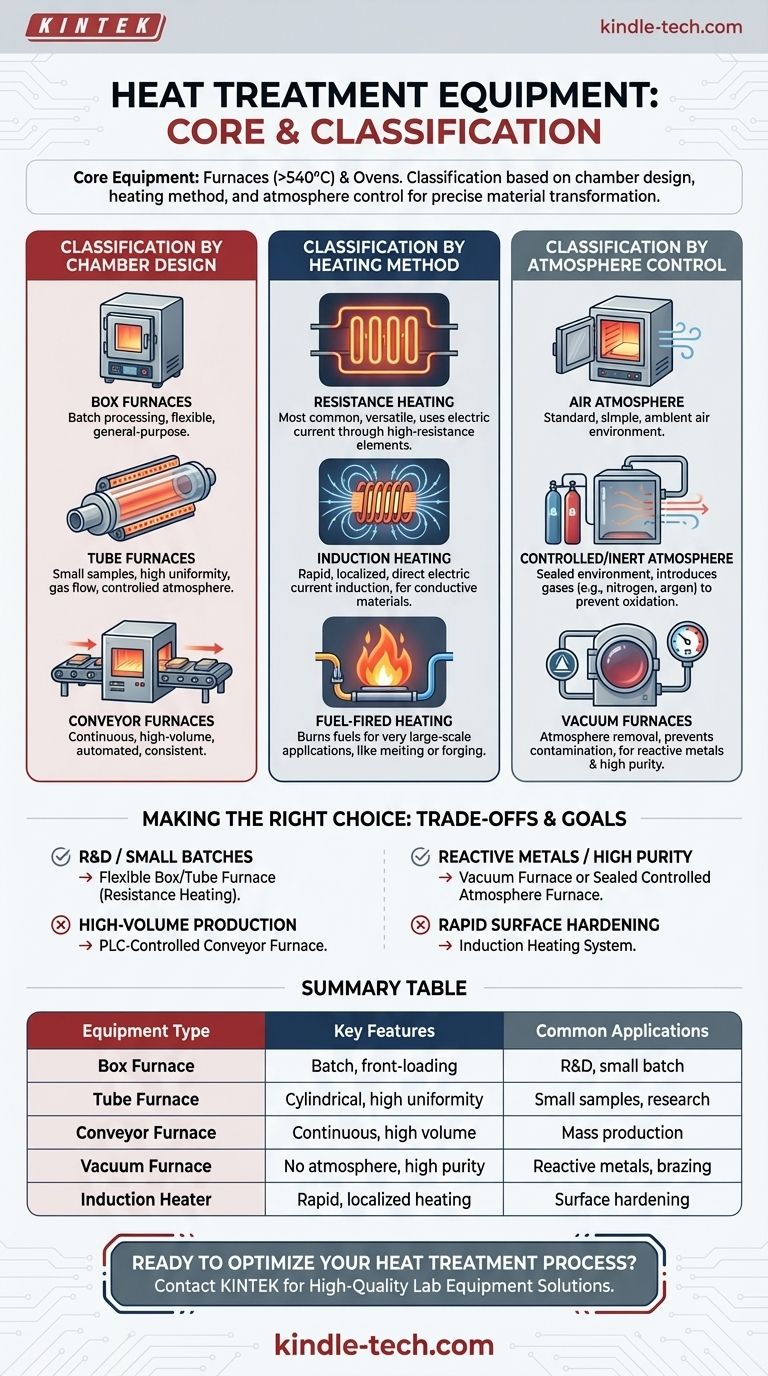
At its core, the equipment used for heat treatment falls into two main categories: furnaces and ovens. These systems are primarily classified by the shape of their heating chamber, the method used to generate heat, and their ability to control the internal atmosphere, all of which dictate their suitability for a specific material and process.
The critical insight is that selecting heat treatment equipment is not merely about reaching a target temperature. It is a strategic decision that balances chamber design, heating method, and atmosphere control to achieve a precise, repeatable transformation in a material's properties.
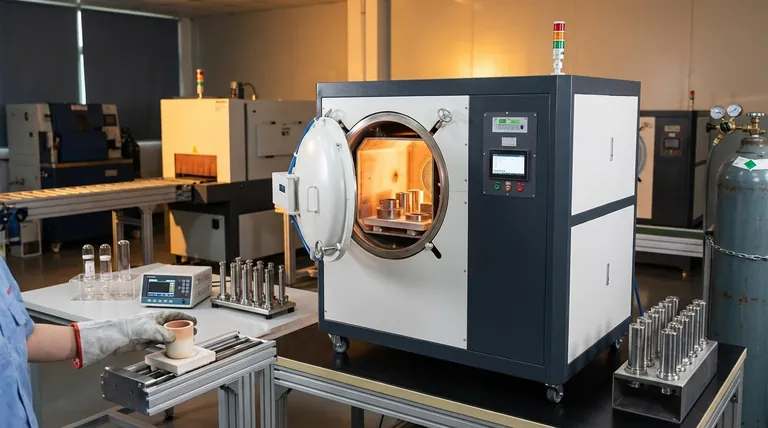

Core Equipment: Furnaces and Ovens
The terms "furnace" and "oven" are often used interchangeably, but furnaces typically operate at higher temperatures (above 1000°F or 540°C). The most useful way to understand this equipment is by its physical design and the environment it creates.
Classification by Chamber Design
The shape and orientation of the heating chamber are the most common ways to categorize equipment, as this directly relates to how material is loaded and processed.
- Box Furnaces: These are the most common general-purpose units. They feature a single chamber with a front-loading door, ideal for processing parts in batches.
- Tube Furnaces: This design uses a cylindrical tube (often ceramic or metal alloy) as the heating chamber. They are perfect for processing small samples, flowing gases over a sample, or achieving high temperature uniformity in a contained space.
- Conveyor (or Belt) Furnaces: Designed for continuous, high-volume production, these furnaces use a moving belt to transport parts through different heating and cooling zones.
Classification by Heating Method
The mechanism for generating heat is a fundamental design choice that affects speed, efficiency, and the types of materials that can be processed.
- Resistance Heating: This is the most common method. An electric current is passed through a high-resistance heating element (a coil, rod, or ribbon), which glows hot and radiates heat. The "resistance boat" used in thermal evaporation is a specialized form of this.
- Induction Heating: An alternating magnetic field is used to induce an electric current directly within the part itself. This allows for extremely rapid and localized heating of conductive materials.
- Fuel-Fired Heating: These furnaces burn natural gas, propane, or other fuels to generate heat. They are often used for very large-scale industrial applications like melting or forging pre-heating.
Classification by Atmosphere Control
Many advanced heat treatments require the exclusion of oxygen or the introduction of specific gases to prevent oxidation and influence surface chemistry.
- Air Atmosphere: This is the standard, simplest configuration where the part is heated in ambient air.
- Controlled/Inert Atmosphere: These furnaces are sealed to allow for the introduction of specific gases like nitrogen or argon, creating an inert environment that prevents reactions on the material's surface.
- Vacuum Furnaces: These systems pump all atmosphere out of the chamber, creating a vacuum. This is the ultimate way to prevent contamination and is essential for processing highly reactive metals and for applications like brazing.
Essential Auxiliary and Control Systems
A complete heat treatment solution involves more than just a hot chamber. A host of supporting systems are required for safety, environmental compliance, and process repeatability.
Environmental and Exhaust Control
Processing materials at high temperatures can release fumes or byproducts that must be managed.
- Thermal Oxidizers: These units are used to burn off harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the furnace exhaust before they are released into the atmosphere.
- Scrubbers and Bag Houses: Wet scrubbers and bag houses are used to capture particulate matter (dust) or acidic gases from the exhaust stream, ensuring clean emissions.
Process Monitoring and Automation
Precision and repeatability are paramount in modern manufacturing.
- Automation and PLCs: Most modern furnaces use a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) to automate the heating cycle. This system controls temperature ramps, soak times, and gas flow, ensuring every part is processed identically.
- Data Logging: These automation systems continuously track and record data points, providing a complete record of the process for quality control and certification.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right equipment requires balancing competing priorities of cost, volume, flexibility, and the specific material requirements.
Batch vs. Continuous Processing
A Box Furnace offers high flexibility for R&D or low-volume production with varied parts (batch processing). In contrast, a Conveyor Furnace is built for efficiency and low per-part cost in high-volume, standardized production (continuous processing), but lacks flexibility.
Heating Method vs. Material
Resistance heating is versatile and cost-effective for a wide range of materials. Induction heating is more expensive and complex but offers unparalleled speed and precision for conductive metals, making it ideal for surface hardening.
Atmosphere Control vs. Cost
Heating in an air atmosphere is simple and cheap. However, introducing controlled atmospheres or vacuum capabilities dramatically increases the cost and complexity of the equipment but is non-negotiable for protecting sensitive materials from oxidation and achieving high-purity results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's primary driver will dictate the ideal equipment configuration.
- If your primary focus is R&D or processing small, varied batches: A flexible, resistance-heated Box or Tube Furnace is your most logical starting point.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable production of a standard part: A PLC-controlled Conveyor Furnace is the only way to achieve the necessary throughput and consistency.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals or achieving high-purity results: A Vacuum Furnace or a sealed Controlled Atmosphere Furnace is absolutely essential.
- If your primary focus is rapid, localized surface hardening of steel components: An Induction Heating system is the superior technical choice.
Ultimately, understanding these core components and their trade-offs empowers you to select a system that precisely controls the thermal process and delivers the exact material properties you require.
Summary Table:
| Equipment Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Box Furnace | Batch processing, front-loading, general-purpose | R&D, small batch heat treatment |
| Tube Furnace | Cylindrical chamber, high uniformity, gas flow | Small samples, research, controlled atmospheres |
| Conveyor Furnace | Continuous processing, high volume, automated | Mass production, consistent results |
| Vacuum Furnace | No atmosphere, prevents contamination, high purity | Reactive metals, brazing, high-purity processes |
| Induction Heater | Rapid, localized heating, high precision | Surface hardening of conductive materials |
Ready to Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process?
Choosing the right equipment is critical to achieving the precise material properties you need. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique challenges. Whether you're in R&D or high-volume production, our experts can help you select the perfect furnace or oven to ensure repeatable, reliable results.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact us today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions



















