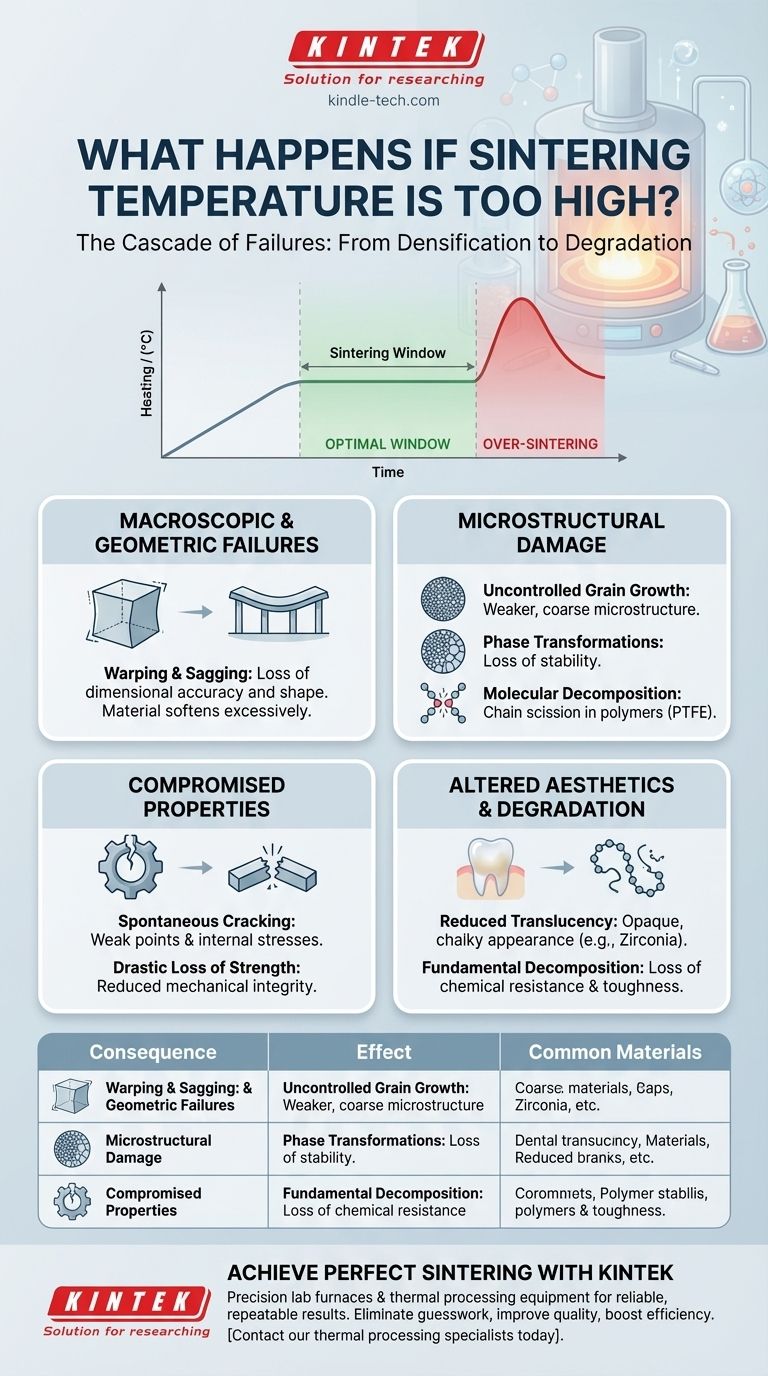
Using an excessively high sintering temperature causes a cascade of failures, leading to irreversible damage in the final part. These defects range from visible warping and cracking to a fundamental degradation of the material's microstructure, mechanical strength, and aesthetic properties. Instead of strengthening the part, over-sintering begins to break it down.
Sintering is a balancing act between densification and degradation. While higher temperatures accelerate the bonding of particles, exceeding the material's optimal window initiates destructive processes like uncontrolled grain growth or molecular breakdown. This ultimately compromises the part's structural integrity and intended properties.

The Goal of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a thermal process for compacting and forming a solid mass of material from a powder. The goal is to reduce the porosity between particles, creating a dense, strong, and stable final part.
The Optimal Temperature Window
Every material has an optimal sintering "window"—a range of temperatures and times where densification occurs efficiently. In this window, atomic diffusion causes the boundaries of individual particles to fuse, eliminating voids and increasing density.
Crossing the Threshold: From Densification to Degradation
When the temperature is too high, the energy input into the system becomes excessive. Instead of promoting controlled bonding, this energy triggers harmful mechanisms that actively damage the material you are trying to create.
The Consequences of Over-Sintering
Exceeding the optimal sintering temperature does not create a "stronger" part. It creates a weaker, flawed one. The specific failures depend on the material, but generally fall into several categories.
Macroscopic and Geometric Failures
The most immediately obvious defects are changes to the part's overall shape and size.
Excess heat can cause the material to soften excessively, leading to warping or sagging under its own weight or due to friction with the furnace surface. This results in a loss of dimensional accuracy.
Microstructural Damage and Instability
At the microscopic level, excessive heat leads to uncontrolled grain growth. Instead of a fine, uniform grain structure, you get large, coarse grains. This larger structure is almost always mechanically weaker.
For certain materials like zirconia, high temperatures can trigger unwanted phase transformations, lowering the material's chemical and structural stability and making it prone to failure later.
Compromised Mechanical Properties
The direct result of microstructural damage is a loss of mechanical integrity.
Large grains and internal stresses from rapid phase changes create weak points within the material, often leading to spontaneous cracking either during cooling or when subjected to minimal stress.
Altered Optical and Aesthetic Properties
For materials where appearance is critical, such as dental ceramics, over-sintering is highly detrimental.
The formation of large grains and the elimination of specific pore structures can dramatically reduce translucency, making a material like zirconia appear opaque and chalky rather than natural.
Molecular Decomposition in Polymers
In polymers like PTFE, excessive heat can cause chain scission, which is the breaking of the long molecular chains that give the material its properties.
This is measured as a reduction in the number average molecular weight. The material is fundamentally decomposing, leading to a drastic loss of strength, toughness, and chemical resistance.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Sintering Window
The key challenge of sintering is not simply heating a part, but navigating the narrow window between an incomplete process and a destructive one.
Too Low vs. Too High
If the temperature is too low or the time is too short, the result is insufficient sintering. The part will not reach its target density, remaining porous and mechanically weak.
If the temperature is too high or the time is too long, the result is over-sintering. The part suffers from the grain growth, warping, and decomposition detailed above.
The Critical Role of Time
Temperature is not the only variable. A part held for too long even at a "correct" temperature can exhibit the same over-sintering defects as a part heated to an excessive temperature for a shorter time. These two factors are inextricably linked.
Optimizing Your Sintering Process
Your approach to temperature control should be dictated by the most critical properties of your final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Your goal is to find the highest possible temperature within the optimal window, just before significant grain growth begins.
- If your primary focus is preserving fine features or translucency: You should err on the lower side of the temperature window, as these properties are often the first to be damaged by over-sintering.
- If your primary focus is processing polymers (like PTFE or PEEK): You must adhere strictly to the manufacturer's specified temperature profile to prevent irreversible molecular decomposition.
Ultimately, mastering sintering means treating temperature not as a brute force tool, but as a precision instrument to achieve targeted material properties.
Summary Table:
| Consequence | Effect on the Part | Common in Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Warping & Sagging | Loss of dimensional accuracy and shape | Metals, Ceramics |
| Uncontrolled Grain Growth | Weaker, coarse microstructure; reduced strength | Metals, Technical Ceramics |
| Phase Transformations | Loss of chemical/structural stability | Zirconia |
| Reduced Translucency | Opaque, chalky appearance | Dental Zirconia |
| Molecular Decomposition (Chain Scission) | Drastic loss of strength & chemical resistance | Polymers (PTFE, PEEK) |
Achieve Perfect Sintering Results with KINTEK
Is inconsistent temperature control causing warping, cracking, or weak parts in your lab? Over-sintering doesn't just waste materials—it compromises your research and product quality.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for reliable, repeatable sintering. We help laboratories like yours eliminate guesswork and achieve optimal material properties batch after batch.
Let us help you master the sintering window. Our experts can guide you to the right equipment for your specific materials—whether you're working with advanced ceramics, metals, or polymers.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your sintering process, improve part quality, and boost your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum sintering furnace facilitate MgO densification? Optimize Purity and Density with KINTEK Solutions
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace in the final processing stage of ODS ferritic steel? Optimizing ODS Alloy Integrity
- Why is a vacuum drying system utilized for PDVB nanoparticle preparation? Preserve Structure and Chemical Activity
- What are the different types of EAF? AC vs. DC and Charging Methods Explained
- What is the function of a high-precision industrial furnace for Alloy 718? Master Strengthening & Microstructure Control
- What is a vacuum furnace and how does it work? Achieve High-Purity Thermal Processing
- What is a retort in heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Quality and Metallurgical Control
- Can a furnace melt tungsten? Unlocking the Secrets of Extreme Temperature Processing



















