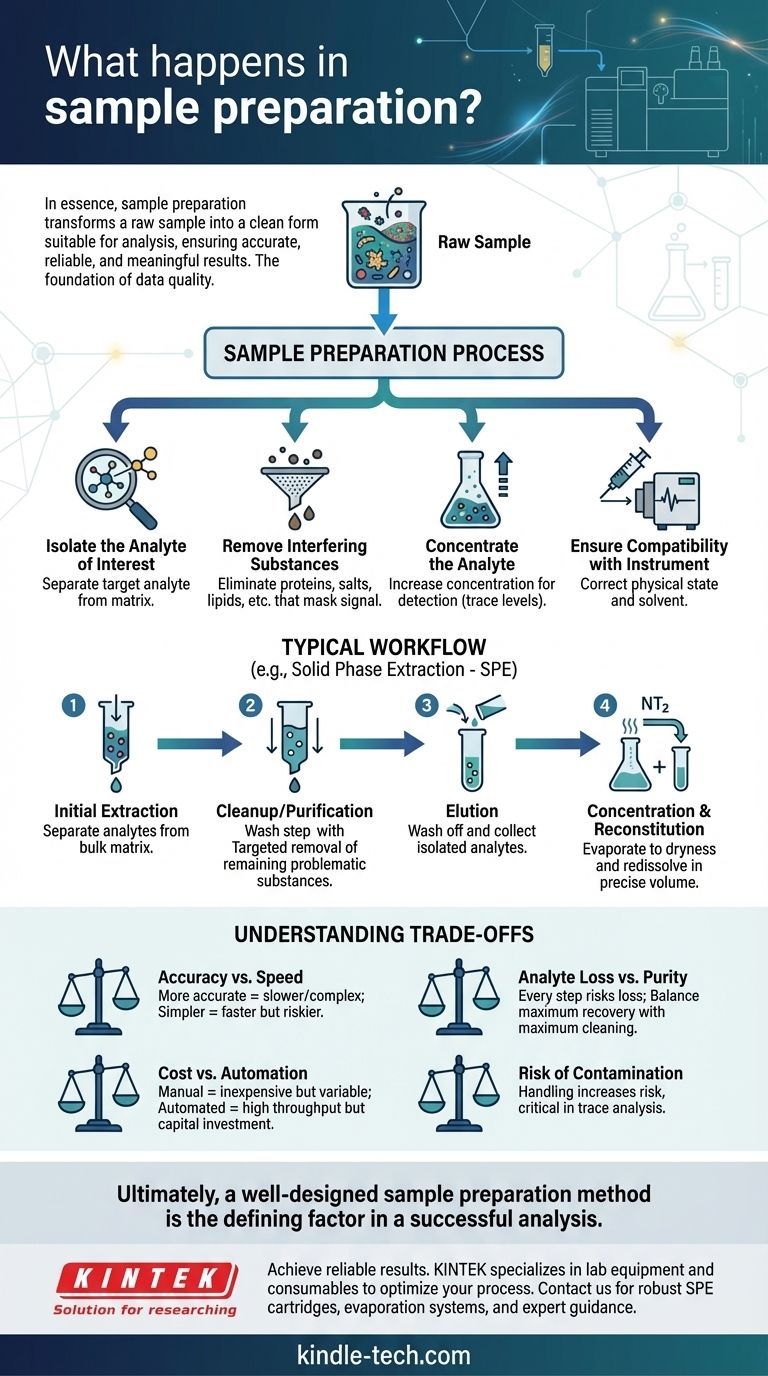
In essence, sample preparation is the critical series of steps performed to transform a raw, often complex sample into a refined, clean form that is suitable for analysis by an instrument. It involves isolating the specific components of interest (analytes) and removing any other substances (the matrix) that could interfere with the measurement. This process ensures the final analytical result is accurate, reliable, and meaningful.
The core purpose of sample preparation is not just to prepare a sample, but to guarantee the quality of the final data. It is often the most labor-intensive and error-prone stage of an entire analysis, yet it is the foundation upon which the validity of the result rests.

The Core Goals of Sample Preparation
Every sample preparation protocol is designed to achieve a few fundamental objectives. Understanding these goals clarifies why this process is non-negotiable in serious analytical work.
Isolate the Analyte of Interest
The "analyte" is the specific chemical or substance you are trying to measure. Your raw sample, however, contains countless other compounds. The first goal is to separate this target analyte from everything else.
Remove Interfering Substances
The material surrounding your analyte is called the "matrix." In a blood sample, the matrix includes proteins, salts, and lipids. These substances can mask the analyte's signal or damage the analytical instrument, so they must be removed.
Concentrate the Analyte
In many cases, the analyte is present in very low concentrations (trace levels). Sample preparation often includes steps to concentrate the analyte into a smaller volume, making it easier for the instrument to detect and quantify accurately.
Ensure Compatibility with the Instrument
Analytical instruments, such as a mass spectrometer or chromatograph, have strict requirements for the samples they can analyze. The sample must be in the correct physical state (e.g., a clean liquid) and dissolved in a solvent that works with the system.
A Typical Sample Preparation Workflow
While methods vary widely depending on the sample type and analytical goal, many protocols follow a general sequence of extraction, cleanup, and concentration.
Step 1: Initial Extraction
This is the first major step to separate the analytes from the bulk of the sample matrix. A common technique is Solid Phase Extraction (SPE), where the sample is passed through a cartridge containing a material (sorbent) that selectively retains the analytes while allowing interferences to pass through.
Step 2: Cleanup or "Purification"
After initial extraction, some interfering compounds may remain. A cleanup step provides a more targeted removal of these problematic substances. This might involve washing the SPE cartridge with a specific solvent or using a different purification technique altogether.
Step 3: Elution
Once the analytes are isolated and the interferences have been removed, the analytes are "eluted"—washed off the SPE sorbent using a strong solvent. This collects your purified analytes in a clean solution.
Step 4: Concentration and Reconstitution
The eluted sample is often too dilute for analysis and may be in a solvent that is incompatible with the instrument. The sample is typically evaporated to dryness (e.g., under a stream of nitrogen) and then "reconstituted" in a small, precise volume of a suitable solvent.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sample preparation method involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" method, only the best method for a specific application.
Accuracy vs. Speed
More exhaustive, multi-step preparation methods yield cleaner samples and more accurate data. However, they are time-consuming and complex. Simpler methods like "dilute-and-shoot" are fast but risk matrix interference and lower sensitivity.
Analyte Loss vs. Purity
Every manipulation step—extraction, washing, evaporation—carries the risk of losing some of your target analyte. The goal is to design a process that removes the maximum amount of interference while retaining the maximum amount of analyte.
Cost vs. Automation
Manual sample preparation is inexpensive but prone to human error and inconsistency. Fully automated systems provide excellent reproducibility and high throughput but require a significant capital investment.
The Risk of Contamination
Every time the sample is handled or transferred, there is a chance of introducing external contaminants. This is especially critical in trace analysis, where even microscopic contamination can invalidate results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sample preparation strategy is dictated entirely by the objective of your analysis.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening (e.g., routine quality control): Prioritize speed and simplicity with methods that can be easily automated, even if it means sacrificing some sensitivity.
- If your primary focus is trace-level quantitation (e.g., environmental or forensic analysis): Invest time in a comprehensive, multi-step cleanup and concentration protocol to ensure maximum accuracy and sensitivity.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a complex biological matrix (e.g., plasma or tissue): Your main challenge is removing major interferences like proteins and phospholipids, which will dictate your choice of technique.
Ultimately, a well-designed sample preparation method is the defining factor in a successful analysis.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Goal | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Extraction | Isolate analyte from the sample matrix. | Technique choice (e.g., SPE) impacts selectivity and recovery. |
| Cleanup | Remove interfering substances. | Balances analyte purity against potential analyte loss. |
| Concentration | Increase analyte levels for detection. | Essential for trace analysis; must avoid contamination. |
| Final Preparation | Make sample compatible with the instrument. | Solvent choice and final volume are critical for instrument performance. |
Achieve reliable results from the very first step. The right sample preparation is the foundation of any successful analysis. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable tools and expert support your laboratory needs to optimize this critical process. Whether you require robust SPE cartridges, efficient evaporation systems, or guidance on method development, we are here to help. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific sample preparation challenges and enhance your lab's data quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- High Performance Lab Homogenizer for Pharma Cosmetics and Food R&D
People Also Ask
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination
- What is the function of an Agate Mortar and Pestle in sodium battery preparation? Ensure Contaminant-Free Mixing
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- What is the particle size for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Results with the Right Preparation

















