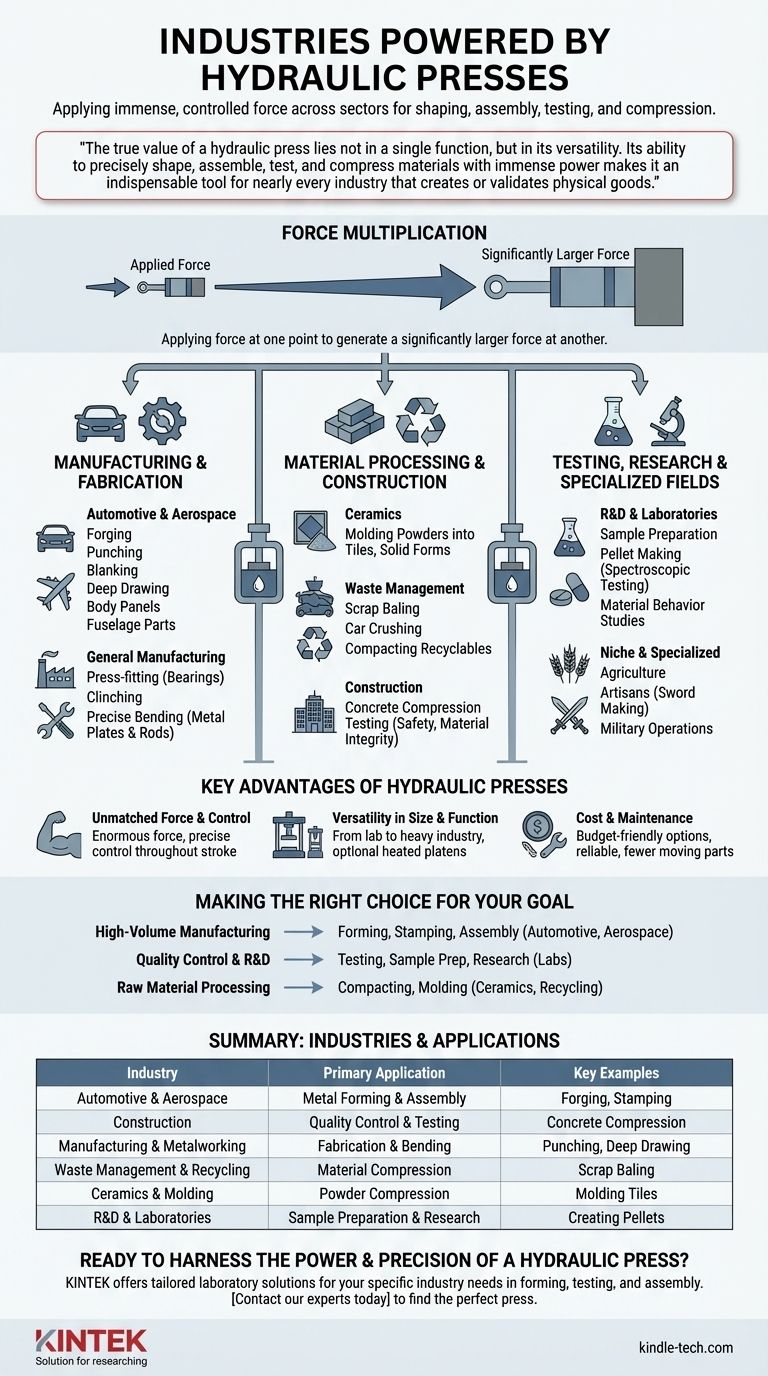
At its core, a hydraulic press is a machine for applying immense, controlled force. This capability makes it a cornerstone technology across a vast range of sectors, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and general manufacturing. From shaping the body panels of a car to testing the strength of concrete, its applications are fundamental to modern industrial processes.
The true value of a hydraulic press lies not in a single function, but in its versatility. Its ability to precisely shape, assemble, test, and compress materials with immense power makes it an indispensable tool for nearly every industry that creates or validates physical goods.

How Industries Use Hydraulic Force
A hydraulic press operates on a simple principle: applying force at one point to generate a significantly larger force at another. This force multiplication is the key to its widespread use in transforming materials.
Metal Forming and Fabrication
This is the most common application, forming the backbone of the automotive, aerospace, and metalworking industries.
Presses are used for forging, punching, blanking, and deep drawing operations to create everything from car door panels and chassis components to aircraft fuselage parts. The controlled, even pressure is ideal for shaping metal sheets without creating weak points.
Assembly and Bending
In general manufacturing, hydraulic presses are critical for assembly.
They press-fit parts together with high precision, such as inserting bearings into housings or joining components with clinching. They are also used for creating precise bends in metal plates and rods.
Material Compression and Molding
Several industries rely on the press's ability to compact loose material into a dense, solid form.
The ceramics industry uses presses to mold powders into tiles and other shapes before firing. Similarly, the waste management sector uses massive presses for scrap baling, crushing old cars and compacting scrap metal into dense, transportable blocks. This same principle applies to compacting powders for various industrial and scientific uses.
Beyond the Factory Floor
While most associated with manufacturing, the hydraulic press serves critical functions in testing, research, and other specialized fields.
Construction and Quality Control
In the construction industry, safety and material integrity are paramount.
Small-scale hydraulic presses are used for concrete compression testing, where they apply force to concrete cylinders until they fail. This process verifies that the concrete mix meets the required strength standards for use in buildings, bridges, and roads.
Research and Development
Academic and corporate R&D labs use specialized laboratory hydraulic presses.
These compact, benchtop units are ideal for preparing samples for analysis, such as compressing material into pellets for spectroscopic testing. They are also used to study how different substances behave under extreme pressure, contributing to materials science advancements.
Niche and Specialized Tasks
The versatility of the hydraulic press has led to its adoption in many unique fields.
These include agriculture for processing materials, specialized artisans for tasks like sword making, and even the military for various manufacturing and maintenance operations.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The dominance of the hydraulic press isn't accidental. It stems from a few core advantages that make it more suitable than other machine types for a wide range of tasks.
Unmatched Force and Control
The primary benefit of a hydraulic system is its ability to generate enormous force from a relatively simple and compact design. Unlike mechanical presses, a hydraulic press can apply its full force at any point in the stroke, giving the operator precise control over the entire process.
Versatility in Size and Function
Hydraulic presses are not one-size-fits-all. They range from small, manually operated lab presses to massive, automated systems used in heavy industry. Features like heated platens can be added for molding applications, further expanding their utility.
Cost and Maintenance
While large industrial presses are significant investments, smaller electric hydraulic presses offer a powerful and budget-friendly option for metalworking shops and smaller operations. Their relatively simple design with fewer moving parts often translates to high reliability and straightforward maintenance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your industry dictates how you will leverage a hydraulic press.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: You will use hydraulic presses for forming, stamping, and assembling key components in sectors like automotive and aerospace.
- If your primary focus is quality control and R&D: You will rely on smaller laboratory presses for material strength testing, sample preparation, and fundamental research.
- If your primary focus is raw material processing: You will use presses for tasks like compacting scrap metal, molding ceramics, or processing agricultural products.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press is a foundational tool, enabling industries to transform raw materials into the functional products that shape our world.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application | Key Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & Aerospace | Metal Forming & Assembly | Forging parts, stamping body panels, press-fitting bearings |
| Construction | Quality Control & Testing | Concrete compression testing, material strength validation |
| Manufacturing & Metalworking | Fabrication & Bending | Punching, blanking, deep drawing, bending plates |
| Waste Management & Recycling | Material Compression | Scrap metal baling, car crushing, compacting recyclables |
| Ceramics & Molding | Powder Compression | Molding tiles, compacting powders into solid forms |
| R&D & Laboratories | Sample Preparation & Research | Creating pellets for analysis, studying material behavior under pressure |
Ready to harness the power and precision of a hydraulic press in your operation?
Whether you are in high-volume manufacturing, require rigorous quality control testing, or need a reliable press for R&D and sample preparation, KINTEK has the right laboratory equipment for you. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you get a solution tailored to your specific industry needs, helping you achieve superior results in forming, testing, and assembly.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and find the perfect hydraulic press for your laboratory or facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.



















