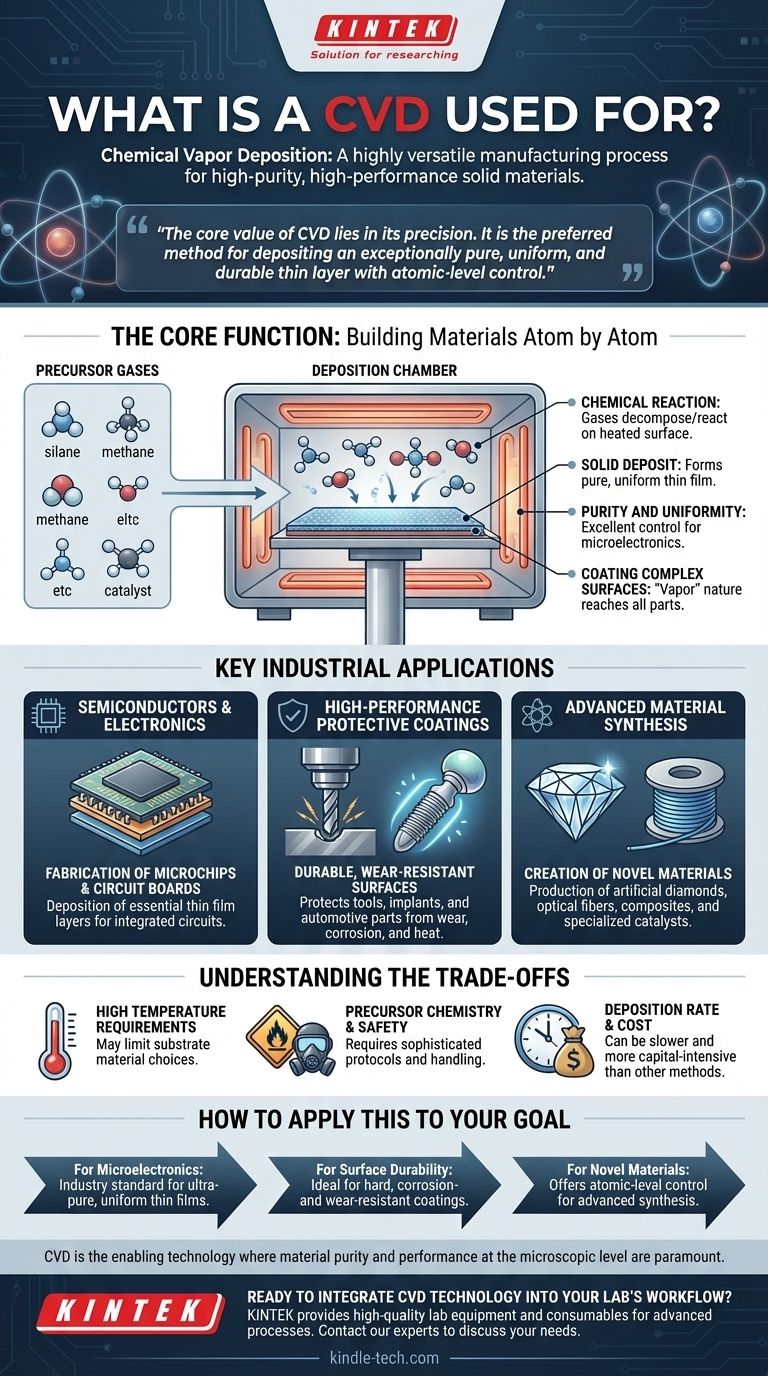
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a highly versatile manufacturing process used to create exceptionally high-purity, high-performance solid materials, typically as a thin film or coating on a substrate. Its most prominent applications are in the semiconductor industry for fabricating microchips, applying durable protective coatings on everything from machine tools to medical implants, and synthesizing advanced materials like artificial diamonds.
The core value of CVD lies in its precision. It is the preferred method when the goal is not just to coat a surface, but to deposit an exceptionally pure, uniform, and durable thin layer of material with atomic-level control, a critical requirement for today's most advanced technologies.
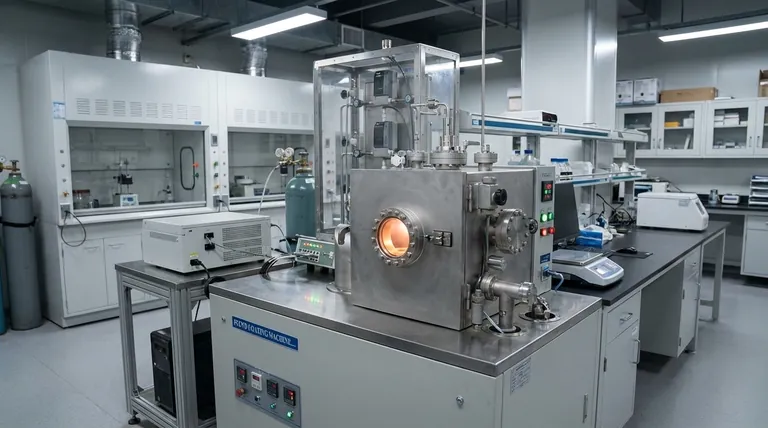

The Core Function: Building Materials Atom by Atom
CVD is fundamentally a process of construction. It involves introducing reactive gases (precursors) into a chamber, where they decompose or react on a heated surface (the substrate) to form a solid deposit. This chemical reaction is the key to its precision and quality.
The Hallmark of a CVD Film: Purity and Uniformity
Because the material is built up through a chemical reaction on the surface, the process allows for extremely fine control over the final product.
This results in films with excellent purity and uniformity in thickness, which is a non-negotiable requirement in microelectronics.
Coating Complex and Diverse Surfaces
The "vapor" nature of the process allows the precursor gases to reach all parts of a substrate, even complex shapes.
This makes CVD highly effective for coating a wide variety of materials and objects, from flat silicon wafers to intricate medical or automotive tools.
Key Industrial Applications of CVD
The unique capabilities of CVD have made it indispensable across several high-tech industries. Its applications are defined by the need for materials with superior performance characteristics.
The Semiconductor and Electronics Industry
This is the largest and most well-known application. CVD is used to deposit various thin films that form the essential layers of integrated circuits, or microchips.
It's also used in the fabrication of circuit boards and other microfabrication processes where precise, high-quality material layers are essential.
High-Performance Protective Coatings
CVD is used to apply hard, durable coatings that protect surfaces from wear, corrosion, and high temperatures.
Key examples include coatings on machine tools, automotive components, and biomedical implants. It's also used on architectural glass for heat protection and on bottles to improve mechanical shock resistance.
Advanced Material Synthesis
The process allows for the creation of materials that are difficult or impossible to produce with other methods.
The most famous example is the production of artificial diamonds for industrial and jewelry use. Other applications include creating optical fibers, composites, and specialized catalysts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is balanced by certain operational requirements and limitations that must be considered.
High Temperature Requirements
Traditional CVD processes often require very high temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions on the substrate. This can limit the types of materials that can be coated, as some may not withstand the heat.
Precursor Chemistry and Safety
The precursor gases used in CVD can be toxic, flammable, or highly reactive. This necessitates sophisticated safety protocols, specialized handling equipment, and careful exhaust management, which can increase operational complexity and cost.
Deposition Rate and Cost
While CVD produces exceptionally high-quality films, the deposition rate can sometimes be slower than alternative methods like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The specialized equipment and precursor materials can also make it a more capital-intensive process.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on the required properties of the final product. CVD excels where material quality is the primary concern.
- If your primary focus is microelectronics: CVD is the industry standard for depositing the ultra-pure, uniform thin films required to fabricate modern semiconductor devices.
- If your primary focus is surface durability and protection: CVD provides the ideal solution for creating hard, corrosion-resistant, and wear-resistant coatings on industrial tools, implants, and high-performance components.
- If your primary focus is creating novel, high-purity materials: CVD offers the atomic-level control needed to synthesize advanced materials like synthetic diamonds, barrier layers, and specialized optical fibers.
Ultimately, CVD is the enabling technology for any application where material purity and performance at the microscopic level are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Cases | CVD Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors & Electronics | Microchip fabrication, circuit boards | Ultra-pure, uniform thin films |
| Protective Coatings | Machine tools, medical implants, automotive parts | Durable, wear-resistant surfaces |
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Artificial diamonds, optical fibers, composites | Atomic-level control for high-purity materials |
Ready to integrate CVD technology into your lab's workflow?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for advanced processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition. Whether you are developing next-generation microchips, applying durable protective coatings, or synthesizing novel materials, having the right tools is critical for success.
Contact our experts today via our simple form to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve superior material purity and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does CVD graphene work? Scaling Up High-Quality 2D Material Production
- What advantages do CVD furnaces offer for Wf/W composites? Preserving Fiber Ductility and Interface Integrity
- What is the use of thin film in optics? Mastering Light Control for Lenses, Mirrors, and Filters
- What are the applications of thin film deposition? From Electronics to Medical Devices
- What are the advantages of RF plasma? Superior Processing for Insulating Materials
- What is the process of CVD? A Step-by-Step Guide to Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What are the catalysts for CNT synthesis? The Key to Controlling Carbon Nanotube Growth
- What are the ingredients in synthetic diamonds? Unlocking the Science of Lab-Grown Carbon Crystals



















