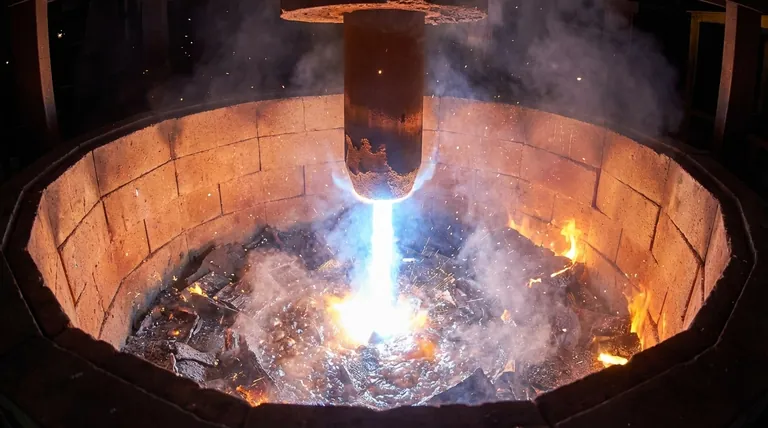
In smelting, a graphite rod primarily functions as an electrode in an electric arc furnace (EAF). Its purpose is to conduct massive amounts of electricity and generate an intensely hot electric arc—a bolt of lightning, essentially—that melts scrap metal or other raw materials. This process does not rely on burning fuel, but rather on the raw power of electricity converted into thermal energy.
The core reason for using graphite is its unique combination of properties that no other material can offer economically. It is an excellent electrical conductor that can withstand temperatures far beyond the melting point of steel, all while remaining chemically stable and strong enough for the harsh furnace environment.

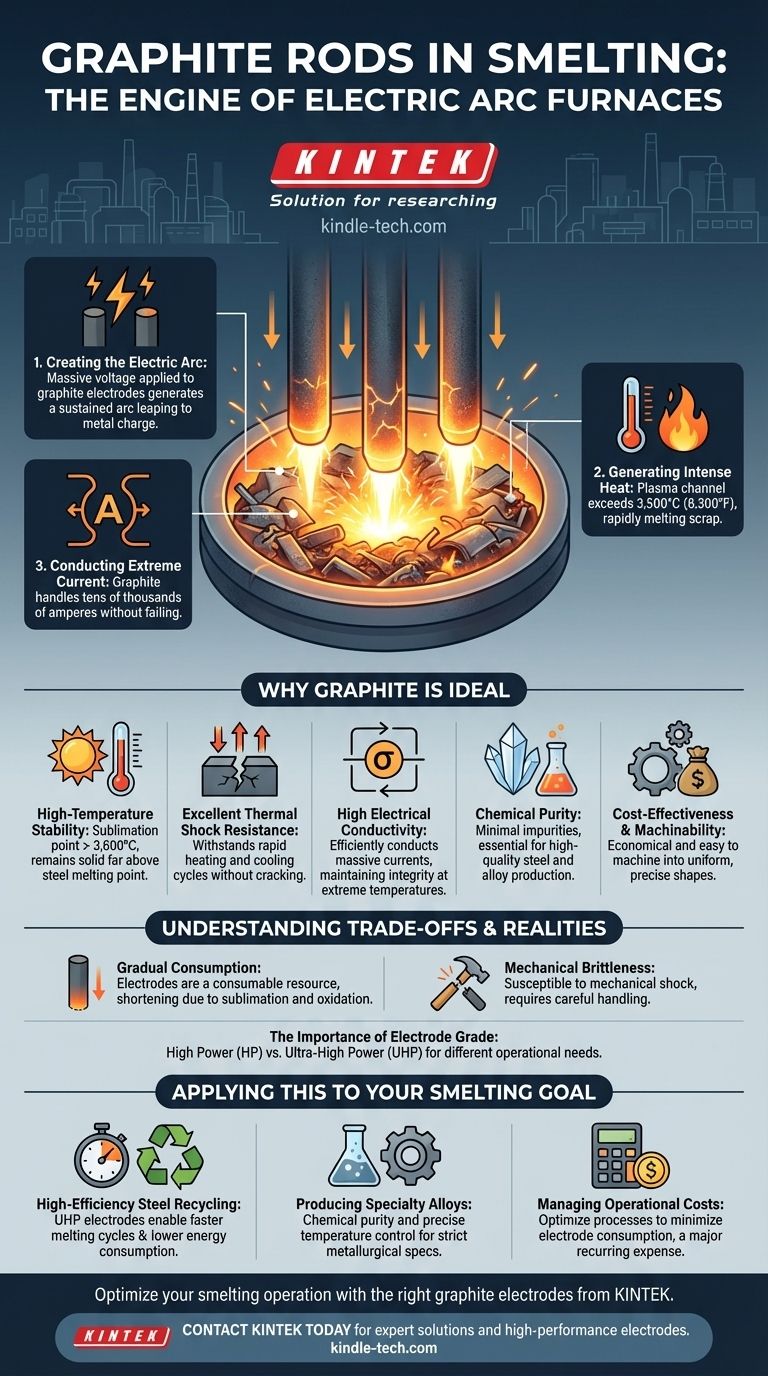
How the Electrode Drives the Smelting Process
An electric arc furnace uses graphite electrodes to turn solid metal into a liquid bath. The process is a demonstration of controlled, immense power.
Creating the Electric Arc
The large graphite electrodes are positioned inside the furnace, above the solid charge of scrap metal. They are lowered until they are close to the metal, and a massive voltage is applied. This creates a sustained electric arc that leaps from the electrode tip to the metal charge.
Generating Intense Heat
This arc is a plasma channel with a temperature that can exceed 3,500°C (6,300°F). This is more than double the melting point of steel. The intense radiant heat from the arc rapidly melts the charge below it. This method is incredibly fast and efficient for melting large quantities of metal.
Conducting Extreme Electrical Current
To sustain such an arc, the electrodes must safely conduct enormous currents, often in the range of tens of thousands of amperes. The graphite's structure allows it to handle this electrical load without failing, a task that common metallic conductors like copper could not perform at these temperatures.
Why Graphite is the Ideal Material
The choice of graphite is not accidental; it is a material perfectly engineered by nature and manufacturing for this extreme role. Several key properties make it the undisputed standard.
Unmatched High-Temperature Stability
Graphite has one of the highest sublimation points of any element, turning directly from a solid to a gas at over 3,600°C (6,500°F). It does not melt at atmospheric pressure, ensuring it remains a solid, stable tool far above the temperatures needed to smelt steel and other metals.
Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnaces go through rapid heating and cooling cycles. Graphite can withstand these drastic temperature changes without cracking or shattering, a property known as thermal shock resistance. This durability is critical for operational reliability.
High Electrical Conductivity
While not as conductive as copper at room temperature, graphite's conductivity is more than sufficient for the task and, crucially, it maintains its structural integrity at temperatures that would instantly vaporize other conductors.
Chemical Purity
Graphite is a very clean material, primarily composed of carbon. When used as an electrode, it introduces minimal impurities into the molten metal, which is essential for producing high-quality steel and other alloys.
Cost-Effectiveness and Machinability
Despite its extreme properties, graphite can be manufactured into the large, uniform cylinders required for electrodes at a lower cost than other refractory metals like tungsten. It is also relatively easy to machine into precise shapes with threaded sockets for connecting multiple electrodes together.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
While ideal, graphite is not without its operational challenges. Understanding these limitations is key to managing an efficient smelting operation.
Gradual Electrode Consumption
The single biggest trade-off is that electrodes are a consumable resource. The tip of the electrode is slowly consumed through sublimation due to the arc's heat. Furthermore, the hot surface of the electrode oxidizes (burns) when exposed to air, causing it to gradually shorten over time. This consumption is a significant operational cost.
Mechanical Brittleness
Compared to metals, graphite is brittle and can be damaged by mechanical shock. Care must be taken during handling and furnace operation to prevent the electrodes from breaking, which can lead to costly downtime.
The Importance of Electrode Grade
Not all graphite is the same. Electrodes are produced in different grades, such as High Power (HP) and Ultra-High Power (UHP). UHP electrodes are made from higher-quality raw materials and can handle greater current densities with lower consumption rates, making them essential for the most demanding furnaces.
Applying This to Your Goal
The function of the graphite electrode is straightforward, but its implications vary depending on your operational focus.
- If your primary focus is high-efficiency steel recycling: UHP graphite electrodes are non-negotiable, as they enable faster melting cycles (tap-to-tap times) and lower energy consumption per ton of steel produced.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty alloys: The chemical purity and precise temperature control afforded by the graphite electrode arc are critical for meeting strict metallurgical specifications.
- If your primary focus is managing operational costs: The key is to optimize processes to minimize electrode consumption, as this is a major recurring expense in electric furnace operations.
Ultimately, the graphite electrode is not just a component; it is the very engine of modern electric smelting, enabling a process that is both powerful and precise.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Smelting |
|---|---|
| High-Temperature Stability | Withstands temperatures exceeding 3,500°C (6,300°F) without melting. |
| Excellent Electrical Conductivity | Safely conducts massive currents (10,000s of amperes) required for the arc. |
| Superior Thermal Shock Resistance | Resists cracking during rapid heating and cooling cycles in the furnace. |
| Chemical Purity | Minimizes impurities in the molten metal, ensuring high-quality alloy production. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Provides unmatched performance at a lower cost than alternative refractory metals. |
Optimize your smelting operation with the right graphite electrodes.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including graphite electrodes for demanding industrial applications. Whether your goal is maximizing efficiency in steel recycling, producing high-purity specialty alloys, or managing operational costs, the right electrode grade is critical.
Our experts can help you select the ideal High Power (HP) or Ultra-High Power (UHP) graphite electrodes to reduce consumption rates, improve melt times, and enhance your final product quality.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can power your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Glassy Carbon Electrochemical Electrode
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics and applications of a graphite sheet electrode? Maximize Reaction Area for Bulk Electrolysis
- What is the thermal conductivity of graphite at room temperature? A Guide to Its Anisotropic Nature
- What are graphite grades? Find the Right Material for Your Industrial Application
- What is the typical role of a graphite electrode in an electrochemical setup? Complete Your Circuit Efficiently
- What are the properties and applications of a graphite disk electrode? Precision Tools for Electroanalysis



















