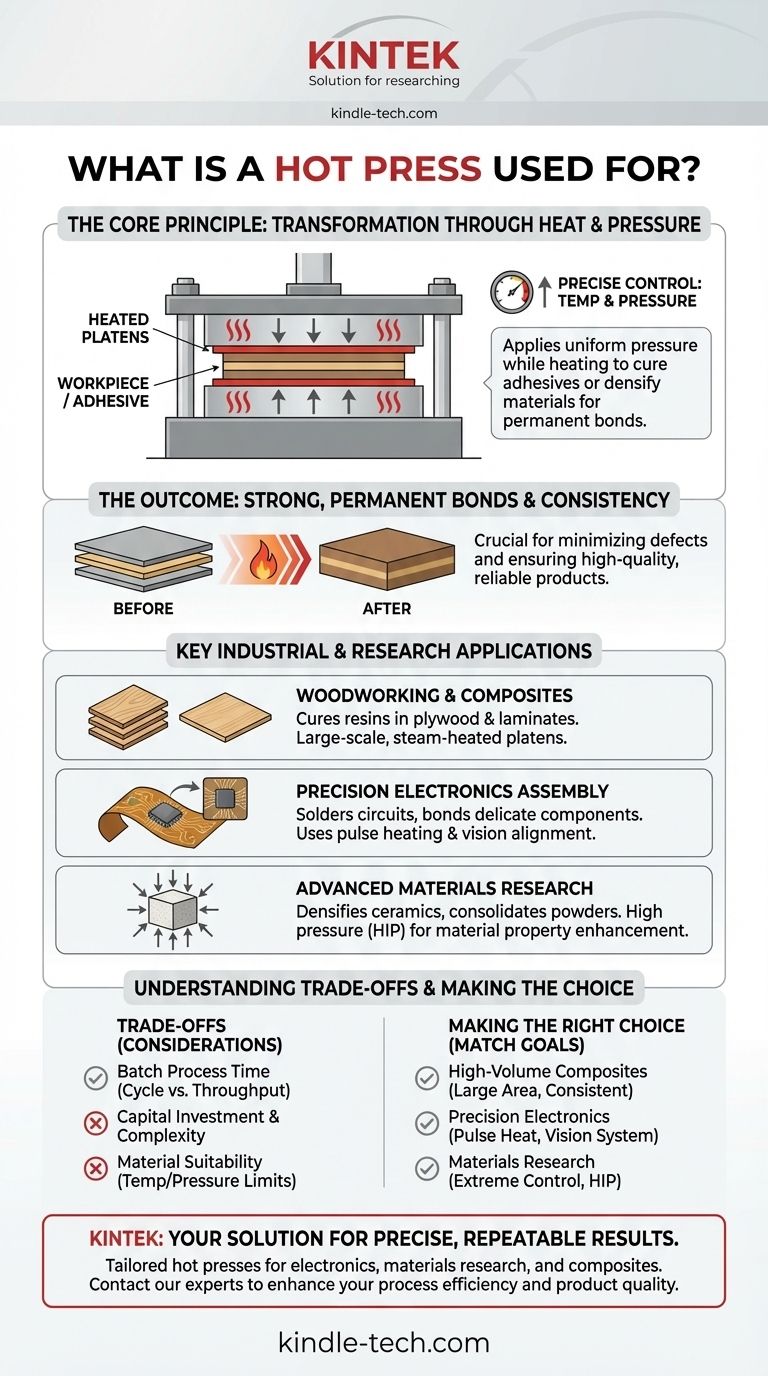
At its core, a hot press is a machine used to bond, form, or alter materials using a combination of precise heat and controlled pressure. It is a fundamental tool in industries ranging from woodworking, where it's used to manufacture plywood, to high-tech electronics, where it creates permanent electrical and mechanical connections for delicate components. The machine works by applying uniform pressure to a workpiece while heating it to a specific temperature, often to cure an adhesive or fundamentally change the material's properties.
The true value of a hot press lies not just in applying heat and pressure, but in the precise and repeatable control over those forces. This control is what enables manufacturers and researchers to create strong, consistent bonds and engineer materials with specific, high-performance characteristics.

The Core Principle: Transformation Through Heat and Pressure
A hot press operates on a simple but powerful premise: combining thermal energy and mechanical force initiates a physical or chemical change. This controlled transformation is the key to its wide range of applications.
How It Works
The fundamental process involves placing a workpiece, often with an adhesive or bonding agent, between two heated plates called platens. A hydraulic or pneumatic system then applies a specific amount of pressure for a set duration. This combination activates the bonding agent or, in some cases, causes the material itself to densify or change form.
The Goal: Strong, Permanent Bonds
The primary function of most hot press applications is to create a robust and permanent bond. For example, in plywood manufacturing, the heat and pressure cure the resin that holds the layers of wood veneer together, forming a single, strong panel. In electronics, the process can solder flexible circuits or bond components permanently.
The Outcome: Quality and Consistency
By ensuring even temperature distribution and uniform pressure application, a hot press minimizes common manufacturing defects like workpiece deformation. This level of control is critical for producing high-quality, reliable products, whether it's a perfectly flat sheet of plywood or a precisely aligned electronic sensor.
Key Industrial and Research Applications
The versatility of the hot press allows it to be used in vastly different fields, each leveraging its core capabilities for a specific outcome.
Woodworking and Composite Manufacturing
This is one of the most common applications. In the plywood industry, large-scale hot presses use steam-heated platens to bake and compress panels of veneer and core, curing the adhesive that binds them. This same principle applies to creating other composite materials and laminates.
Precision Electronics Assembly
Modern electronics rely on hot presses for highly sensitive tasks. Features like pulse heating (for rapid heating and cooling) and CCD vision systems (for perfect alignment) are essential for bonding fine-pitch flexible circuits, heat-sealing connectors, and performing hot bar soldering without damaging delicate components.
Advanced Materials and Research
In materials science, specialized hot presses are used for cutting-edge applications. Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) units, for example, use high pressure from all directions to densify ceramics, consolidate superalloy powders into solid parts, and impregnate materials with carbon to enhance their properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a hot press is a specialized tool with specific considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Cycle Time vs. Throughput
The process of heating, pressing, and cooling takes time. This makes hot pressing a batch or semi-batch process. For applications where speed is the absolute priority, other bonding methods like ultrasonic welding or simple mechanical fasteners might be more suitable.
Capital Investment and Complexity
A hot press, particularly a high-precision model with advanced vision and heating controls, represents a significant capital investment. The complexity also requires skilled operation and maintenance compared to simpler assembly methods.
Material Suitability
The core process requires materials that can withstand the necessary temperatures and pressures without degrading. This makes it an unsuitable choice for bonding certain heat-sensitive plastics or extremely delicate components that cannot tolerate direct pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right type of hot press depends entirely on the intended application, as different goals demand different capabilities.
- If your primary focus is high-volume composite manufacturing (like plywood): You need a large-scale hydraulic or steam-powered press designed for consistent heat and pressure over a large surface area.
- If your primary focus is precision electronics assembly: Your priority should be a system with advanced features like pulse heating, CCD vision for alignment, and programmable, multi-stage temperature profiles.
- If your primary focus is materials science research: You require a smaller, highly controllable unit, possibly a hot isostatic press, to achieve extreme pressures and temperatures for material densification and property analysis.
Ultimately, selecting the right hot press is about matching its precision control capabilities to your specific material and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Function | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Woodworking & Composites | Bond layers of wood/veneer | Large platens, uniform pressure, steam heating |
| Precision Electronics | Create permanent connections | Pulse heating, CCD vision systems, precise alignment |
| Advanced Materials Research | Densify materials, alter properties | High pressure (e.g., Hot Isostatic Pressing), extreme temperatures |
Ready to achieve precise, repeatable results in your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including hot presses tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're in electronics assembly, materials research, or composite manufacturing, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for strong, consistent bonds and material transformations.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hot press can enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What is a hot hydraulic press? Harness Heat and Pressure for Advanced Manufacturing
- How does a hydraulic hot press contribute to the fabrication of all-solid-state battery cells? Enhance Ion Transport
- What is the purpose of using a laboratory hydraulic press for nanocomposites? Ensure Precise Material Characterization
- Why is a hydraulic press used for pre-deformation treatment? Enhance Coating Hardness & Thermal Stability



















