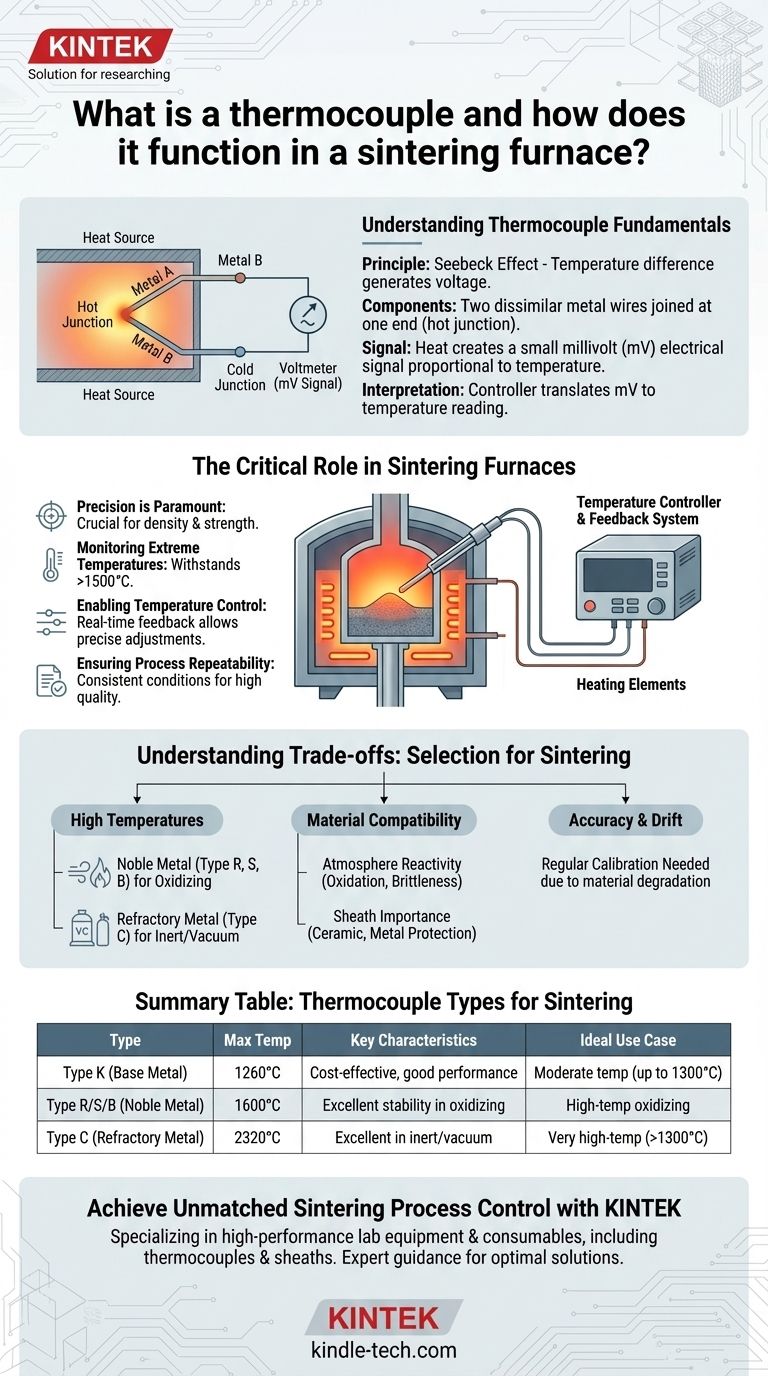
A thermocouple is a temperature sensor that leverages the principle that two dissimilar metals, when joined at a junction and heated, produce a small, measurable electrical voltage directly proportional to the temperature. In a sintering furnace, this electrical signal is read by a controller, enabling precise monitoring and control of the high temperatures critical for the material consolidation process.
Thermocouples are indispensable in sintering furnaces, providing the accurate and reliable temperature feedback necessary to control the complex thermal cycles that dictate the final properties of sintered materials. Their ability to operate effectively at extreme temperatures ensures consistent product quality and process repeatability.
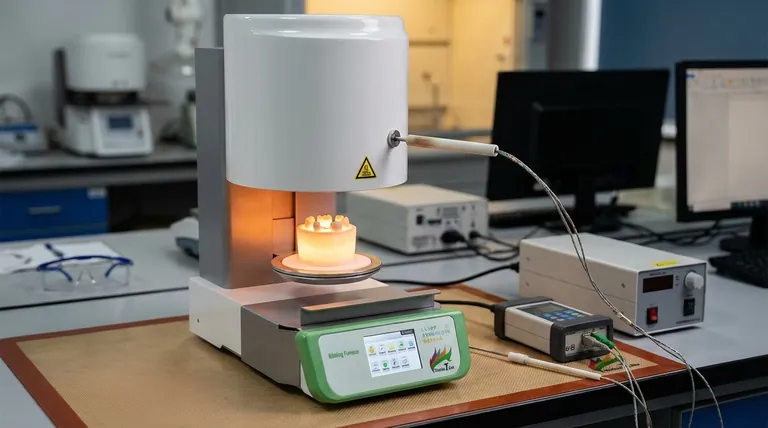

Understanding Thermocouple Fundamentals
The Core Principle: Seebeck Effect
A thermocouple operates on the Seebeck effect. This phenomenon describes how a temperature difference across a junction of two dissimilar conductors or semiconductors generates a voltage.
Components of a Thermocouple
It consists of two wires made from different metals, such as iron and constantan (Type J) or chromel and alumel (Type K). These wires are welded together at one end, forming the measuring junction, often called the "hot junction" or "sensing bead."
Generating an Electrical Signal
When the measuring junction is exposed to heat, the temperature difference between this junction and the unheated "cold junction" (where the wires connect to the measuring instrument) creates a small millivolt (mV) electrical signal. The magnitude of this voltage is directly related to the temperature difference.
Interpreting the Temperature Reading
An electronic temperature controller or data acquisition system measures this millivolt output. It then uses known conversion tables or algorithms specific to the thermocouple type to translate the voltage into an accurate temperature reading.
The Critical Role in Sintering Furnaces
Why Precision is Paramount
Sintering is a heat treatment process where powdered materials are heated to a temperature below their melting point, causing particles to fuse together. The precise temperature profile during sintering is crucial for achieving desired density, strength, and microstructure in the final product.
Monitoring Extreme Temperatures
Sintering furnaces often operate at extremely high temperatures, sometimes exceeding 1500°C (2700°F) or even higher for advanced ceramics or metals. Standard temperature sensors cannot withstand these conditions. Thermocouples, particularly specific types, are designed for such harsh environments.
Enabling Temperature Control
The thermocouple provides real-time temperature feedback to the furnace's control system. This feedback loop allows the controller to adjust power to heating elements, ensuring the furnace maintains the exact temperature setpoint required throughout the sintering cycle.
Ensuring Process Repeatability
Accurate temperature measurement ensures consistent processing conditions from batch to batch. This repeatability is vital for manufacturing high-quality, uniform products and minimizing defects.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Thermocouple Selection for Sintering
High-Temperature Capabilities
Standard base-metal thermocouples (like Type K or J) are suitable for moderate high temperatures. For very high sintering temperatures, noble metal thermocouples (e.g., Type R, S, B, using Platinum-Rhodium alloys) or refractory metal thermocouples (e.g., Type C, using Tungsten-Rhenium alloys) are essential.
Material Compatibility and Contamination
The furnace atmosphere (e.g., vacuum, inert gas, reducing atmosphere) can react with thermocouple materials. Type C thermocouples with Tungsten-Rhenium are often chosen for extremely high temperatures in vacuum or inert gas, as they can be brittle and oxidize in air.
Protection Sheath Importance
A protective sheath is critical to shield the thermocouple wires from the aggressive environments inside a sintering furnace. Materials like tungsten, molybdenum, or various ceramics (e.g., alumina, zirconia) are selected based on temperature, atmosphere, and chemical compatibility. The sheath prevents contamination and corrosion, extending sensor lifespan and accuracy.
Accuracy and Drift
Even the most robust thermocouples can experience drift over time, where their voltage output at a given temperature changes due to material degradation or contamination. Regular calibration or replacement is necessary to maintain accuracy, especially in demanding sintering applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
If your primary focus is precise temperature control in high-temperature sintering (above 1300°C): Prioritize refractory metal thermocouples like Type C, carefully considering the appropriate sheath material for your furnace atmosphere. If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for moderate sintering temperatures (up to 1300°C): Base-metal thermocouples like Type K or N, protected by suitable ceramic sheaths, offer a good balance of performance and economy. If your primary focus is chemical resistance in oxidizing atmospheres at high temperatures: Noble metal thermocouples (Type R, S, B) with robust ceramic sheaths are generally preferred due to their stability in these conditions.
Choosing the correct thermocouple type and protection system is fundamental to achieving successful and repeatable sintering processes.
Summary Table:
| Thermocouple Type | Typical Max Temperature | Key Characteristics | Ideal Sintering Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type K (Base Metal) | Up to 1260°C (2300°F) | Cost-effective, good performance | Moderate temperature sintering (up to 1300°C) |
| Type R/S/B (Noble Metal) | Up to 1600°C (2912°F) | Excellent stability in oxidizing atmospheres | High-temperature sintering with oxidizing atmospheres |
| Type C (Refractory Metal) | Up to 2320°C (4200°F) | Excellent for extreme temperatures in inert/vacuum | Very high-temperature sintering (above 1300°C) |
Achieve Unmatched Sintering Process Control with KINTEK
Selecting the right thermocouple is critical for the success of your sintering operations. The precise temperature control they enable directly impacts the density, strength, and microstructure of your final product.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including thermocouples and protection sheaths engineered for the demanding environments of sintering furnaces. We understand that your laboratory's success depends on repeatable, accurate thermal cycles.
Let our experts help you choose the optimal thermocouple solution for your specific application, furnace atmosphere, and temperature requirements. We provide the reliable components you need to ensure consistent quality, minimize defects, and maximize your process efficiency.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sintering furnace needs and discover how our specialized thermocouples can enhance your results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















