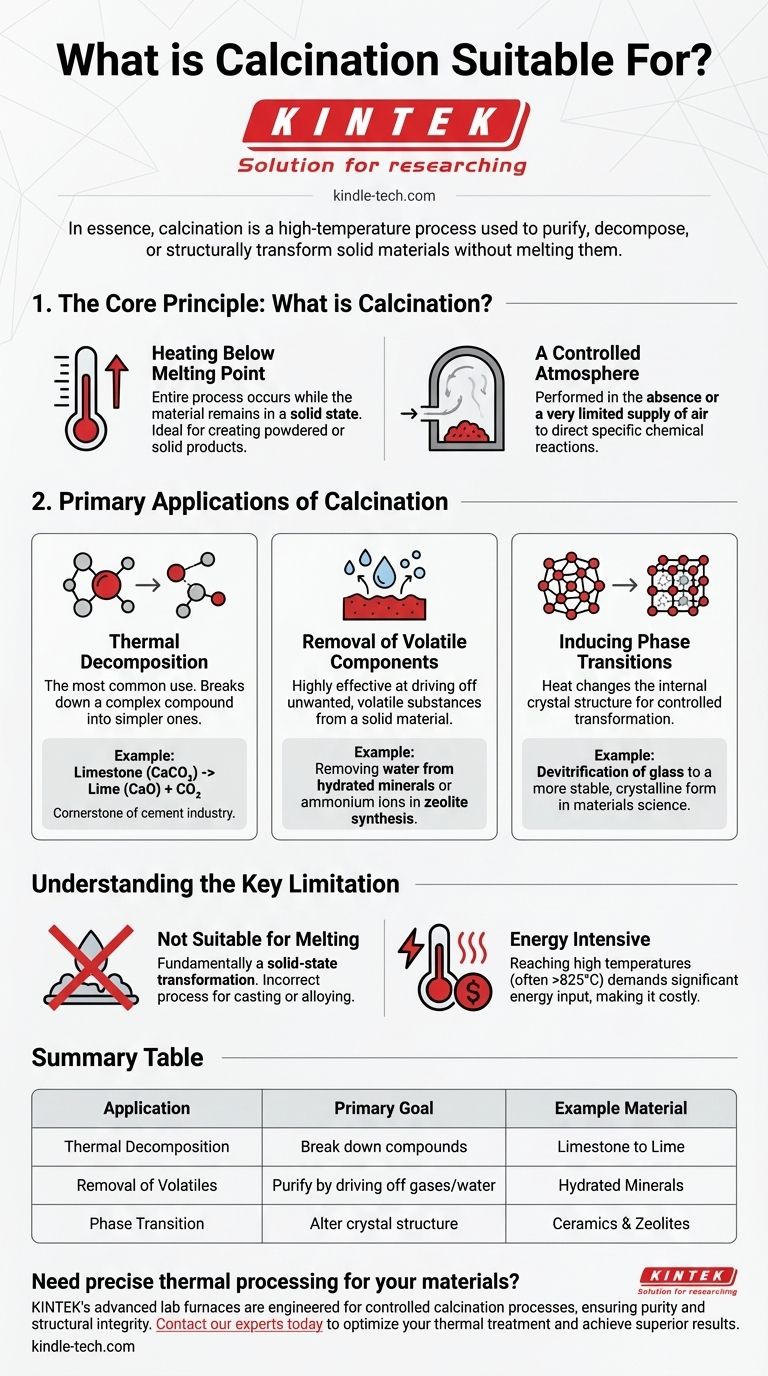
In essence, calcination is a high-temperature process used to purify, decompose, or structurally transform solid materials without melting them. It is most famously suitable for the industrial-scale production of cement and lime from limestone, but its applications extend to creating specialized materials like zeolites and ceramics.
Calcination is not simply about intense heating. It is a precise thermal treatment designed to change a material's fundamental chemistry or physical structure, primarily by removing volatile components like water and carbon dioxide to create a new, more useful substance.
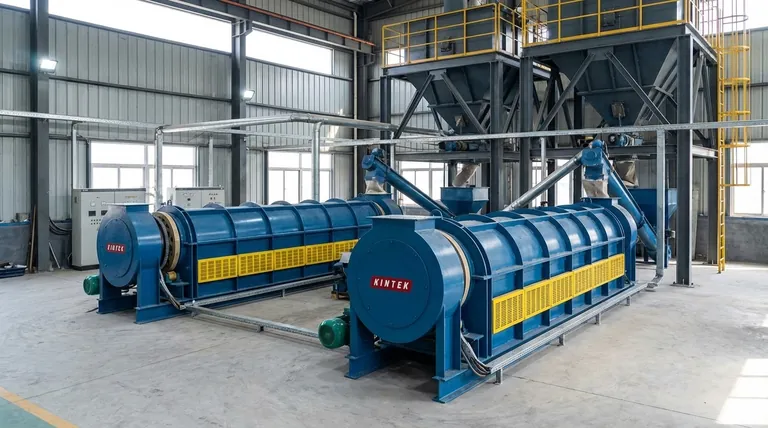

The Core Principle: What is Calcination?
Calcination is a specific type of heat treatment. Its suitability for certain tasks comes from two defining characteristics that separate it from other thermal processes.
Heating Below the Melting Point
The entire process occurs while the material remains in a solid state. The goal is to provide enough thermal energy to break chemical bonds or alter crystal structures, but not so much that the material liquefies.
This makes it ideal for creating powdered or solid products, like the lime that results from heating limestone.
A Controlled Atmosphere
Calcination is performed in the absence or a very limited supply of air. This is a critical distinction from a process like roasting, which uses abundant air to promote oxidation.
By controlling the atmosphere, the process can be directed toward specific chemical reactions, such as pure decomposition rather than combustion.
Primary Applications of Calcination
The unique conditions of calcination make it suitable for several key industrial and scientific objectives.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the most common use of calcination. The process breaks down a complex compound into simpler ones.
The archetypal example is the decomposition of calcium carbonate (limestone) into calcium oxide (lime or quicklime) and carbon dioxide gas. This reaction is the cornerstone of the global cement industry.
Removal of Volatile Components
Calcination is highly effective at driving off unwanted, volatile substances from a solid material.
This includes removing physically absorbed water from hydrated minerals or chemically bound water from crystals. It's also used in more advanced applications, such as removing ammonium ions during the synthesis of zeolites, which are critical materials for catalysts and adsorbents.
Inducing Phase Transitions
Heat can change the internal crystal structure of a material, and calcination provides a controlled way to achieve this.
In materials science, this is used for processes like the devitrification of glass, where a disordered, amorphous solid is transformed into a more stable, crystalline one, fundamentally altering its physical properties.
Understanding the Key Limitation
While powerful, calcination is a specialized tool with a clear boundary condition that defines its suitability.
Not Suitable for Melting
The process is fundamentally a solid-state transformation. Its primary advantage is that it modifies the material without changing its state from solid to liquid.
If your goal is to melt a substance for casting or alloying, calcination is the incorrect process. You would need a smelting or melting furnace for that purpose.
Energy Intensive
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for calcination (often above 825°C or 1500°F for limestone) demands a significant energy input, making it a costly process at industrial scales.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if calcination is suitable, you must first define your desired outcome for the material.
- If your primary focus is creating an oxide from a carbonate (like limestone): Calcination is the definitive, industry-standard method for producing lime and cement.
- If your primary focus is purifying a material by removing water or trapped gases: The process is ideal for driving off these volatile fractions without altering the core substance you wish to keep.
- If your primary focus is altering a material's internal crystal structure: Calcination provides the controlled thermal energy needed for solid-state phase transformations, essential in ceramics and advanced materials manufacturing.
Ultimately, calcination is the correct choice when your objective is to fundamentally change a solid's composition or structure while ensuring it remains in a solid form.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Example Material |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Break down compounds | Limestone to Lime |
| Removal of Volatiles | Purify by driving off gases/water | Hydrated Minerals |
| Phase Transition | Alter crystal structure | Ceramics & Zeolites |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials? KINTEK's advanced lab furnaces are engineered for controlled calcination processes, ensuring purity and structural integrity for your limestone, ceramics, and specialized material projects. Contact our experts today to optimize your thermal treatment and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the equipment for pyrolysis laboratory? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Research
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals



















