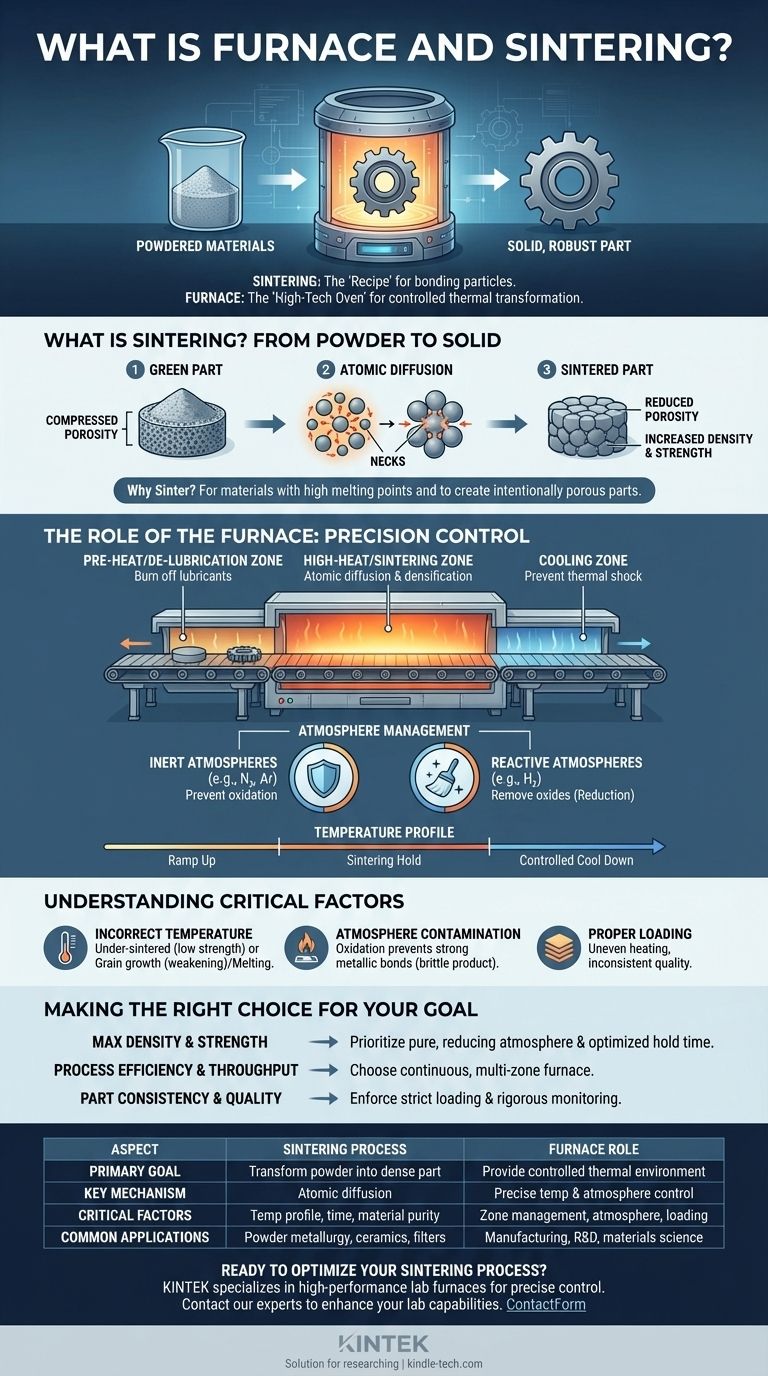
In manufacturing and materials science, sintering is a thermal process that bonds particles of a material together below its melting point, and a furnace is the specialized high-temperature oven where this transformation occurs. Sintering transforms loose powder into a dense, solid object by applying controlled heat and, often, a specific atmospheric environment.
Think of sintering as the 'recipe' for strengthening powdered materials. The furnace is the high-tech 'oven' that must provide the exact temperature, atmosphere, and timing to execute that recipe perfectly, turning a fragile component into a robust, functional part.
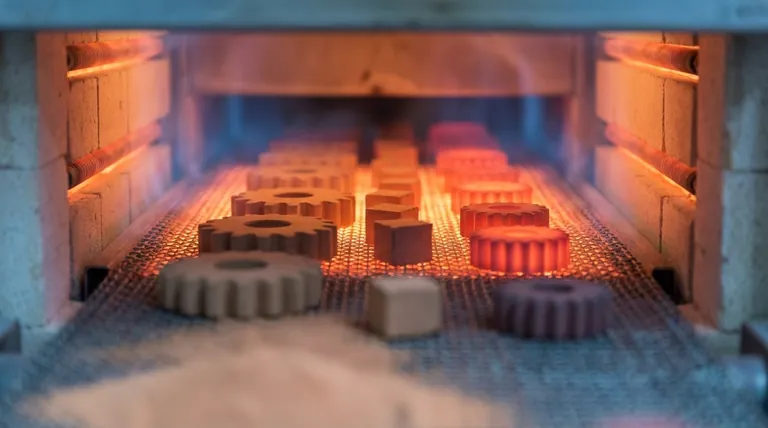

What is Sintering? A Deeper Look
Sintering is a core process in powder metallurgy, ceramics, and other fields where melting a material is impractical or undesirable. It relies on atomic-level changes to achieve consolidation.
The Goal: From Powder to Solid
The primary goal of sintering is to take a component made from compressed powder (known as a "green" part) and significantly increase its strength, density, and integrity. This green part is often fragile and porous.
The Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works by heating the material to a temperature where the atoms in the individual particles become mobile. These atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles, forming solid "necks" or bridges between them.
As the process continues, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer together. This reduces the empty space (porosity) between them, causing the entire component to shrink and become denser.
Why Not Just Melt It?
Sintering is preferred over melting for several key reasons. It allows for the creation of parts from materials with extremely high melting points (like tungsten or molybdenum) and enables the manufacturing of intentionally porous materials for applications like filters or self-lubricating bearings.
The Role of the Furnace: More Than Just Heat
A sintering furnace is not a simple oven. It is a precision instrument designed to create a highly controlled environment that facilitates the complex stages of the sintering process.
Controlling the Temperature Profile
The furnace applies a specific temperature profile, not just a single temperature. This involves a carefully planned sequence of ramping up the heat, holding it at a specific sintering temperature for a set duration, and then cooling it down in a controlled manner.
Managing the Atmosphere
The furnace atmosphere is equally critical. Different atmospheres achieve different goals:
- Inert Atmospheres (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon): These prevent unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, from occurring on the material's surface.
- Reactive Atmospheres (e.g., Hydrogen): These can be used to actively remove existing surface oxides, a process called "reduction," which is essential for creating strong metallic bonds.
The Concept of "Zoning"
Many modern sintering furnaces are continuous and operate with distinct zones. A component moving through the furnace on a conveyor belt will pass through:
- Pre-Heat/De-lubrication Zone: A lower temperature zone to safely burn off any lubricants used during the initial powder compaction stage.
- High-Heat/Sintering Zone: The hottest part of the furnace where atomic diffusion and densification occur.
- Cooling Zone: A controlled cooling section to prevent thermal shock and unwanted microstructural changes.
Understanding the Critical Factors
Achieving a successful sintering outcome depends on precise control over several variables. Failure to manage these can lead to scrapped parts and process inefficiency.
The Risk of Incorrect Temperature
If the temperature is too low or the hold time is too short, the part will be under-sintered, resulting in low density and poor mechanical strength. If the temperature is too high, it can cause unwanted grain growth (weakening the part) or even partial melting, which ruins the component's shape.
The Impact of Atmosphere Contamination
Even small amounts of oxygen or moisture leaking into the furnace can cause oxidation on the surface of metal parts. This oxide layer prevents the strong, clean metallic bonds from forming, resulting in a weak and brittle final product.
The Importance of Proper Loading
As the references highlight, how parts are loaded into the furnace is crucial. Overloading or incorrect placement can lead to uneven heating. Some parts may receive the correct temperature while others are too hot or too cold, leading to inconsistent quality across a single batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The furnace settings you use must be directly aligned with the final properties you want to achieve in your component.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: Your process must prioritize a pure, often reducing, furnace atmosphere and an optimized hold time at the peak sintering temperature.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and throughput: A continuous, multi-zone furnace is the superior choice, as it combines the de-lubrication, reduction, and sintering steps into a single, streamlined flow.
- If your primary focus is part consistency and quality control: You must enforce strict, repeatable furnace loading procedures and implement rigorous monitoring of both the temperature profile and atmospheric composition.
Ultimately, the sintering process dictates the material's final properties, and the furnace is the critical tool you use to control that process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Sintering Process | Furnace Role |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform powder into dense, solid part | Provide controlled thermal environment |
| Key Mechanism | Atomic diffusion between particles | Precise temperature & atmosphere control |
| Critical Factors | Temperature profile, time, material purity | Zone management, atmosphere purity, loading |
| Common Applications | Powder metallurgy, ceramics, filters | Manufacturing, R&D, materials science |
Ready to optimize your sintering process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for precise temperature control and atmospheric management. Whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or advanced materials, our sintering solutions deliver consistent results and improved throughput. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and achieve your material strength goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace in the fabrication of Ni-Al2O3-TiO2 composites?
- Why is a horizontal tube furnace with a H2-N2 atmosphere used for NiO pre-treatment? Key to Catalyst Activation
- Why is a high-precision atmosphere furnace essential for high-nickel cathode sintering? Unlock Battery Performance
- What is the function of a tube atmosphere furnace in Li2MnSiO4 synthesis? Achieve High-Purity Battery Materials
- Why Use Ultra-High Vacuum Furnaces for LLZO? Ensure Chemical Stability & Interface Integrity in Solid Electrolytes



















