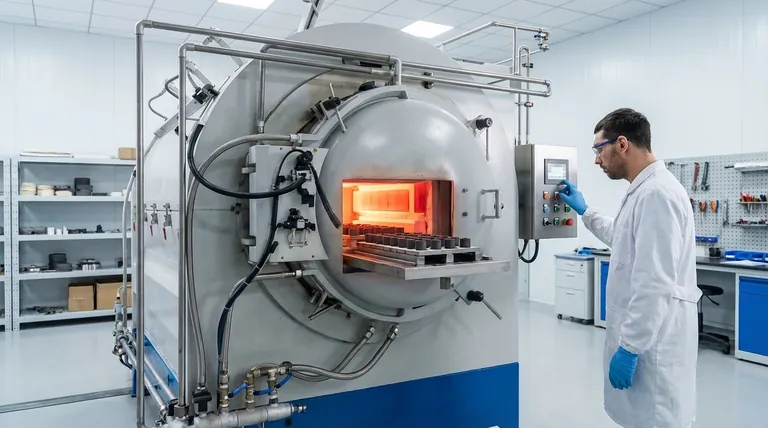
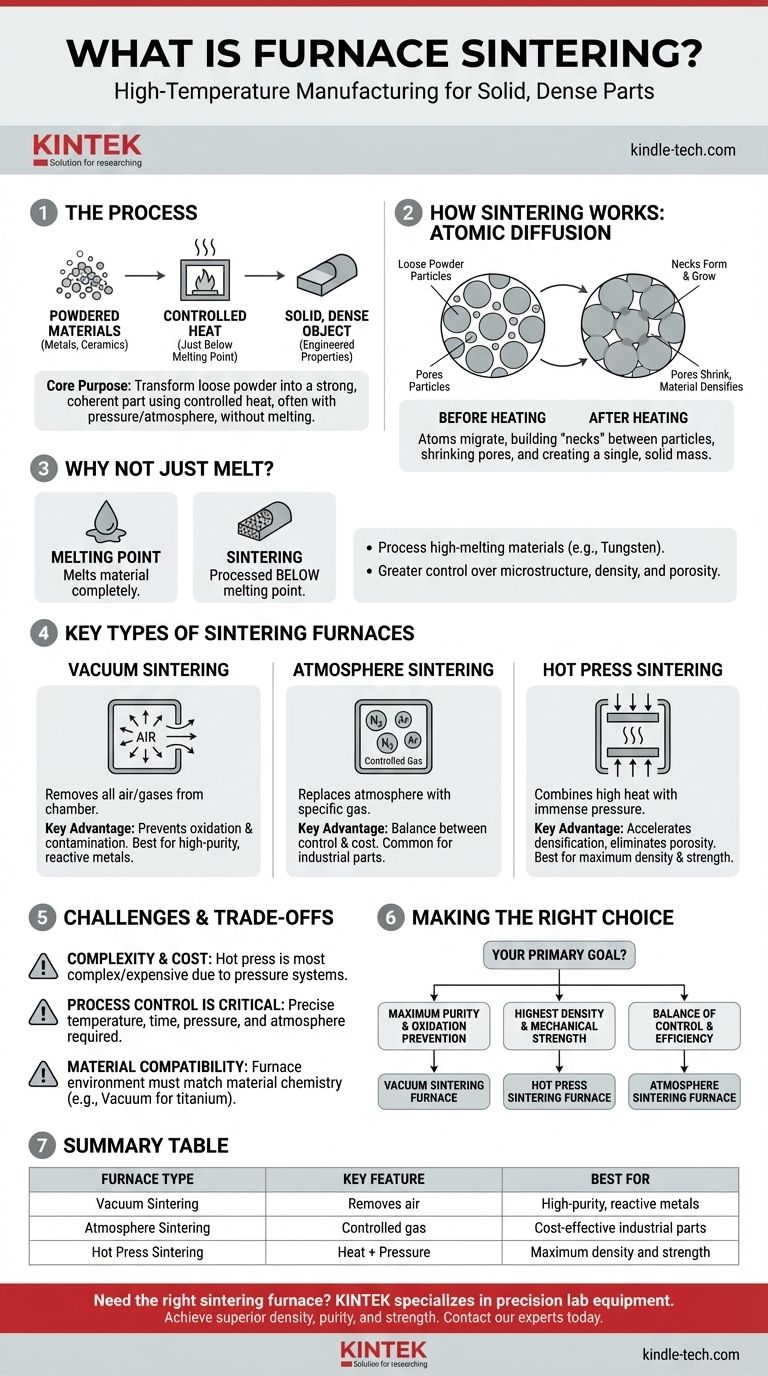
In simple terms, furnace sintering is a high-temperature manufacturing process that uses a specialized furnace to bond powdered materials, such as metals or ceramics, into a solid, dense object. This is accomplished by heating the material to a temperature just below its melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together.
The core purpose of furnace sintering is not to melt a material, but to use controlled heat—often combined with pressure or a specific atmosphere—to transform loose powder into a strong, coherent part with precisely engineered properties.

The Fundamental Principle: How Sintering Works
Sintering is a critical process in fields like powder metallurgy, ceramics manufacturing, and even 3D printing. It allows for the creation of components from materials that are difficult or impossible to shape by other means.
What Happens at the Atomic Level
The process relies on a phenomenon called atomic diffusion. When the powder is heated, the atoms in the individual particles become more energetic and begin to move across the boundaries where particles touch.
This migration of atoms effectively builds "necks" or bridges between the particles. As the process continues, these necks grow, pores between particles shrink or close, and the material becomes a single, solid mass.
Why Not Just Melt the Material?
Sintering is deliberately performed below the material's melting point. This is crucial for several reasons.
It allows for the processing of materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten or molybdenum, which would be impractical to cast. It also provides greater control over the final product's microstructure, density, and porosity, which directly influence its mechanical properties.
Key Types of Sintering Furnaces
The specific furnace used depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome. Each type controls the environment in a unique way to achieve different results.
Vacuum Sintering Furnaces
A vacuum furnace works by removing all air and gases from the heating chamber before the process begins.
The primary advantage of this is preventing oxidation and contamination. By creating a vacuum, you ensure the material doesn't react with oxygen or other elements, which is critical for reactive metals and achieving high-purity components.
Atmosphere Sintering Furnaces
Instead of removing the atmosphere, these furnaces replace it with a specific, controlled gas, such as nitrogen or argon.
This controlled atmosphere can be inert to prevent reactions, or it can be reactive to facilitate specific chemical changes on the material's surface. This method offers a balance between control and cost for many industrial applications.
Hot Press Sintering Furnaces
This is the most intensive method, combining high temperature with immense mechanical pressure inside a vacuum environment.
The furnace simultaneously heats the powder and physically presses it together. This dual action dramatically accelerates the densification process, helping to eliminate virtually all porosity and create parts with superior strength and performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, furnace sintering is a complex process with specific limitations that must be considered. Choosing the wrong method can lead to failed parts and wasted resources.
Complexity and Cost
Hot press sintering furnaces produce the densest parts but are also the most complex and expensive. They require robust systems for applying pressure and aggressive cooling for the furnace body, leading to higher design and manufacturing costs.
Process Control is Critical
Sintering is not a simple baking process. It requires precise, automated control over temperature ramps, holding times, pressure application, and atmospheric conditions. Any deviation can result in a component with poor mechanical properties, internal cracks, or incorrect dimensions.
Material Compatibility
The choice of furnace is dictated by the material. A vacuum furnace is essential for reactive metals like titanium, while an atmosphere furnace might be sufficient for less sensitive materials. The furnace environment must be perfectly matched to the material's chemistry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal sintering method depends directly on the performance requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is maximum material purity and preventing oxidation: A vacuum sintering furnace is the definitive choice for its clean, non-reactive environment.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible density and mechanical strength: A hot press sintering furnace is the most effective solution, as it combines heat with pressure to eliminate porosity.
- If your primary focus is a balance of environmental control and production efficiency: An atmosphere sintering furnace offers a versatile and widely used method for a variety of ceramic and metal parts.
Ultimately, understanding these distinct furnace technologies empowers you to select the precise manufacturing process to achieve your desired material properties.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Sintering | Removes air to prevent oxidation | High-purity, reactive metals |
| Atmosphere Sintering | Uses controlled gas (e.g., nitrogen) | Cost-effective industrial parts |
| Hot Press Sintering | Combines heat with high pressure | Maximum density and strength |
Need the right sintering furnace for your lab's materials? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering vacuum, atmosphere, and hot press sintering solutions tailored to your precision manufacturing needs. Achieve superior part density, purity, and strength—contact our experts today to discuss your project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is oxidation in brazing? How to prevent it for strong, durable joints
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining



















