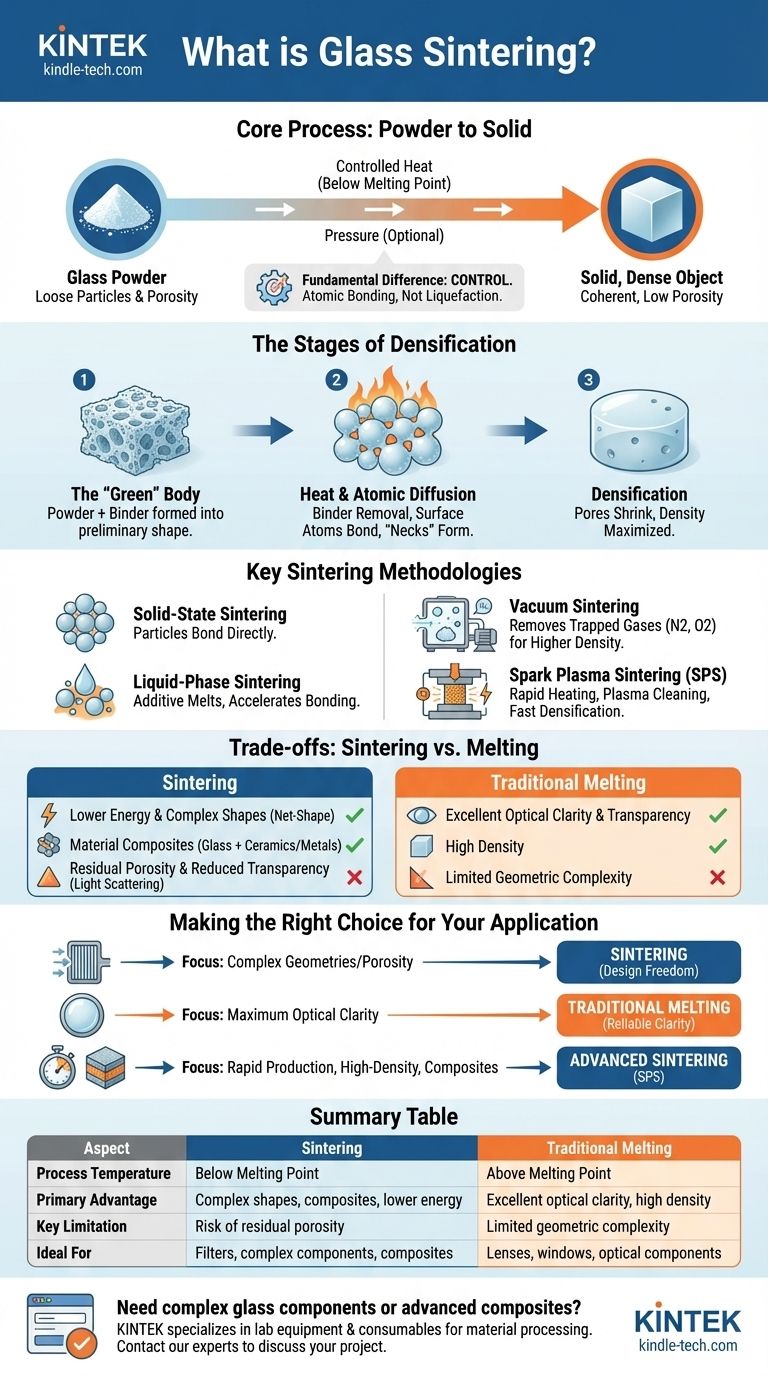
At its core, glass sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms glass powder into a solid, dense object using heat and often pressure. Crucially, this is achieved at temperatures below the glass's full melting point, causing the individual particles to fuse together at their contact surfaces rather than turning into a liquid.
The fundamental difference between sintering and melting is control. Instead of liquefying the entire material, sintering uses controlled heat to encourage atoms at the surface of glass particles to bond, methodically eliminating the empty spaces between them to form a solid structure.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
The primary objective of sintering is densification. The process begins with a loose collection of glass particles with significant empty space, or porosity, between them. The goal is to eliminate this porosity and create a coherent, solid piece.
The "Green" Body
The process starts by forming the glass powder into a desired preliminary shape. This is often done by mixing the powder with a temporary binding agent (like a polymer or wax) that holds the particles together. This initial, fragile form is known as a "green" body.
The Role of Heat and Atomic Diffusion
When the green body is heated, the binder burns away. As the temperature continues to rise, it provides enough energy for atoms on the surfaces of the glass particles to move and diffuse. This atomic diffusion is what allows adjacent particles to form strong bonds, creating "necks" at their points of contact.
The Stages of Densification
As heating continues, these necks grow wider. The network of pores between particles begins to shrink and eventually breaks up into isolated, small voids. With sufficient time and temperature, these final voids are eliminated, and the part reaches its maximum possible density.
Key Sintering Methodologies
While the principle of atomic diffusion is universal, the methods used to drive the process can vary significantly, each suited for different applications and materials.
Solid-State vs. Liquid-Phase Sintering
The most basic distinction is how the particles fuse. In solid-state sintering, the glass particles themselves bond directly without any part of the material melting.
In liquid-phase sintering, a small amount of an additive is included that melts at the sintering temperature. This liquid wets the solid glass particles, and capillary forces pull them together, dramatically accelerating particle rearrangement and densification.
Vacuum Sintering
This process is conducted within a high vacuum (e.g., 3 × 10⁻³ Pa). The primary purpose of the vacuum is to remove atmospheric gases like nitrogen and oxygen from the pores between particles. If these gases were trapped, they would exert internal pressure that prevents the pores from fully closing, resulting in a less dense and weaker final product.
Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS)
SPS is a more advanced and rapid technique. The glass powder is placed in a graphite mold and is simultaneously compressed and heated by a pulsed DC electrical current passing through it. This creates rapid heating and can even generate plasma discharges between particles, which cleans their surfaces and promotes extremely fast bonding and densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sintering vs. Melting
Choosing to sinter glass instead of melting it involves a clear set of engineering trade-offs. It is not inherently better, but rather better for specific goals.
Advantage: Lower Energy and Complex Shapes
Because sintering operates below the full melting point, it typically requires less energy. It also allows for the creation of "net-shape" or near-net-shape parts, where the initial green body is molded into a complex geometry that would be difficult or impossible to achieve by casting molten glass.
Advantage: Material Composites
Sintering is an excellent method for creating glass-matrix composites. Other materials, such as ceramics or metals that have much higher melting points, can be mixed with the glass powder and consolidated into a single solid piece without having to melt all the components.
Limitation: Residual Porosity and Transparency
The primary challenge in sintering is achieving 100% density. Even a tiny amount of residual porosity can scatter light, reducing the optical transparency of the glass. While advanced methods like SPS can achieve near-perfect density, traditional melting and casting remains the standard for producing flawless optical components like lenses.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final goal dictates the correct manufacturing approach.
- If your primary focus is creating complex geometries or porous filters: Sintering offers design freedom that is unmatched by traditional melting and casting.
- If your primary focus is maximum optical clarity and transparency: Traditional melting is often the more reliable path to avoid the light-scattering effects of residual porosity.
- If your primary focus is rapid production of high-density or composite materials: Advanced techniques like Spark Plasma Sintering provide capabilities that other methods cannot match.
Ultimately, understanding glass sintering empowers you to select the right tool for the specific engineering challenge at hand.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Sintering | Traditional Melting |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Below melting point | Above melting point |
| Primary Advantage | Complex shapes, composites, lower energy | Excellent optical clarity, high density |
| Key Limitation | Risk of residual porosity | Limited geometric complexity |
| Ideal For | Filters, complex components, composites | Lenses, windows, optical components |
Need to create a complex glass component or explore advanced material composites? The glass sintering process offers unique advantages for specialized applications. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing, serving R&D and production laboratories. Our expertise can help you select the right sintering technology for your specific needs. Contact our experts today via our contact form to discuss how we can support your project with precision equipment and consumables.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the main difference between soldering and brazing? Choose the Right Metal Joining Method
- How does precision temperature control impact TiAl alloy sintering? Master Microstructure Development
- Why are high-precision vacuum sintering furnaces preferred over traditional methods for biofunctional dental ceramics?
- What are five applications of soldering? From Electronics to Art, Master Material Joining
- Why are porcelain fired under vacuum? To Eliminate Porosity for Superior Strength & Translucency



















