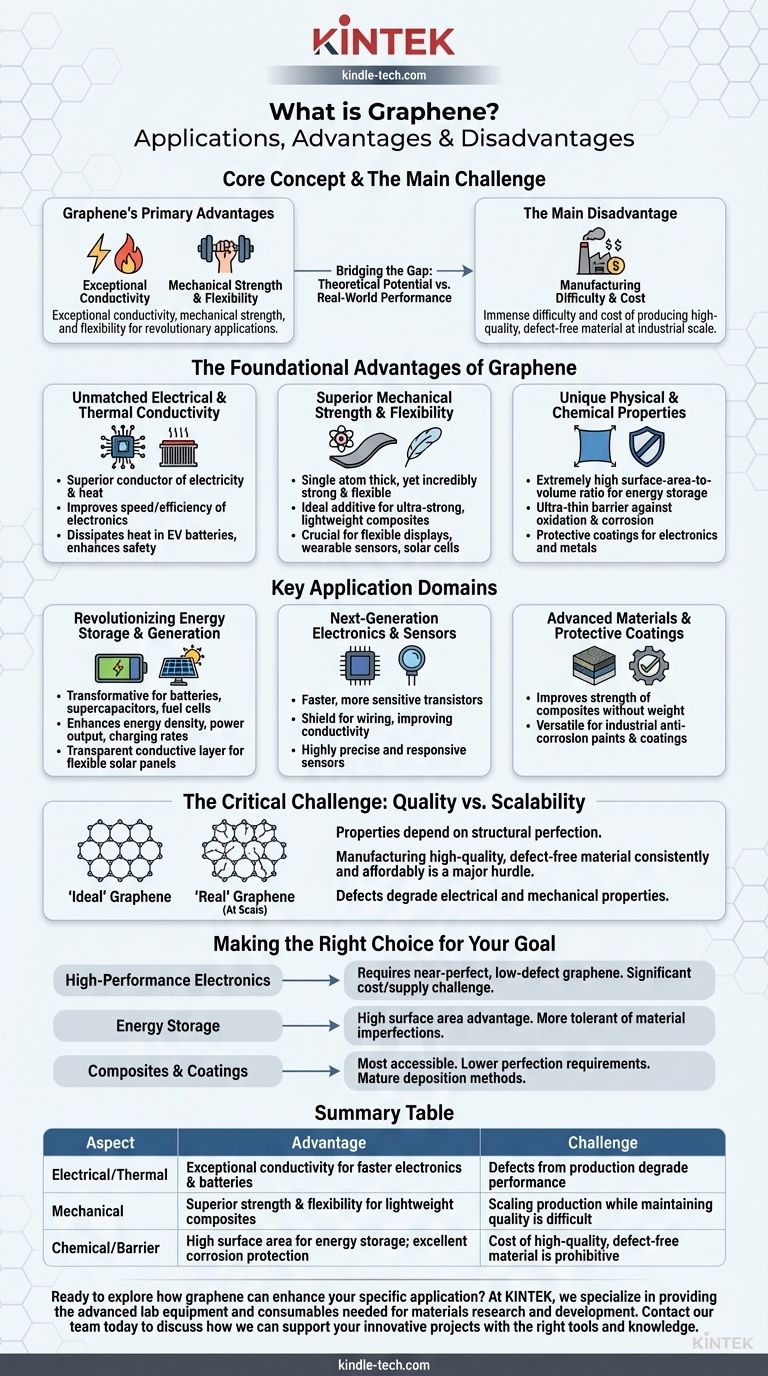
Graphene's primary advantages are its exceptional conductivity, mechanical strength, and flexibility. These properties make it a candidate for revolutionary applications in electronics, energy storage, and advanced materials, but its main disadvantage is the immense difficulty and cost of producing high-quality, defect-free material at an industrial scale.
The core challenge with graphene is bridging the gap between its theoretical potential and its real-world performance. While its properties are extraordinary in a lab setting, practical applications are currently constrained by manufacturing hurdles related to material quality, consistency, and cost.

The Foundational Advantages of Graphene
Graphene is a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice. This unique structure gives rise to a combination of properties not found in any other material.
Unmatched Electrical and Thermal Conductivity
Graphene is an exceptional conductor of both electricity and heat. This allows it to improve the speed and efficiency of electronic circuits and transistors.
In applications like electric vehicle batteries, it can serve as a conductive barrier to dissipate heat, improving safety, charging speed, and overall lifespan.
Superior Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Despite being only one atom thick, graphene is incredibly strong and flexible. This makes it an ideal additive for creating ultra-strong, lightweight composite materials.
Its flexibility and transparency are also crucial for developing next-generation technologies like flexible displays, wearable sensors, and more efficient solar cells.
Unique Physical and Chemical Properties
Graphene has an extremely high surface-area-to-volume ratio, which is ideal for applications in batteries and supercapacitors, enabling them to store more energy.
Its ultra-thin nature forms a potent barrier against oxidation and corrosion. This can be used to create protective coatings that extend the life of electronic components like pin connectors or prevent rust on metal surfaces.
Key Application Domains
Graphene's versatile properties open doors in numerous high-tech fields, from energy to electronics.
Revolutionizing Energy Storage and Generation
Graphene is a transformative material for batteries, supercapacitors, and fuel cells. It enhances energy density, power output, and charging rates far beyond current material limitations.
In solar cells, its use as a transparent and conductive layer promises to increase efficiency and enable the production of flexible, lightweight solar panels.
Next-Generation Electronics and Sensors
The material's high carrier mobility leads to faster and more sensitive transistors. It can also be used as a shield for wiring, improving conductivity and current handling in circuits.
Graphene coatings can be used to create highly precise and responsive sensors, capable of detecting minute changes in their environment.
Advanced Materials and Protective Coatings
When added to polymers or metals, graphene can create composites with vastly improved strength without adding significant weight.
The ease of depositing graphene onto various materials makes it a versatile choice for industrial coatings, such as anti-corrosion paints that provide superior protection.
The Critical Challenge: Quality vs. Scalability
The primary obstacle preventing widespread adoption of graphene is the difficulty of manufacturing it. The properties that make it so promising are highly dependent on its structural perfection.
The Gap Between 'Ideal' and 'Real' Graphene
Most practical applications require large-area, high-quality graphene with very few structural defects. However, producing this "ideal" material consistently and affordably remains a major engineering challenge.
"Real" graphene, which is produced at scale, often contains defects, impurities, and cracks that degrade its electrical and mechanical properties.
The Impact of Defects
Defects in the graphene lattice disrupt the flow of electrons, reducing conductivity and performance in high-end electronics. They also compromise the material's strength and barrier properties.
Applications must be designed to work with the characteristics of available, imperfect graphene, not the theoretical perfection often cited.
Application-Specific Requirements
The required quality of graphene varies significantly by use case. High-performance electronics and optoelectronics demand a near-perfect crystal structure.
In contrast, applications like composites or some energy storage devices may be more tolerant of minor imperfections, making them more commercially viable in the near term.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the trade-offs between graphene's quality and its intended application is essential for any project's success.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics: Success is contingent on sourcing near-perfect, low-defect graphene, which remains a significant cost and supply chain challenge.
- If your primary focus is energy storage: Graphene's high surface area offers clear advantages, and this field is often more tolerant of the material imperfections found in commercially available graphene.
- If your primary focus is in composites or coatings: These are among the most accessible applications, as the requirements for structural perfection are generally lower and deposition methods are more mature.
Successfully harnessing graphene's power depends on realistically matching the material's current capabilities with the demands of the application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical/Thermal | Exceptional conductivity for faster electronics & batteries | Defects from production degrade performance |
| Mechanical | Superior strength & flexibility for lightweight composites | Scaling production while maintaining quality is difficult |
| Chemical/Barrier | High surface area for energy storage; excellent corrosion protection | Cost of high-quality, defect-free material is prohibitive |
Ready to explore how graphene can enhance your specific application? At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed for materials research and development. Whether you're working on next-generation electronics, energy storage solutions, or advanced composites, our expertise can help you navigate the challenges of material quality and scalability. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your innovative projects with the right tools and knowledge.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How do nanotubes affect the environment? Balancing Low Carbon Footprint with Ecological Risks
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What are the challenges of carbon nanotubes? Overcoming Production and Integration Hurdles



















