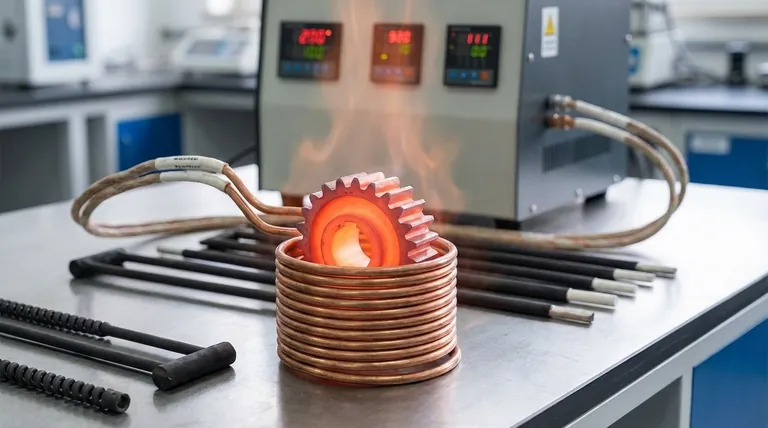
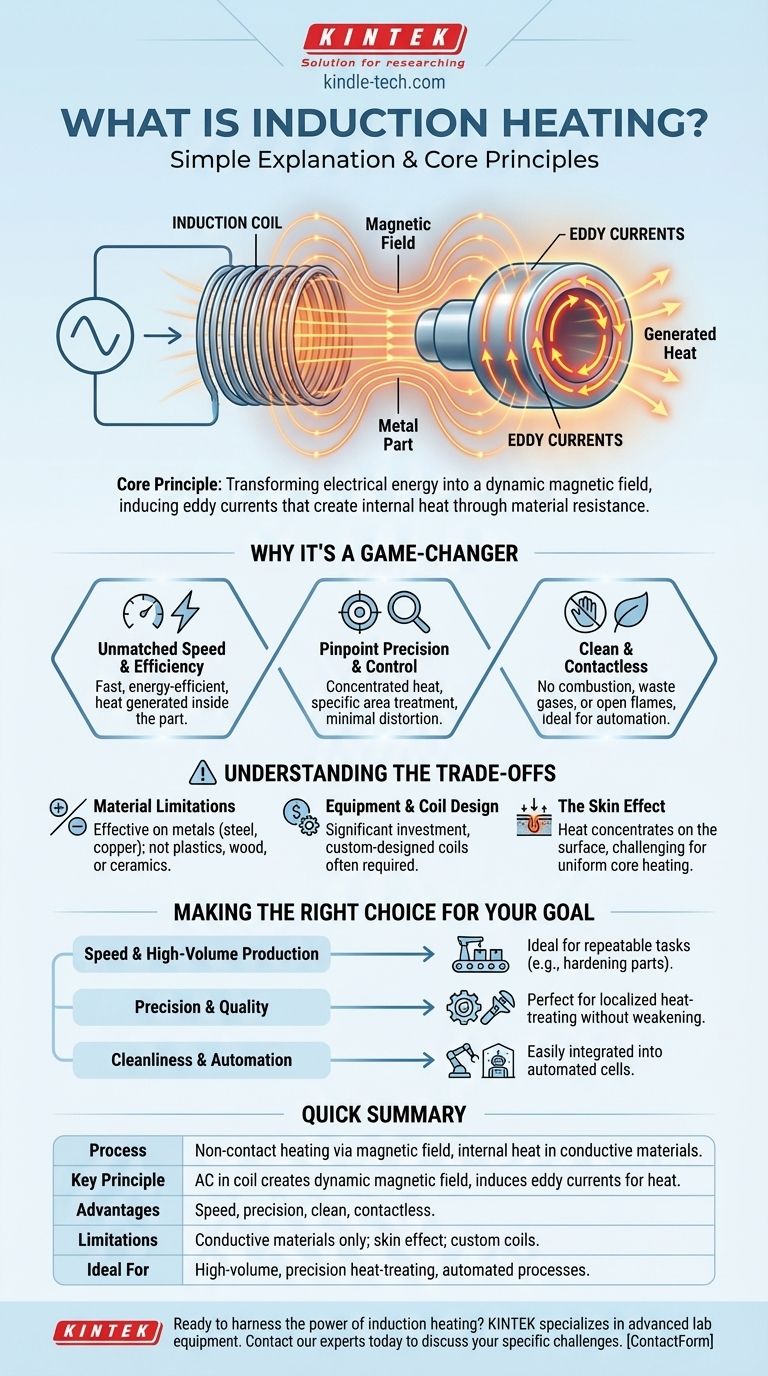
In simple terms, induction heating is a non-contact process that uses a powerful, changing magnetic field to create heat directly inside a conductive material, like metal. Instead of using a flame or a hot surface, it makes the metal heat itself from the inside out, offering incredible speed and precision.
The core principle is transforming electrical energy into a magnetic field and then back into electrical energy within the target material. This internal electrical flow, called an "eddy current," generates intense heat due to the material's natural resistance, all without any physical contact.

The Core Principle: How Magnetism Creates Heat
Understanding induction heating is about following a chain of energy transformation. The process is clean, contained, and happens in milliseconds.
Step 1: The Induction Coil and Alternating Current
It all begins with an alternating current (AC). This is an electrical current that rapidly reverses its direction, flowing back and forth many thousands of times per second. This AC is sent through a copper coil, known as an induction coil, which is often shaped to fit around or near the part being heated.
Step 2: Generating the Magnetic Field
According to the laws of electromagnetism, any flowing electrical current creates a magnetic field. Because the current in the coil is alternating, it produces a dynamic magnetic field that continuously and rapidly changes its polarity.
Step 3: Inducing Eddy Currents
This is the "induction" step. When you place a conductive part (like a steel gear) into this rapidly changing magnetic field, the field induces small, circular flows of electricity within the metal itself. These are called eddy currents.
Step 4: Heat from Electrical Resistance
The metal is not a perfect conductor; it has internal electrical resistance. As the eddy currents swirl through the metal, they encounter this resistance, which generates friction and creates intense, localized heat. This is the same principle that makes an old lightbulb's filament glow.
Why This Method is a Game-Changer
Induction's unique mechanism provides significant advantages over traditional heating methods like furnaces or torches.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The heat is generated inside the part, exactly where it's needed. There's no need to wait for heat to transfer from an external source, making the process incredibly fast and energy-efficient.
Pinpoint Precision and Control
The heating effect is concentrated only where the magnetic field is strongest. By carefully designing the induction coil, you can heat a very specific area—like the teeth of a gear or the tip of a blade—without affecting the rest of the component.
Clean and Contactless Process
Because there is no physical contact and no combustion, the process is extremely clean. There are no waste gases, no open flames, and a reduced risk of contamination, making it ideal for modern, automated manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. It has specific requirements and limitations that must be considered.
Material Limitations
The process relies on a material's ability to conduct electricity. It works exceptionally well on metals like steel, iron, copper, and aluminum but is ineffective on non-conductive materials like plastics, glass, wood, or ceramics.
Equipment and Coil Design
The initial investment for induction power supplies can be significant. Furthermore, the induction coil is a critical component that often must be custom-designed and built for the specific geometry of the part being heated, adding to the engineering complexity.
The "Skin Effect"
At the high frequencies used in induction heating, the eddy currents tend to concentrate on the surface of the material. This is known as the skin effect. While this is perfect for applications like surface hardening, it makes it more challenging to uniformly heat a large, thick part all the way to its core.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use induction heating depends entirely on your specific manufacturing objective.
- If your primary focus is speed and high-volume production: Induction is ideal for repeatable tasks like hardening thousands of engine parts or brazing components on an assembly line.
- If your primary focus is precision and quality: The precise, localized heating is perfect for heat-treating specific zones without distorting or weakening the rest of the part.
- If your primary focus is process cleanliness and automation: The contactless, flameless nature of induction allows it to be easily and safely integrated into automated robotic cells.
By understanding its principles, you can effectively determine where this powerful heating technology can solve your most demanding manufacturing challenges.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Non-contact heating using a magnetic field to generate internal heat in conductive materials. |
| Key Principle | Alternating current in a coil creates a dynamic magnetic field, inducing eddy currents that generate heat. |
| Primary Advantages | Unmatched speed, pinpoint precision, clean and contactless process. |
| Material Limitations | Only effective on conductive materials (e.g., metals); not for plastics, wood, or ceramics. |
| Ideal For | High-volume production, precision heat-treating, and automated, clean manufacturing processes. |
Ready to harness the power of induction heating in your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction heating systems, to help you achieve faster cycle times, superior process control, and cleaner results. Our solutions are designed to meet the precise needs of laboratories and manufacturing facilities.
Contact our experts today to discuss how induction heating can solve your specific challenges and enhance your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments
- What is SiC elements? The Ultimate High-Temperature Heating Solution
- What are the uses of silicon carbide rod? The Ultimate Heating Solution for Extreme Temperatures



















