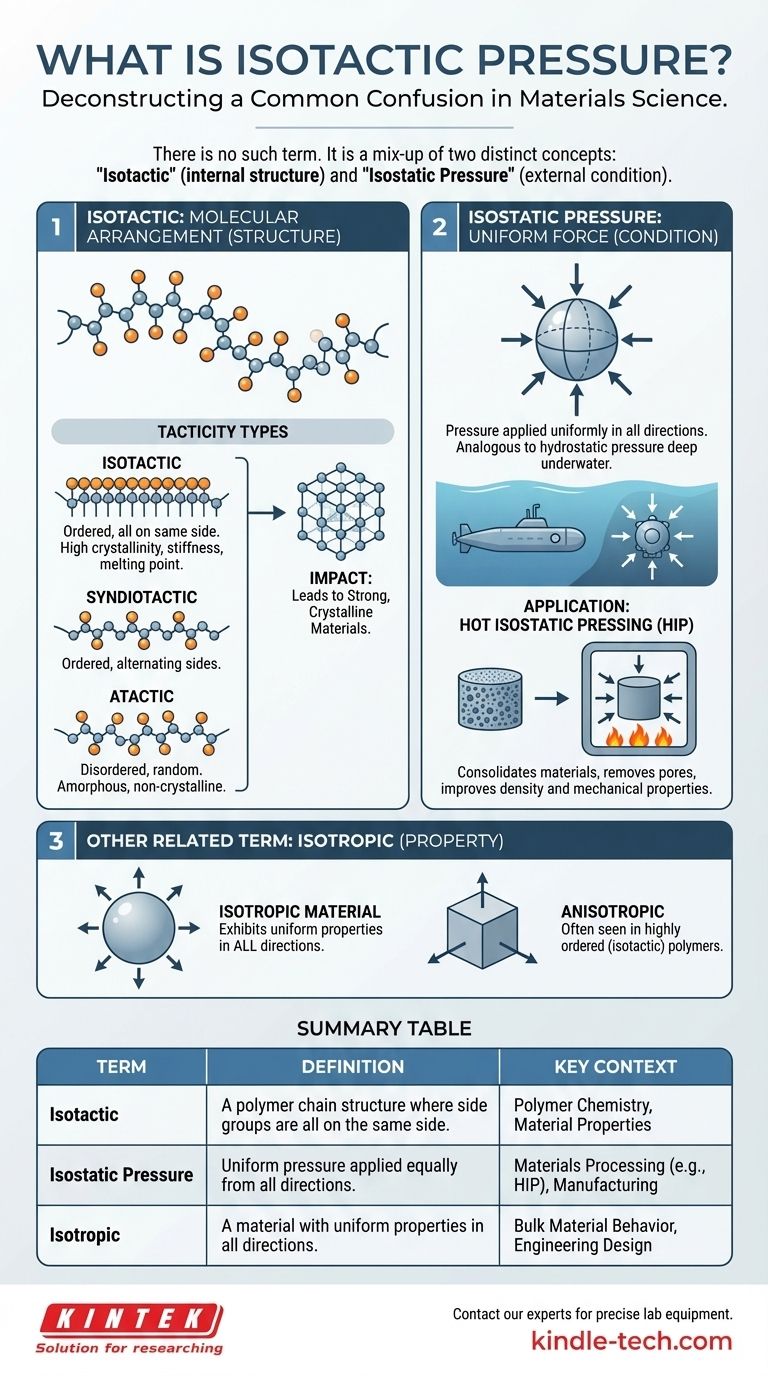
While "isotactic pressure" is not a recognized scientific term, your question points to a common and important area of confusion in materials science. It merges two distinct concepts: "isotactic," which describes a material's internal molecular structure, and "pressure," which is an external force or condition. Understanding the difference is fundamental to polymer chemistry and materials engineering.
The term you are likely looking for is isostatic pressure, which means uniform pressure applied from all directions. This is often confused with isotactic, which describes a specific, highly ordered arrangement of atoms in a polymer chain.

Deconstructing the Terms: Structure vs. Condition
To solve a problem, we must first define our terms correctly. The confusion between "isotactic" and "pressure" stems from mixing up a material's intrinsic structure with the external conditions it experiences.
What "Isotactic" Truly Means: A Matter of Molecular Arrangement
Tacticity describes the stereochemistry of a polymer—how the side-groups (substituents) are arranged along the main chain or "backbone" of the molecule.
Imagine a long chain with hands sticking out from it.
- Isotactic: All the hands are on the same side of the chain. This regular, ordered structure allows the polymer chains to pack together tightly, leading to high crystallinity.
- Syndiotactic: The hands alternate in a regular pattern from one side to the other. This also creates an ordered structure.
- Atactic: The hands are arranged randomly on either side of the chain. This disorder prevents the chains from packing well, resulting in an amorphous (non-crystalline) material.
This structural difference is not trivial. An isotactic structure, like that found in most commercial polypropylene, is what gives the material its high melting point, stiffness, and strength.
The Role of Pressure: A Condition for Synthesis and Processing
Pressure is a physical force applied to a material. In the context of polymers, it is a critical process variable during synthesis.
High pressure, along with specific temperatures and catalysts (like Ziegler-Natta catalysts), can be essential for creating polymers with a desired tacticity. It influences reaction rates and the final molecular structure, but it is not a property of the polymer itself.
The Likely Confusion: Isostatic vs. Isotactic
The term "isotactic pressure" is almost certainly a confusion with "isostatic pressure." They sound similar but describe completely different concepts.
Defining Isostatic Pressure
Isostatic pressure is pressure that is uniform in all directions. Think of an object submerged deep in the ocean; the water pushes on it with equal force from every side. This is also known as hydrostatic pressure.
In materials engineering, this principle is used in a process called Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP). During HIP, a component is subjected to both high temperature and high isostatic pressure, which consolidates materials, closes internal pores, and dramatically improves mechanical properties.
Another Possible Confusion: Isotropic Materials
You may also be thinking of the term isotropic. An isotropic material is one that exhibits the same physical properties (e.g., strength, thermal expansion) in all directions.
Ironically, a highly ordered isotactic polymer is often anisotropic, not isotropic. Because its chains are neatly aligned, its properties can be very different when measured along the chain direction versus perpendicular to it.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why This Distinction Matters
Using the right term is critical because structure and processing conditions have different and independent effects on the final product.
Impact of an Isotactic Structure
An isotactic molecular arrangement directly creates crystallinity. This results in materials that are generally stronger, stiffer, and have a higher melting point and better chemical resistance compared to their atactic counterparts. The choice of an isotactic polymer is a design choice based on desired final properties.
Impact of Isostatic Processing
Applying isostatic pressure is a manufacturing step. It doesn't change the polymer's tacticity, but it can remove voids and defects in a finished part made from that polymer (or from metals or ceramics). This process improves density and mechanical reliability but adds cost and complexity to manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure clarity in your work, select the term that accurately describes your focus.
- If your primary focus is on polymer chemistry: Concentrate on tacticity (isotactic, syndiotactic, atactic), as this molecular structure dictates the material's fundamental properties.
- If your primary focus is on materials processing or manufacturing: You are likely concerned with isostatic pressure, a tool used in processes like HIP to create dense, high-performance parts.
- If you are describing a material's bulk properties: Use isotropic or anisotropic to specify whether its properties are uniform in all directions.
Using precise language is the foundation of effective engineering and scientific communication.
Summary Table:
| Term | Definition | Key Context |
|---|---|---|
| Isotactic | A polymer chain structure where side groups are all on the same side. | Polymer Chemistry, Material Properties |
| Isostatic Pressure | Uniform pressure applied equally from all directions. | Materials Processing (e.g., HIP), Manufacturing |
| Isotropic | A material with uniform properties in all directions. | Bulk Material Behavior, Engineering Design |
Need precise lab equipment to analyze polymer structures or apply controlled pressure? KINTEK specializes in high-performance laboratory equipment and consumables for materials science. Whether you're synthesizing polymers or processing materials, our solutions deliver the accuracy and reliability your research demands. Contact our experts today to find the perfect tool for your laboratory's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting the quality of powder in powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Manufacturing Process
- Is oil sludge hazardous? Understanding the Critical Risks and Regulations
- How do magnetic stirrers and vacuum drying ovens work together to optimize catalyst performance? Expert Prep Guide
- What is difference between FTIR and IR? The Revolutionary Leap in Modern Spectroscopy
- For what purpose is an ultra-low temperature freezer used prior to oxide experiments? Ensure Atomic-Level Sample Purity
- How does rapid quenching equipment stabilize actinide elements? Mastering Advanced Nuclear Waste Treatment
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven assist in processing raw COF products? Master Material Activation
- What is the difference between hardening and tempering? Achieve the Perfect Balance of Strength and Toughness



















