In the world of high-temperature materials, a Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating element is a specialized component designed for electric furnaces operating at extreme temperatures. Composed of a molybdenum disilicide composite, its defining feature is the ability to form a protective, self-healing layer of silicon dioxide on its surface, allowing it to function reliably in air at temperatures up to 1900°C (3452°F).
The core value of a MoSi2 element is not just its high-temperature tolerance, but its "smart" material property: it creates its own protective, renewable shield against oxidation, making it uniquely suited for continuous, high-heat operations in an oxygen-rich environment.
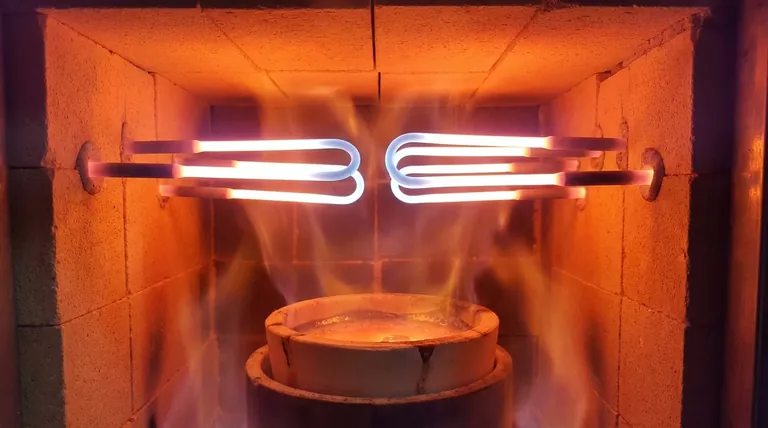

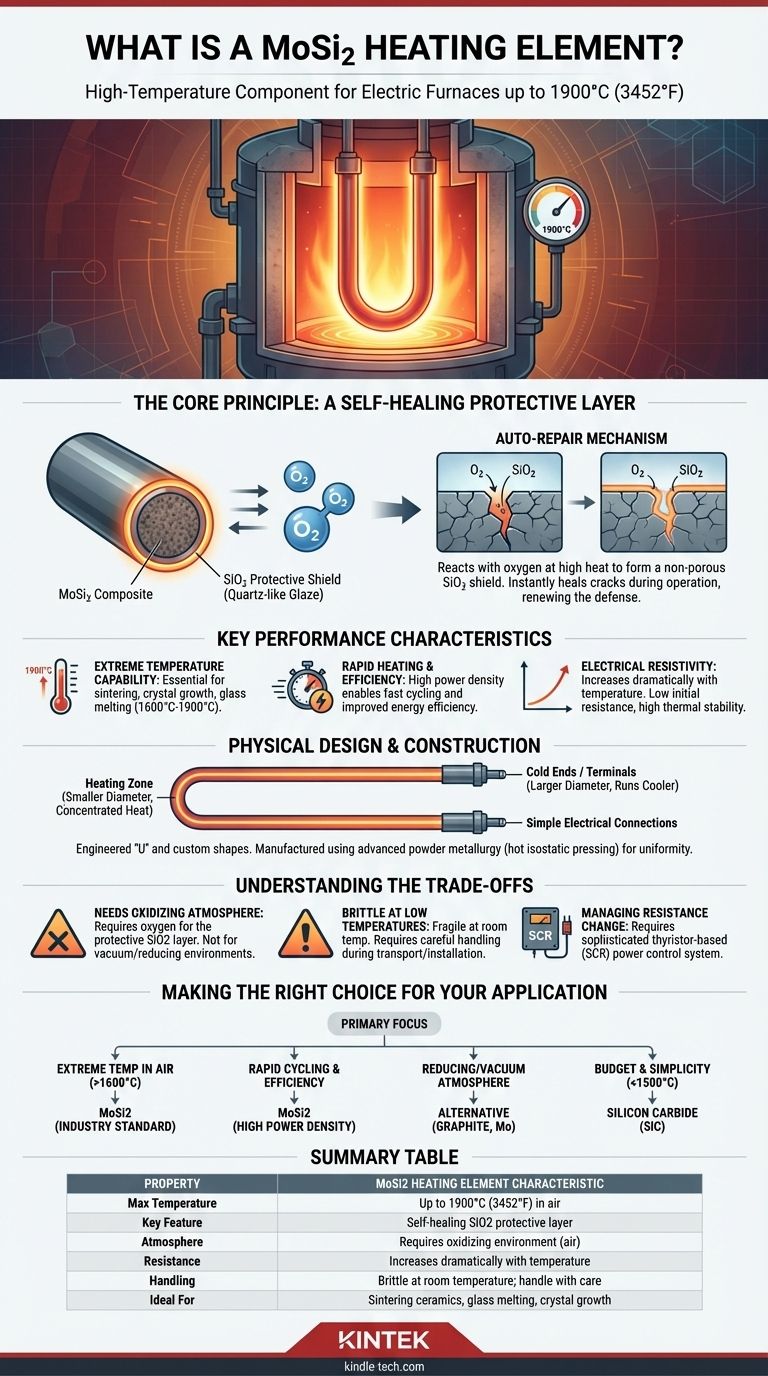
The Core Principle: A Self-Healing Protective Layer
The remarkable performance of MoSi2 elements stems from a chemical reaction that occurs at high temperatures. This is the key to their longevity and reliability in harsh furnace environments.
How MoSi2 Creates Its Own Defense
When a MoSi2 element is heated in an atmosphere containing oxygen, its surface oxidizes. This process forms a thin, non-porous, and highly stable layer of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2), often described as a quartz-like glaze.
This glaze acts as a physical barrier, preventing further oxidation of the underlying MoSi2 material.
The "Self-Healing" Mechanism
The true advantage is the element's auto-repair function. If a crack or spall appears in the protective SiO2 layer during operation, the newly exposed MoSi2 material immediately reacts with oxygen in the furnace.
This reaction instantly forms new silicon dioxide, effectively "healing" the breach and restoring the protective shield. This makes the element ideal for long, continuous operating cycles.
Key Performance Characteristics
Beyond its self-healing nature, MoSi2 elements have several distinct properties that define their use in industrial and laboratory settings.
Extreme Temperature Capability
MoSi2 elements are a default choice for applications requiring process temperatures between 1600°C and 1900°C. This makes them essential for sintering advanced ceramics, growing crystals, melting glass, and various high-temperature material science tests.
Rapid Heating and Efficiency
These elements possess a high power density, allowing for very rapid heating rates. This can significantly shorten furnace cycle times, improving productivity and overall energy efficiency compared to other heating technologies.
Electrical Resistivity Profile
A critical characteristic of MoSi2 is that its electrical resistivity increases dramatically as temperature rises. The element has low resistance when cold, allowing high current to flow for rapid initial heating. As it reaches operating temperature, its high resistance helps maintain thermal stability.
Physical Design and Construction
MoSi2 elements are not simple rods; they are engineered components with distinct zones and shapes designed for optimal performance and installation.
The 'U' Shape and Other Forms
The most common design is a two-shank 'U'-shaped element, which allows for simple electrical connections at one end. They are also produced as straight, multi-shank, and custom-bent elements to fit specific furnace geometries.
Differentiated Zones: Hot vs. Cold Ends
An element is constructed with two distinct sections. The heating zone has a smaller diameter to concentrate electrical resistance and generate heat. The terminals, or "cold ends," have a much larger diameter (often double), which keeps their resistance low and allows them to run cooler as they pass through the furnace insulation.
Manufacturing for Uniformity
MoSi2 elements are manufactured using advanced powder metallurgy techniques like hot isostatic pressing. This ensures a highly dense and uniform grain structure, which is critical for consistent electrical properties, mechanical strength, and predictable service life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
To use MoSi2 elements effectively, it is crucial to understand their operational limitations. These are not flaws but inherent properties that must be managed.
The Need for an Oxidizing Atmosphere
The self-healing mechanism is entirely dependent on the presence of oxygen. Using MoSi2 elements in reducing atmospheres or high vacuum will prevent the formation of the protective SiO2 layer, leading to rapid degradation.
Brittleness at Low Temperatures
Like many advanced ceramics, MoSi2 is brittle and fragile at room temperature. It requires careful handling during transport and installation to prevent fracture. The material only gains ductility at very high temperatures.
Managing Drastic Resistance Change
The sharp increase in resistance with temperature requires a sophisticated power control system. Simple on/off controllers are inadequate. A thyristor-based controller (SCR) that can manage the phase angle is necessary to handle the high inrush current when the elements are cold and to provide stable power as they heat up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating element technology depends entirely on your process requirements.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 1600°C) in air: MoSi2 is the industry-standard choice due to its self-healing oxide layer and thermal stability.
- If your primary focus is rapid furnace cycling and energy efficiency: The high power density and fast response time of MoSi2 elements make them an excellent choice for improving throughput.
- If your primary focus is operating in a reducing atmosphere or vacuum: You must consider alternative elements like graphite or molybdenum metal, as MoSi2 will not perform reliably without oxygen.
- If your primary focus is budget and simplicity below 1500°C: Silicon carbide (SiC) elements may offer a more cost-effective solution without the need for complex SCR power control.
Understanding these core principles allows you to harness the unique power of Molybdenum Disilicide for the most demanding thermal processes.
Summary Table:
| Property | MoSi2 Heating Element Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 1900°C (3452°F) in air |
| Key Feature | Self-healing SiO2 protective layer |
| Atmosphere | Requires oxidizing environment (air) |
| Resistance | Increases dramatically with temperature |
| Handling | Brittle at room temperature; handle with care |
| Ideal For | Sintering ceramics, glass melting, crystal growth |
Upgrade your lab's high-temperature capabilities with KINTEK.
MoSi2 heating elements are engineered for precision and durability in demanding applications. Whether you're sintering advanced ceramics, melting glass, or conducting material science research, KINTEK's lab equipment ensures reliable performance up to 1900°C.
We provide:
- High-quality MoSi2 elements with uniform heating and long service life.
- Expert guidance to select the right heating solution for your specific process.
- Comprehensive support for furnace systems and consumables.
Ready to enhance your thermal processes? Contact our experts today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK can power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Square Bidirectional Pressure Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- How do coaxial heating coils in a TDS system determine hydrogen trap activation energy? Precise Thermal Control Guide
- How do heating units used in dry electrode processes contribute to energy efficiency? Cut Energy Use by 30%+
- How does a graphite heater work? Achieve Extreme Temperatures with Unmatched Precision
- Does molybdenum conduct heat? Unlocking Its Role in High-Temperature Applications
- How do multiple cartridge heaters and K-type thermocouples work together? Achieve Optimal Temperature Uniformity
- Is molybdenum a good thermal conductor? Its High-Temperature Performance Explained
- What industry uses tungsten? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Hardness for Industrial Applications



















