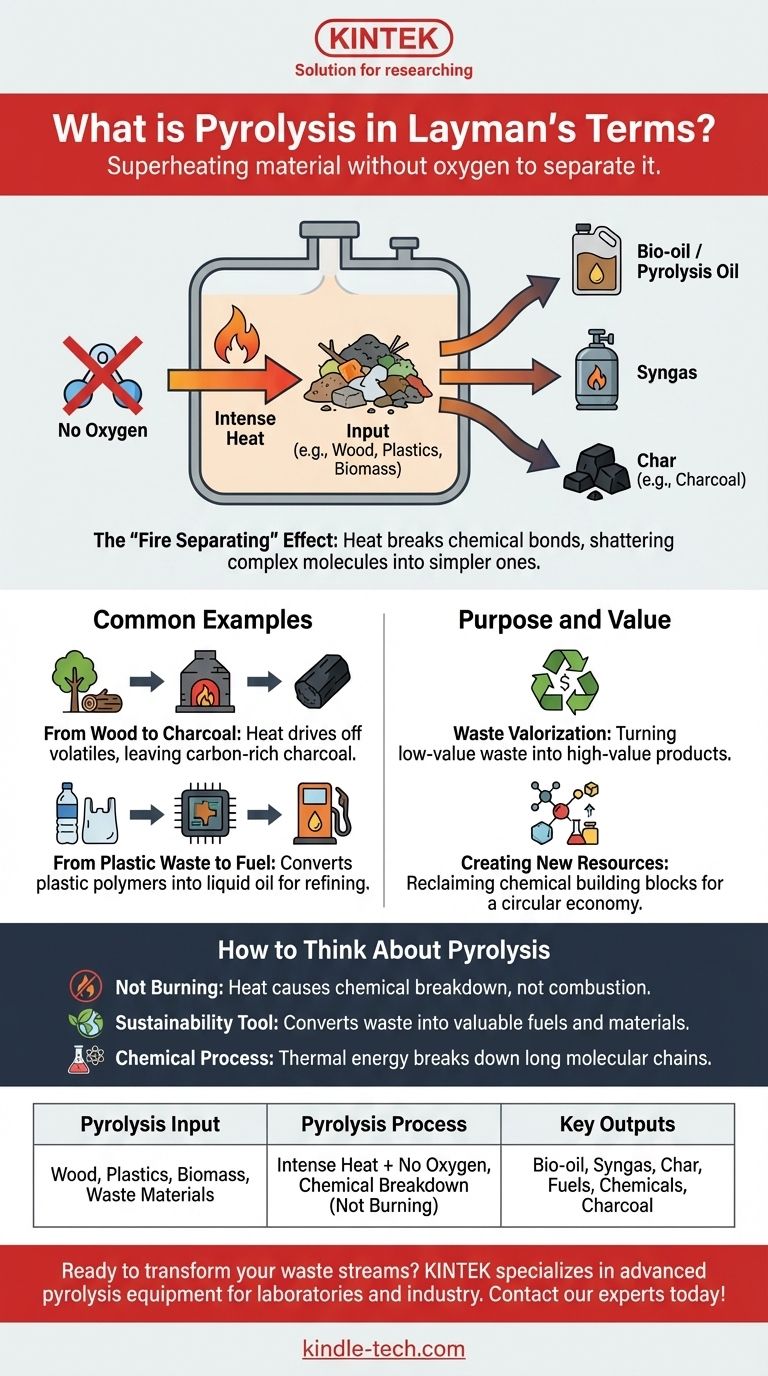
In simple terms, pyrolysis is the process of superheating a material in a container with no oxygen. This intense heat, without any oxygen to cause burning, forces the material to chemically break down and separate into different, often useful, substances. The name itself comes from the Greek for “fire separating,” which perfectly describes what it does.
Pyrolysis is not burning; it's the controlled chemical breakdown of a substance using heat in an oxygen-free environment. This process transforms complex materials like plastic or wood into simpler, often valuable, products like fuel and charcoal.

How Pyrolysis Works: The Core Principle
Pyrolysis is a powerful thermochemical process that fundamentally changes the makeup of organic materials. Understanding its core mechanism reveals why it is such a versatile tool for waste management and resource creation.
Heat Without Oxygen is Key
The most critical element of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When you heat something with oxygen present, it combusts—it burns.
By removing oxygen, you prevent burning. Instead, the intense heat energy directly breaks the chemical bonds holding the material together.
The "Fire Separating" Effect
Think of the heat as a force that violently shakes the complex molecules of a substance. Unable to simply burn, these long molecular chains shatter into smaller, simpler, and more stable molecules.
This decomposition results in a mix of products. Typically, these include a synthetic gas (syngas), a liquid oil (pyrolysis oil or bio-oil), and a solid, carbon-rich residue (char).
Common Examples of Pyrolysis in Action
While the term may sound technical, the process has been used for centuries and is now being applied to modern challenges.
From Wood to Charcoal
The creation of charcoal is a classic example of pyrolysis. Wood is heated in a kiln or other low-oxygen environment.
The heat drives off water, sap, and other volatile compounds, leaving behind a block of nearly pure carbon—the charcoal.
From Plastic Waste to Liquid Fuel
A modern application is tackling plastic pollution. Pyrolysis can take mixed plastic waste and break down its complex polymers.
The process converts the plastic into a liquid oil that can be refined into fuel, providing a way to turn a persistent environmental problem into a valuable resource.
Understanding the Purpose and Value
Pyrolysis is not just a chemical reaction; it's a strategic tool for transformation. Its value lies in its ability to unlock potential from materials that are often considered waste.
Waste Valorization
The core purpose of modern pyrolysis is valorization—the process of turning low-value or zero-value waste streams into products with higher economic value.
It offers an alternative to landfills or incineration by treating waste as a feedstock for new materials and energy.
Creating New Resources
By deconstructing materials at a molecular level, pyrolysis allows us to reclaim the chemical building blocks within them. This creates a pathway for a more circular economy, where the end of one product’s life becomes the beginning of another's.
Applying This Understanding
To best grasp the concept of pyrolysis, it's helpful to frame it based on its core function and application.
- If you think of it as burning: Remember the key difference is the lack of oxygen, which prevents combustion and forces the material to separate instead.
- If you're focused on sustainability: View it as a powerful tool for converting waste materials like plastics or biomass into valuable resources like fuel and charcoal.
- If you're interested in the chemistry: Focus on how thermal energy is used to break down long, complex molecular chains into smaller, simpler ones.
Ultimately, pyrolysis is a transformative process that uses heat to deconstruct materials, unlocking the value hidden within them.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Input | Pyrolysis Process | Key Outputs |
|---|---|---|
| Wood, Plastics, Biomass | Intense Heat + No Oxygen | Bio-oil, Syngas, Char |
| Waste Materials | Chemical Breakdown (Not Burning) | Fuels, Chemicals, Charcoal |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources? KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis equipment for laboratories and industry. Our solutions help you convert materials like plastic and biomass into fuel and chemicals efficiently and sustainably. Contact our experts today to discuss how our lab equipment can power your pyrolysis research and applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting the yield of bio-oil from the pyrolysis of coconut shell? Control 4 Key Parameters
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process



















