In essence, a quartz heating tube is a specialized component used in various heating applications that leverages the unique properties of high-purity quartz glass. It typically acts as a protective and functional envelope for an electric heating element, allowing it to efficiently emit thermal energy, most often in the form of infrared radiation.
The true value of a quartz tube isn't just that it contains a heater; its material properties—thermal shock resistance, high purity, and transparency to infrared energy—are what enable rapid, precise, and clean heating that is impossible with other materials.
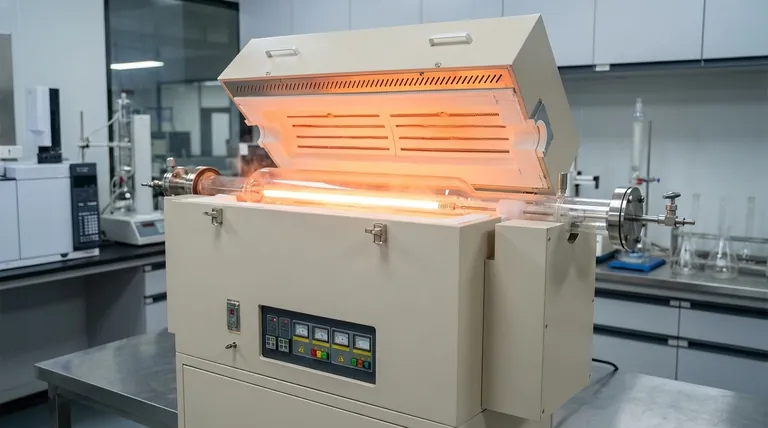

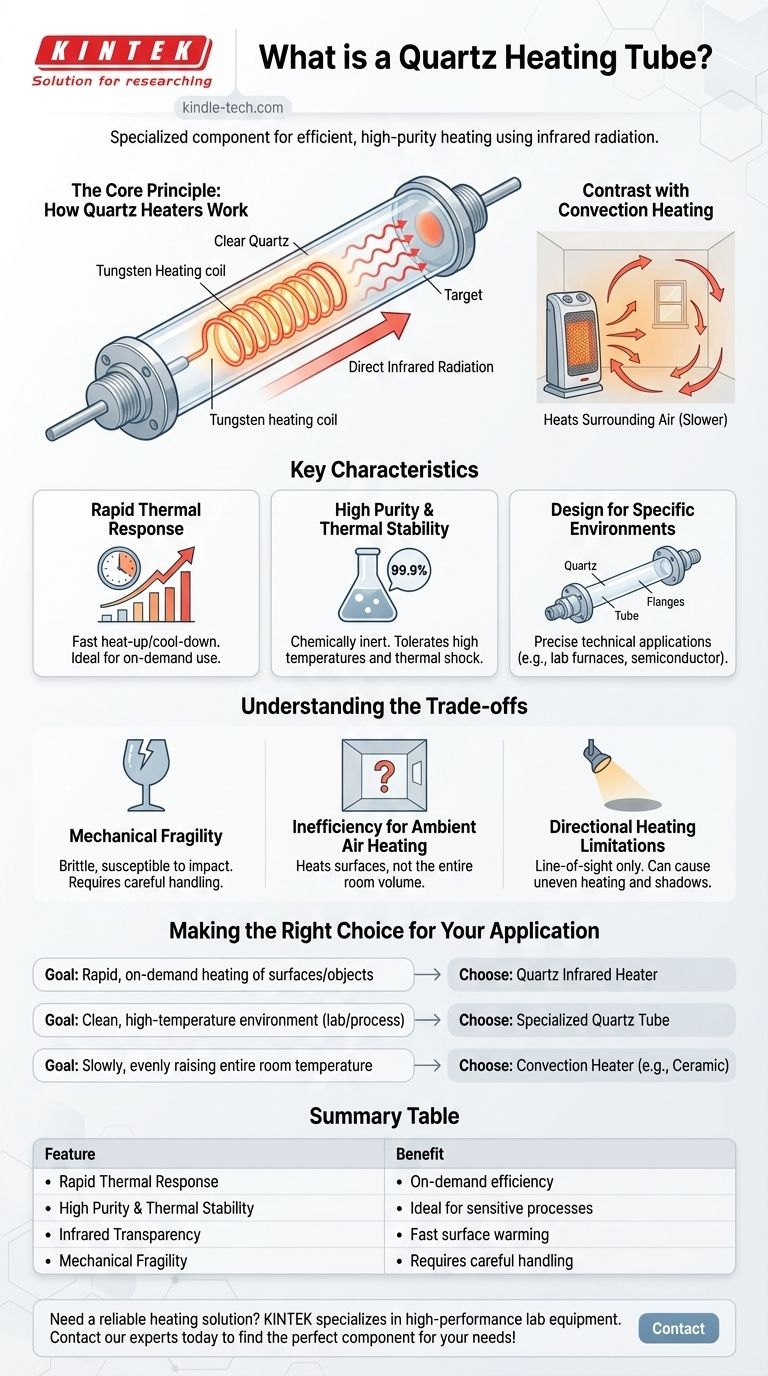
The Core Principle: How Quartz Heaters Work
At its core, a quartz heater is a system for converting electricity into radiant heat. The quartz tube is a critical component in making this conversion efficient and controllable.
The Role of the Heating Element and Tube
A resistive element, often a tungsten wire coil, is placed inside the quartz tube. When electricity passes through this coil, it heats up to a very high temperature. The quartz tube serves as a protective housing that is both chemically inert and resistant to these extreme temperatures.
Emitting Infrared Energy
The hot element inside radiates high-intensity infrared (IR) energy. Quartz glass is exceptionally transparent to IR radiation, meaning it allows this energy to pass through it directly with minimal absorption. This energy then travels until it strikes an object, transferring heat directly to that object's surface.
Contrast with Convection Heating
This is fundamentally different from a convection heater (like many ceramic models), which focuses on heating the surrounding air. The air then circulates to warm a space. Quartz heaters provide direct, line-of-sight radiant heat, which is much faster.
Key Characteristics of Quartz Heating Tubes
The choice to use quartz is driven by a distinct set of performance advantages that are critical for specific applications.
Rapid Thermal Response
Quartz heaters have exceptionally fast heat-up and cool-down times, often reaching operating temperature in seconds. This is because they do not need to heat a large thermal mass or the surrounding air, making them highly efficient for on-demand heating.
High Purity and Thermal Stability
Engineered quartz tubes can be made from over 99.9% pure silica. This makes them chemically inert and prevents them from contaminating sensitive processes. They also offer excellent tolerance for high temperatures and extreme thermal shock (rapid temperature changes) without cracking.
Design for Specific Environments
Quartz tubes can be manufactured with high precision for demanding technical applications. For example, they can be fitted with stainless steel flanges, needle valves for gas control, and interfaces for vacuum pumps, making them suitable for use in laboratory furnaces or semiconductor processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every scenario. Understanding the limitations of quartz is key to using it correctly.
Mechanical Fragility
While highly resistant to thermal shock, quartz is a type of glass. It is inherently more brittle and susceptible to physical impact or vibration than heaters with a metal sheath. Careful handling and installation are essential.
Inefficiency for Ambient Air Heating
Because quartz heaters primarily emit radiant heat, they are not effective at warming the air in an entire room. They heat objects and people directly in their path. For raising the ambient temperature of a large, enclosed space, a convection heater is a better tool.
Directional Heating Limitations
The line-of-sight nature of infrared radiation means that objects not directly exposed to the heater will not get warm. "Shadows" can be cast, leading to uneven heating if the source is not positioned correctly or if the target has a complex shape.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heater depends entirely on your specific goal. The properties of quartz make it the ideal choice for some tasks and a poor choice for others.
- If your primary focus is rapid, on-demand heating of surfaces or objects: A quartz infrared heater is the superior choice due to its fast response time and direct energy transfer.
- If your primary focus is creating a clean, high-temperature environment for a scientific or industrial process: The high purity and thermal stability of a specialized quartz tube are essential.
- If your primary focus is slowly and evenly raising the air temperature in an entire room: A convection heater, such as a ceramic or oil-filled model, will be far more effective.
By matching the fundamental operating principle of the heater to your goal, you ensure efficient and effective performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rapid Thermal Response | Heats up and cools down in seconds for on-demand efficiency. |
| High Purity & Thermal Stability | Chemically inert, ideal for sensitive processes and high temperatures. |
| Infrared Transparency | Emits direct, line-of-sight radiant heat for fast surface warming. |
| Mechanical Fragility | Requires careful handling due to its brittle nature (a key trade-off). |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab or process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including quartz heating tubes designed for precision and durability. Our products ensure rapid heat-up, clean operation, and stability for your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect heating component for your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can a horizontal furnace be used vertically? Understanding the Critical Design and Safety Factors
- Why is a quartz tube reactor selected for the high-temperature steam reforming of naphthalene? Achieve Precise Results
- What conditions does a tube furnace provide for nanocatalysts? Master Precise Annealing and Hydrogen Reduction
- Why are quartz reactors used inside tube furnaces? Protect Your Equipment and Ensure Accurate Biomass Corrosion Data
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in the solid-state synthesis of niobate mixed crystals? Precision Phase Control
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and tubular furnace? A Guide to Choosing the Right Lab Furnace
- What are the uses of ceramic tube? The Ultimate Guide for Extreme Environments



















