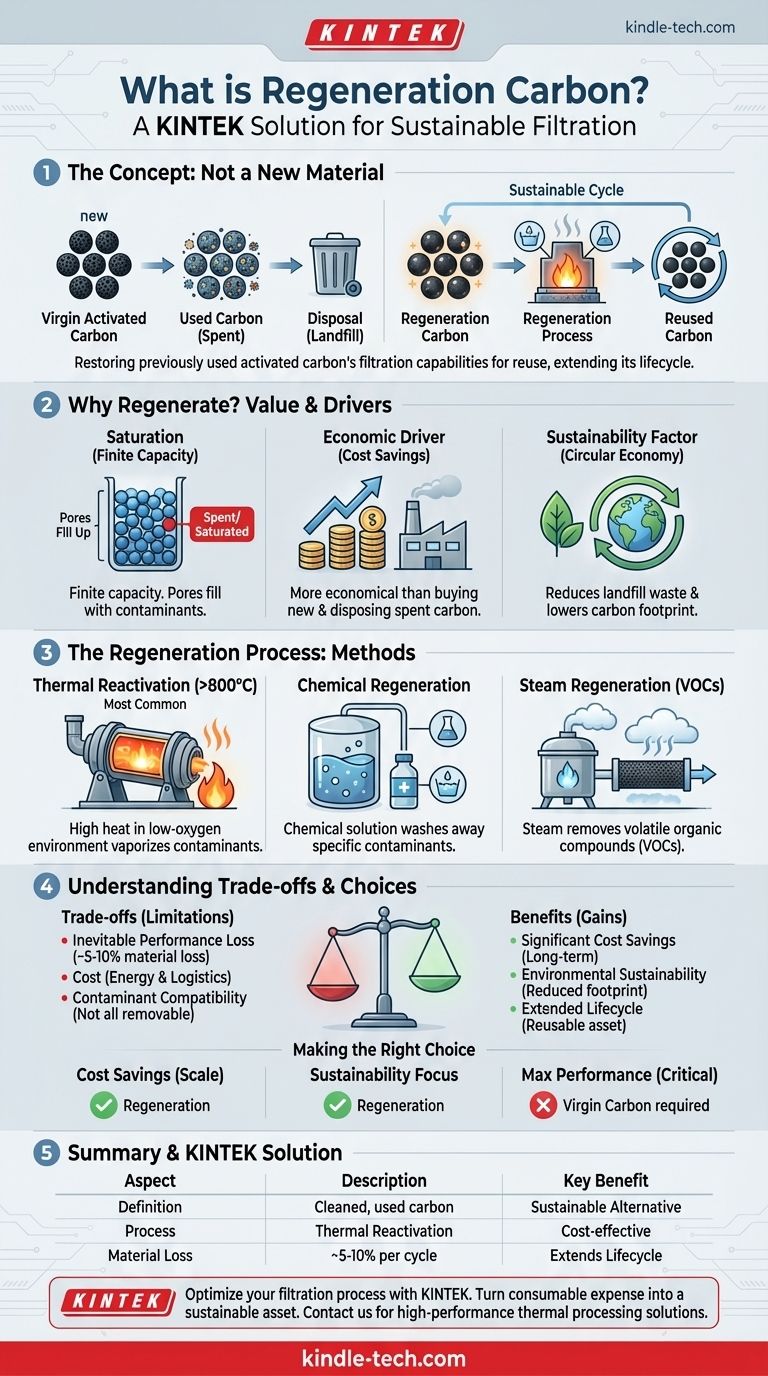
Regeneration carbon is not a distinct type of material. Instead, the term refers to previously used activated carbon that has undergone a process of regeneration or reactivation. This process cleans the carbon by removing the contaminants it has adsorbed, effectively restoring its filtration capabilities so it can be used again.
The core concept is simple: instead of disposing of "spent" activated carbon and replacing it, regeneration offers a cost-effective and environmentally sustainable way to "recharge" and reuse the same material, significantly extending its lifecycle.

Why Regenerate Activated Carbon?
To understand the value of regeneration, one must first understand how activated carbon works. It is a powerful adsorbent because of its incredibly porous structure, which creates a vast internal surface area to trap and hold contaminant molecules.
The Saturation Point
Activated carbon has a finite capacity. As it adsorbs contaminants from a liquid or gas stream, its pores gradually fill up. When it can no longer adsorb effectively, it is considered "spent" or "saturated."
The Economic Driver
Virgin (new) activated carbon is an expensive consumable. For any large-scale industrial or municipal application, the ongoing cost of purchasing new carbon and paying for the disposal of spent carbon can be substantial. Regeneration is often a far more economical alternative.
The Sustainability Factor
Regenerating carbon is a key component of a circular economy. It dramatically reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills and lowers the carbon footprint associated with mining, producing, and transporting new activated carbon.
The Process of Regeneration
Regeneration involves using energy to break the bonds between the carbon and the adsorbed contaminants, effectively "emptying" the pores. The specific method depends on the type of carbon and the contaminants it holds.
Thermal Reactivation
This is the most common and robust method. The spent carbon is heated in a controlled, low-oxygen environment (often a rotary kiln or furnace) to temperatures exceeding 800°C (1500°F). This intense heat vaporizes and thermally destroys the adsorbed organic contaminants, clearing the carbon's pore structure.
Chemical Regeneration
For certain applications, chemical regeneration is used. This process involves washing the spent carbon with a chemical solution (such as a solvent, acid, or base) that dissolves the specific contaminants, releasing them from the carbon's surface without requiring high heat.
Steam Regeneration
A less intensive method involves passing steam through the carbon bed. This is effective for removing more volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are not as strongly bonded to the carbon surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, regeneration is not a perfect process. It's crucial to understand the limitations to make an informed decision.
Inevitable Performance Loss
Each regeneration cycle causes a small amount of damage to the carbon. The high heat can weaken its structure, and some material is inevitably lost as dust during handling and transport. Typically, there is a 5-10% loss of material with each thermal cycle, and the overall adsorption capacity may be slightly diminished.
The Cost-Benefit Analysis
Regeneration is not free. The process requires significant energy, specialized equipment, and logistics to transport the carbon to and from a reactivation facility. The decision to regenerate is an economic one, weighing the cost of reactivation against the cost of new carbon and disposal.
Contaminant Compatibility
Not all contaminants can be removed. Some substances, like heavy metals, may permanently bond to the carbon. Others, like certain polymers, can melt and fuse within the pores, making regeneration impossible. The viability of regeneration depends entirely on what the carbon was used to capture.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing between regeneration and replacement depends entirely on your operational goals and constraints.
- If your primary focus is cost savings at scale: For large industrial users, regeneration is almost always the most economical path forward over the long term.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Regeneration is the clear winner, as it drastically reduces landfill waste and the lifecycle carbon footprint of your filtration process.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance in a critical application: Virgin carbon may be required for sensitive uses (like food, beverage, or pharmaceutical production) where the slight performance degradation or risk of contaminant carry-over from regeneration is unacceptable.
Ultimately, viewing activated carbon as a reusable asset rather than a disposable consumable opens the door to more efficient, economical, and responsible operations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Used activated carbon that has been cleaned to restore its filtration capacity. |
| Primary Benefit | Cost-effective and sustainable alternative to disposal and replacement. |
| Common Process | Thermal reactivation in a furnace (>800°C) to vaporize contaminants. |
| Material Loss | Typically 5-10% of carbon mass is lost per regeneration cycle. |
Optimize your filtration process and reduce costs with KINTEK.
Is your lab or facility managing spent activated carbon? Regeneration is a powerful strategy to turn a major consumable expense into a sustainable, cost-effective asset. KINTEK specializes in the high-performance lab equipment and thermal processing solutions essential for efficient carbon management.
Let our experts help you evaluate if regeneration is the right choice for your application. We provide the reliable technology and support to help you save on material costs and minimize environmental impact.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your activated carbon needs and discover our solutions for a more efficient and sustainable operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How can different materials have different heat capacity? Unlocking the Microscopic Secrets of Energy Storage
- What heat treatment process is used to soften materials or to obtain other desired properties? A Guide to Annealing
- What is the process of making bio-oil? Convert Biomass to Liquid Fuel via Pyrolysis
- What are the hazards of sintering? Manage Process, Financial, and Safety Risks
- What is the effect of heating rate in heat treatment? Control Hardness, Microstructure, and Distortion
- What is the temperature of pyrolysis products? Control the Heat to Control Your Output
- What are the limitations of melting point determination? Understand Purity, Technique, and Material Behavior
- Why carbon coating for SEM? Get Accurate Elemental Analysis with Carbon Coating


















