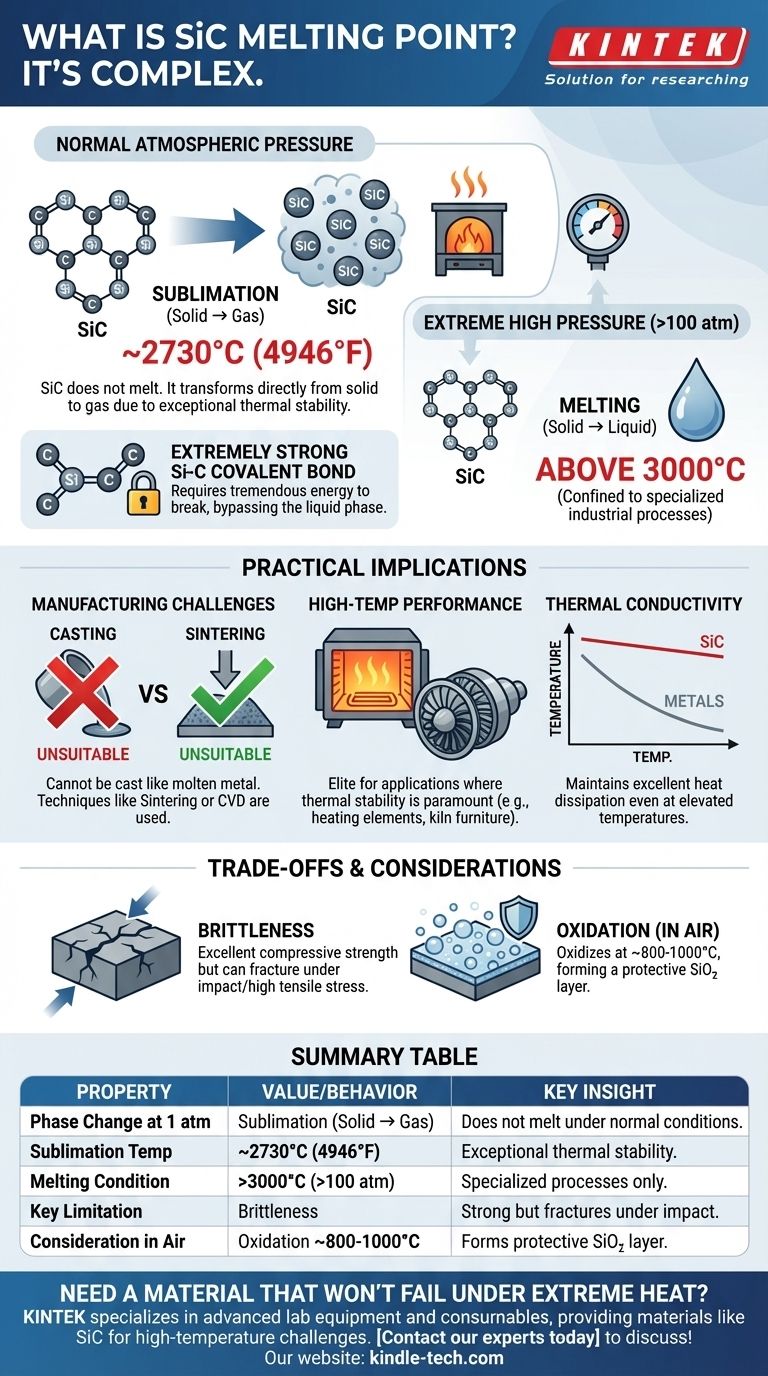
The melting point of silicon carbide (SiC) is a complex topic. Unlike many materials, SiC does not have a distinct melting point at standard atmospheric pressure. Instead, it undergoes sublimation—transforming directly from a solid to a gas—at approximately 2730°C (4946°F). It can only be forced into a liquid state under extremely high pressures.
Understanding silicon carbide's thermal behavior is less about a single melting temperature and more about appreciating its exceptional stability. The fact that it sublimates rather than melts is the very reason it excels in extreme high-temperature environments.

Why SiC Doesn't Melt Under Normal Conditions
The unique thermal properties of silicon carbide are rooted in its atomic structure. This defines its performance and sets it apart from conventional metals and ceramics.
The Strength of the Si-C Bond
Silicon carbide is characterized by an extremely strong and stable covalent bond between its silicon (Si) and carbon (C) atoms.
This bond requires a tremendous amount of thermal energy to break. Before the atoms can gain enough mobility to form a liquid, they absorb enough energy to bypass the liquid phase entirely and escape as a gas.
Sublimation vs. Melting
Sublimation is the direct transition from a solid to a gaseous state. This is what happens to SiC at around 2730°C under normal atmospheric pressure.
Melting requires the material to enter a liquid phase. For SiC, this is only achievable under inert gas pressures exceeding 100 atmospheres, at which point it may melt at temperatures above 3000°C. This is a condition confined to specialized industrial processes, not typical operating environments.
Understanding the Practical Implications
The distinction between sublimation and melting is not just academic. It has direct consequences for how SiC is manufactured and used.
Manufacturing Challenges
Because SiC does not melt easily, it cannot be cast into shapes like molten metal. This necessitates different manufacturing techniques.
The most common method is sintering, where SiC powder is heated under pressure (without melting) until the particles fuse together. Other methods include chemical vapor deposition (CVD), where SiC is grown onto a substrate from a gas.
Performance in High-Temperature Applications
The high sublimation temperature makes SiC an elite material for applications where thermal stability is paramount.
It is used for heating elements in furnaces, components for gas turbines, and kiln furniture because it maintains its structural integrity and strength at temperatures that would cause most metals to melt or deform.
Thermal Conductivity at High Temperatures
Unlike metals, whose thermal conductivity drops as they get hotter, SiC maintains very good thermal conductivity even at elevated temperatures.
This allows it to dissipate heat effectively, which is critical for its use in high-power electronics and as a material for heat exchangers in extreme conditions.
Key Trade-offs and Considerations
While remarkably robust, SiC is not without its limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for proper material selection.
Oxidation in Air
While SiC doesn't melt in air, it will begin to oxidize at very high temperatures (typically starting around 800-1000°C).
The silicon in the material reacts with oxygen to form a protective surface layer of silicon dioxide (SiO₂). This "passivation layer" slows down further oxidation, but it is a factor to consider in long-duration, high-heat applications.
Brittleness
Like most ceramics, SiC is brittle. It has excellent compressive strength but can fracture under sharp impacts or high tensile stress.
This means component design must carefully manage mechanical shocks and stresses, a key difference from ductile metals that can bend or deform before failing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting SiC depends entirely on whether its unique properties align with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme thermal stability: SiC is a superior choice, as it will not melt and will maintain its structure at temperatures far beyond the limits of steel, nickel alloys, or even alumina.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex shapes via casting: SiC is unsuitable due to its lack of a viable melting point under normal conditions; you would need to design for sintering or other ceramic processing methods.
- If your application involves high heat in an oxygen-rich environment: You must account for the formation of a protective but performance-altering silicon dioxide layer on the SiC surface.
By understanding that silicon carbide's strength lies in its refusal to melt, you can leverage its properties to solve problems that are impossible for conventional materials.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value/Behavior | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Phase Change at 1 atm | Sublimation (Solid → Gas) | Does not melt under normal conditions. |
| Sublimation Temperature | ~2730°C (4946°F) | Exceptional thermal stability for high-heat environments. |
| Melting Condition | >3000°C under high pressure (>100 atm) | Confined to specialized industrial processes. |
| Key Limitation | Brittleness | Excellent compressive strength but can fracture under impact. |
| Consideration in Air | Oxidation from ~800-1000°C | Forms a protective SiO₂ layer at high temperatures. |
Need a material that won't fail under extreme heat? Silicon Carbide's unique properties make it the ultimate choice for high-temperature applications where others would melt. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing the materials and expertise to push the boundaries of thermal performance in your laboratory or production process.
Contact our experts today to discuss how SiC can solve your high-temperature challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a silicon carbide heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat for Industrial Processes
- What is the maximum temperature for a SiC heating element? Unlock the Key to Longevity and Performance
- What kind of metal is used in heating elements? A Guide to Materials for Every Temperature & Atmosphere
- What are silicon carbide heating elements used for? Reliable High-Temp Heating for Industrial Processes
- What is silicon carbide rod heated to high temperature used as? A Premier Heating Element for Extreme Environments



















