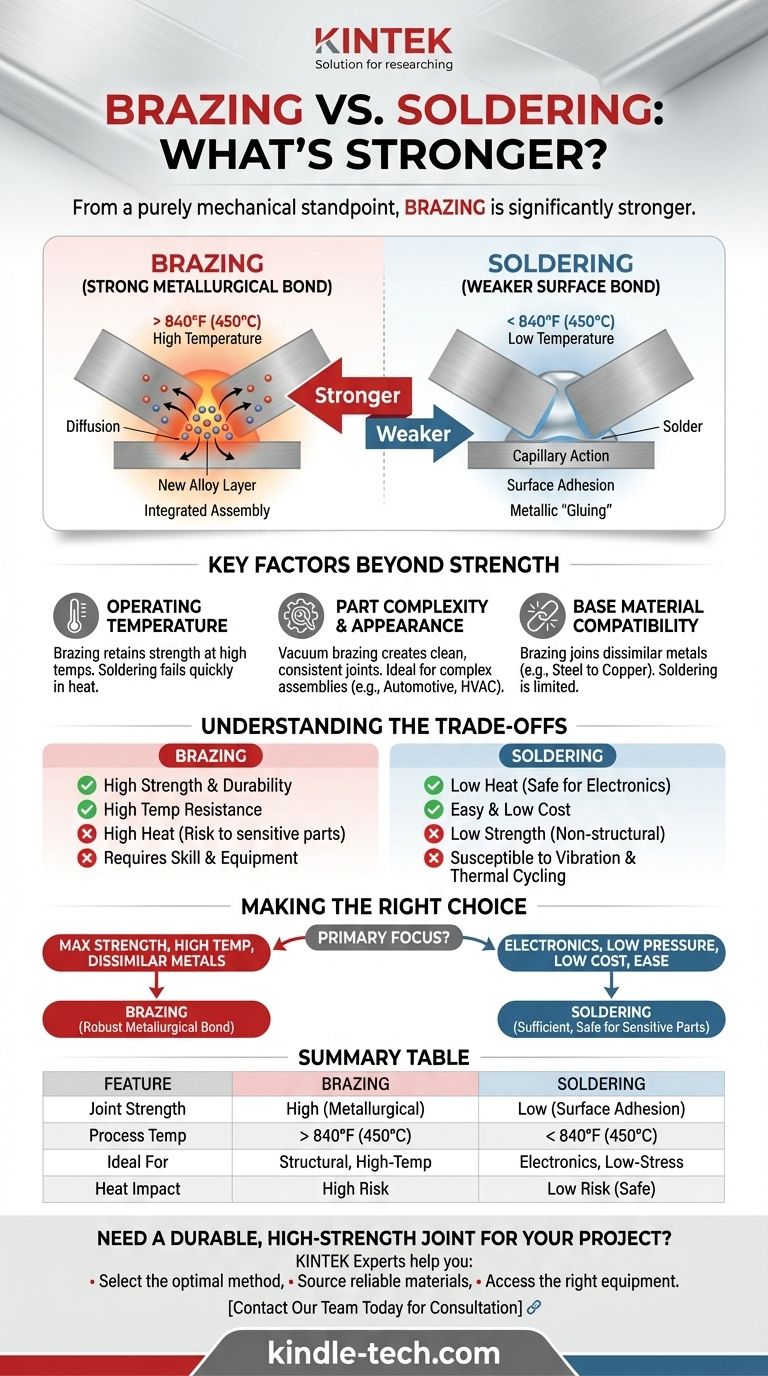
From a purely mechanical standpoint, brazing creates a significantly stronger joint than soldering. The process uses higher temperatures—above 840°F (450°C)—which allows the filler metal to form a deep metallurgical bond with the base materials. This results in a connection that is often as strong, or even stronger, than the metals being joined.
The core difference is not just the filler material, but the nature of the bond itself. Soldering is a surface-level connection, while brazing creates a fused, inter-atomic bond, fundamentally changing the nature of the joint and delivering far superior strength.

The Fundamental Difference: Why Temperature Dictates Strength
The distinction between a brazed and a soldered joint comes down to what happens at a microscopic level. The temperature threshold of 840°F (450°C) is the critical dividing line that determines the type of bond formed.
Soldering: A Surface-Level Bond
Soldering is a low-temperature process. The filler metal, or solder, melts and is pulled into the joint by capillary action, but it primarily adheres to the surface of the base metals.
Think of it as a form of metallic "gluing." While effective for creating electrical continuity or sealing low-pressure connections, the bond itself does not significantly fuse with the parent materials.
Brazing: A Metallurgical Bond
Brazing occurs at much higher temperatures. This intense heat causes diffusion, where atoms from the filler metal and the base metal actively intermingle at the joint interface.
This process creates a new, distinct alloy layer at the seam. The joint becomes an integrated, continuous part of the assembly, not just two pieces stuck together. This metallurgical transformation is the source of brazing's exceptional strength.
Key Factors Beyond Pure Strength
While brazing is stronger, the best choice depends on the specific application. Several other factors are critical to consider.
Operating Temperature
A joint's strength is only useful if it can survive its operating environment. A brazed joint retains its strength at much higher temperatures than a soldered one.
A soldered joint will quickly fail if the service temperature approaches the solder's low melting point.
Part Complexity and Appearance
Brazing techniques, such as vacuum brazing, can produce extremely clean joints free from oxidation. This process is ideal for complex assemblies and provides excellent part-to-part consistency, which is crucial in industries like automotive and HVAC systems.
Base Material Compatibility
Brazing is exceptionally versatile and can be used to join a wide variety of dissimilar metals, such as steel to copper or stainless steel to brass. Soldering is typically more limited to metals like copper, brass, and tin-plated components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the stronger method is not always the right decision. Each process comes with significant trade-offs that may make it unsuitable for a given task.
The Downside of Brazing: Heat and Skill
The high temperatures required for brazing are its greatest strength and its biggest liability. This heat can easily damage nearby sensitive components, such as electronics or seals.
Furthermore, the heat can alter the temper or heat treatment of the base metals, potentially weakening the parts themselves if not controlled properly. Brazing requires more skill and more sophisticated equipment to execute correctly.
The Limitation of Soldering: Mechanical Stress
Soldered joints are simply not designed for high-stress or structural applications. Their strength is orders of magnitude lower than a brazed or welded joint.
They are also more susceptible to failure from factors like vibration, impact, and significant thermal cycling. For anything load-bearing, soldering is almost never the appropriate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision must be guided by the specific engineering demands of your project. Balance the need for strength against the risks of heat and complexity.
- If your primary focus is maximum mechanical strength or high-temperature performance: Brazing is the correct and necessary choice, as it creates a robust metallurgical bond.
- If your primary focus is joining electronic components or low-pressure water lines: Soldering provides sufficient strength at a lower cost and temperature, protecting sensitive parts from heat damage.
- If your primary focus is a clean, structural bond between dissimilar metals: Brazing offers superior strength and compatibility for creating strong, permanent joints between materials like steel and copper.
- If your primary focus is ease of use and low cost for non-structural parts: Soldering is the more accessible and forgiving process, requiring less specialized equipment and skill.
Ultimately, selecting the right method requires a clear understanding of the joint's required strength, its operating environment, and the thermal sensitivity of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Strength | High (Metallurgical Bond) | Low (Surface Adhesion) |
| Process Temperature | > 840°F (450°C) | < 840°F (450°C) |
| Ideal For | Structural, High-Temp, Dissimilar Metals | Electronics, Low-Stress Seals |
| Heat Impact on Parts | High (Risk of Warping/Temper Loss) | Low (Safe for Sensitive Components) |
Need a Durable, High-Strength Joint for Your Project?
Choosing between brazing and soldering is critical for the performance and longevity of your assemblies. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the right equipment and consumables for both processes, ensuring your laboratory or production line achieves perfect, reliable bonds every time.
We help you:
- Select the optimal joining method for your specific materials and performance requirements.
- Source reliable brazing alloys and solders that ensure consistent, high-quality results.
- Access the right equipment for clean, controlled processes like vacuum brazing.
Don't compromise on joint integrity. Let KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables strengthen your work. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can you braze two different metals? Yes, and here’s how to do it successfully.
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are the advantages of brazing compared to welding? Achieve Clean, Low-Distortion Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















