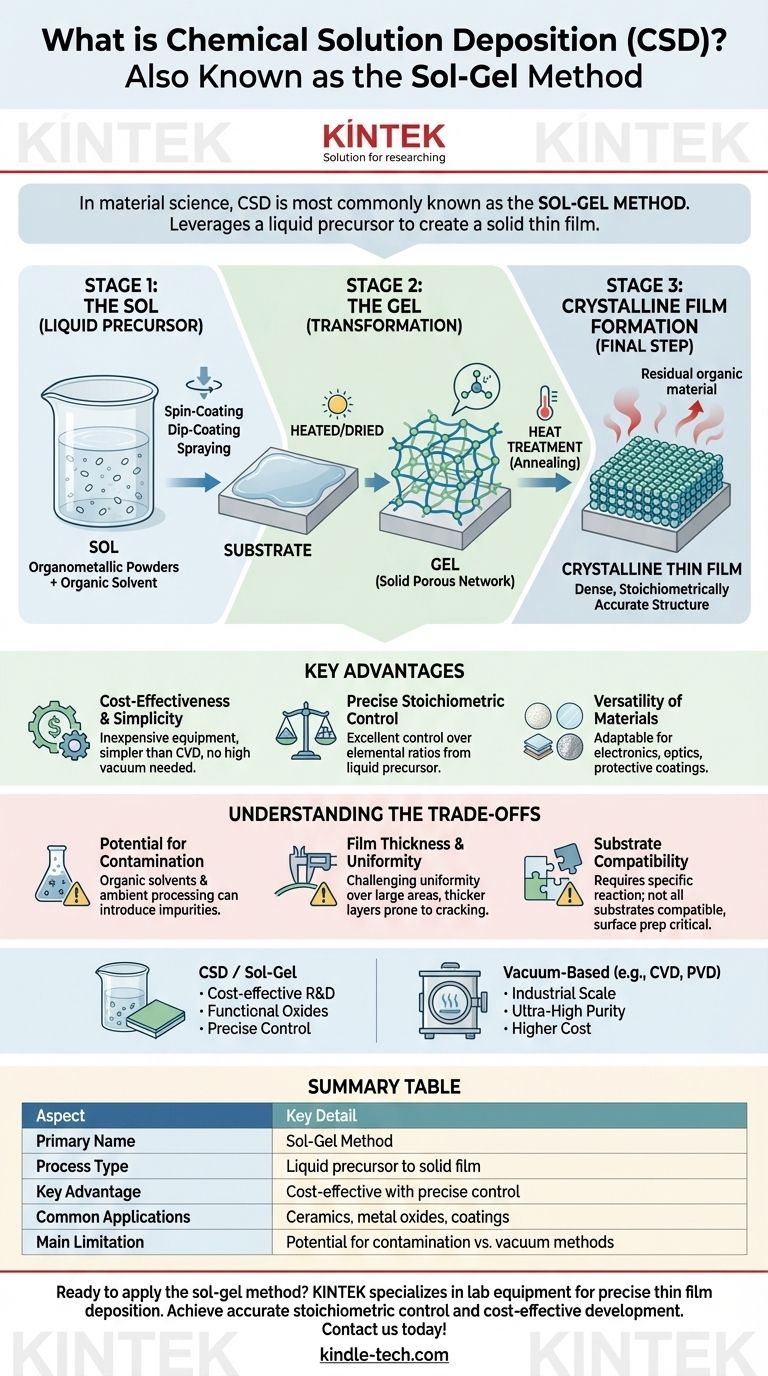
In material science and engineering, the chemical solution deposition (CSD) method is most commonly known as the sol-gel method. This technique leverages a liquid chemical precursor to create a solid thin film on a substrate through a controlled chemical process, distinguishing it from vapor-based methods.
At its core, the CSD / sol-gel process is about transforming a specially designed liquid solution (the 'sol') into a solid, glass-like network (the 'gel') to produce high-quality, crystalline thin films in a simple and cost-effective manner.

Deconstructing Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD)
The name "sol-gel" perfectly describes the two primary stages of the process. It is a journey from a liquid solution to a solid-state material directly on a component's surface.
The Core Principle: A Liquid Precursor
CSD begins with a liquid precursor, typically a solution containing organometallic powders dissolved in an organic solvent. This initial, stable liquid solution is referred to as the "sol."
The composition of this sol is meticulously controlled, as it directly dictates the elemental makeup of the final thin film.
The Transformation: From Sol to Gel
The sol is applied to a substrate using methods like spin-coating, dip-coating, or spraying. A chemical reaction is then initiated, often through heating or drying.
This causes the precursor molecules to link together, forming a solid, porous, three-dimensional network known as a "gel."
The Final Step: Crystalline Film Formation
After the gel is formed, it typically undergoes a heat treatment process (annealing). This step removes residual organic material and encourages the formation of a dense, crystalline structure.
The result is a stoichiometrically accurate crystalline film bonded to the substrate surface.
Key Advantages of the CSD / Sol-Gel Method
Engineers and researchers choose this method for several distinct benefits, especially when compared to more complex vacuum-based techniques like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Cost-Effectiveness and Simplicity
The equipment required for the sol-gel process is relatively inexpensive and simpler to operate. It does not require the high-vacuum chambers or complex gas-handling systems associated with CVD.
Precise Stoichiometric Control
Because the process starts with a liquid, chemists have excellent control over the ratios of different elements in the precursor solution. This precision is directly transferred to the final solid film, ensuring accurate chemical composition (stoichiometry).
Versatility of Materials
The sol-gel method is highly versatile and can be adapted to produce a wide range of materials, including ceramics, glass-ceramics, and metal oxides, for applications in electronics, optics, and protective coatings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the CSD / sol-gel method is not without its limitations. Objectivity requires acknowledging where other methods may be superior.
Potential for Contamination
The use of organic solvents and processing in an ambient environment can introduce impurities or defects into the film, which may be unacceptable for high-purity electronic applications.
Film Thickness and Uniformity
Achieving perfectly uniform films over large areas can be challenging. Furthermore, films produced via sol-gel are often thinner, and building up thick layers can lead to cracking and stress.
Substrate Compatibility
The process often relies on a specific reaction between the solution and the substrate surface. This means not all substrate materials are compatible, and surface preparation is critical for good adhesion and film quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technique depends entirely on your project's constraints and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective R&D or creating functional oxides: The CSD / sol-gel method provides an accessible and flexible pathway for producing high-quality films with precise chemical control.
- If your primary focus is industrial-scale production of ultra-high-purity semiconductor films: A vacuum-based technique like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD) will likely be a more reliable choice, despite the higher initial investment.
By understanding the principles behind the CSD / sol-gel method, you can effectively determine where this powerful technique fits within your material engineering toolkit.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Name | Sol-Gel Method |
| Process Type | Liquid precursor to solid film |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective with precise stoichiometric control |
| Common Applications | Ceramics, metal oxides, protective coatings |
| Main Limitation | Potential for contamination vs. vacuum methods |
Ready to apply the sol-gel method in your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise thin film deposition. Our solutions help you achieve accurate stoichiometric control and cost-effective material development. Contact us today to optimize your CSD process with the right tools and expertise!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance



















