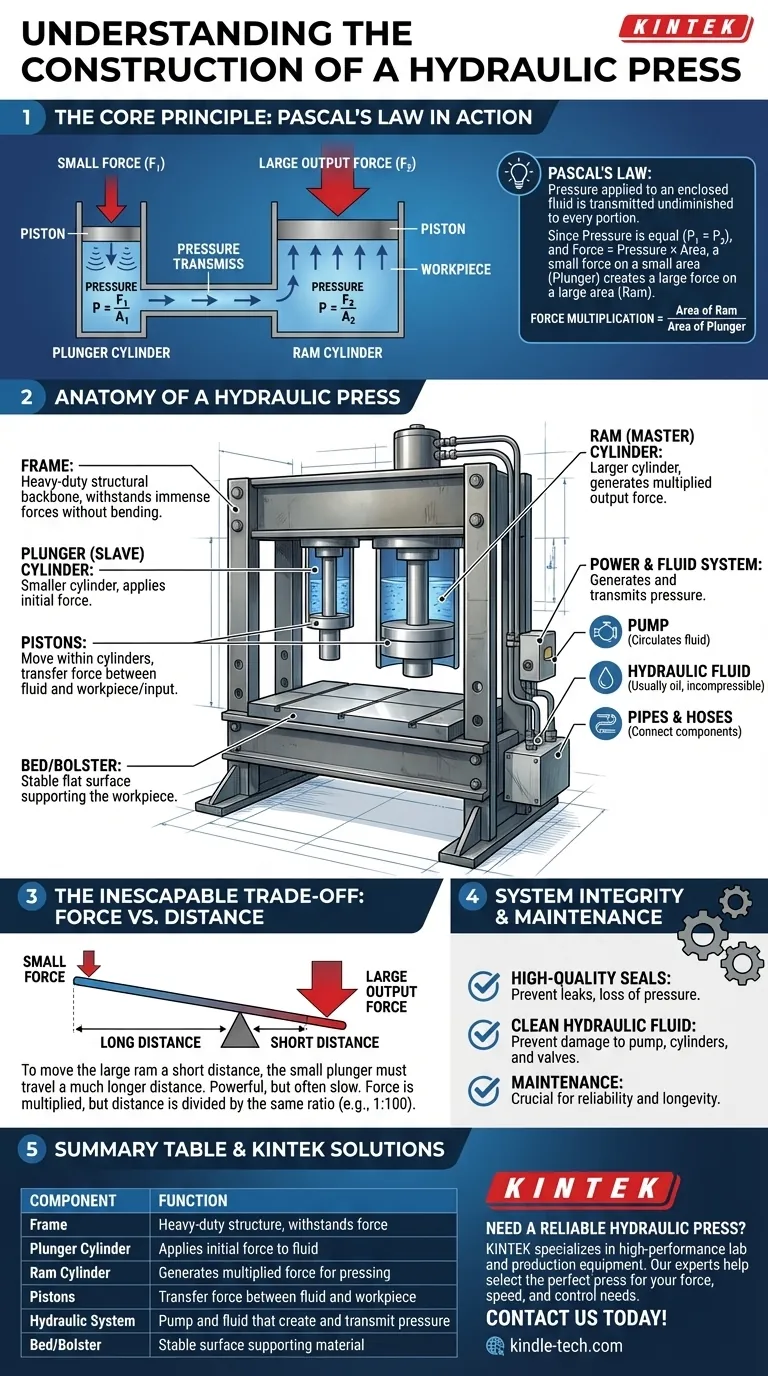
At its core, a hydraulic press is a system of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes filled with an incompressible fluid. The fundamental components include a structural frame, a smaller cylinder called the plunger, a larger cylinder called the ram, pistons that move within these cylinders, and a power system (pump) that circulates the hydraulic fluid, typically oil. This simple construction allows the machine to convert a small applied force into an exceptionally large output force.
The genius of a hydraulic press lies not in its individual parts, but in how their arrangement leverages a fundamental principle of physics: Pascal's Law. This law states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.

The Core Principle: Pascal's Law in Action
To understand the construction, you must first understand the "why" behind it. The entire design is a practical application of force multiplication.
How Pressure Creates Force
Pressure is defined as force per unit area (P = F/A). According to Pascal's Law, the pressure created by the small plunger is transmitted equally throughout the fluid to the large ram.
Because the pressure is the same on both pistons, but their areas are different, the forces they produce are also different. A small force on the small plunger creates a much larger force on the large ram.
The Force Multiplication Formula
The relationship is simple: the force is multiplied by the ratio of the areas of the two pistons. If the ram's piston has 100 times the surface area of the plunger's piston, the output force will be 100 times the input force.
Anatomy of a Hydraulic Press
While designs vary, nearly all hydraulic presses are built from these key functional groups. Each component has a distinct role in generating and containing immense force.
The Frame: The Structural Backbone
The frame is the heavy-duty structure that holds all the components together. It must be incredibly robust to withstand the massive forces generated by the press without bending or breaking.
The Hydraulic Cylinders: Plunger and Ram
This is the heart of the system.
- The Plunger (or slave cylinder) is the smaller cylinder where the initial force is applied.
- The Ram (or master cylinder) is the much larger cylinder where the multiplied force is delivered to do the work.
The Pistons: Translating Force
A piston is a solid cylinder or disc that fits snugly inside each hydraulic cylinder. It moves up and down, transferring force from the hydraulic fluid to the workpiece or vice-versa.
The Power & Fluid System: Generating Pressure
This system creates and transmits the pressure. It consists of:
- A pump to move the hydraulic fluid into the system.
- Hydraulic fluid (usually oil) which is nearly incompressible, making it perfect for transmitting pressure.
- Pipes and hoses to connect the cylinders and the pump.
The Work Area: Bed and Bolster
The bed, base plate, or bolster is the flat, stable surface that supports the material being pressed. It sits directly under the ram and must also be strong enough to resist the pressing force.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The immense force multiplication of a hydraulic press does not come for free. Understanding its primary limitation is crucial for its proper application.
The Inescapable Trade-off: Force vs. Distance
The core trade-off is between force and the distance the ram travels. To move the large ram a small distance, the small plunger must travel a much longer distance.
For example, to lift the ram by 1 inch, a plunger with 1/100th the area must be pushed through 100 inches of travel. This makes hydraulic presses powerful, but often slow.
System Integrity and Maintenance
Hydraulic systems operate under extreme pressure. This demands high-quality seals to prevent leaks, which would cause a loss of pressure and force.
The hydraulic fluid must also be kept clean. Contaminants can damage the pump, score the cylinder walls, and cause valves to fail, compromising the entire system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The construction of a hydraulic press is a direct reflection of its purpose. By understanding how the components work together, you can better appreciate its application.
- If your primary focus is maximizing force: The ratio between the ram and plunger cylinder areas is the most critical design element.
- If your primary focus is speed and control: The sophistication of the pump, valves, and control system is paramount for regulating flow and pressure efficiently.
- If your primary focus is reliability: The quality of the frame's construction and the integrity of the hydraulic seals are non-negotiable.
Ultimately, the construction of a hydraulic press is an elegant and powerful demonstration of fluid mechanics, designed to turn a small input into an immense, controllable output.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Frame | Heavy-duty structure to withstand immense force |
| Plunger Cylinder | Applies initial force to the hydraulic fluid |
| Ram Cylinder | Generates multiplied force for pressing |
| Pistons | Transfer force between fluid and workpiece |
| Hydraulic System | Pump and fluid that create and transmit pressure |
| Bed/Bolster | Stable surface supporting the material being pressed |
Need a reliable hydraulic press for your laboratory or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including robust hydraulic presses designed for precision and durability. Our experts can help you select the perfect press to meet your specific force, speed, and control requirements. Contact us today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- How hot is a hydraulic press? Understanding the Critical Heat in Your Hydraulic System
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















