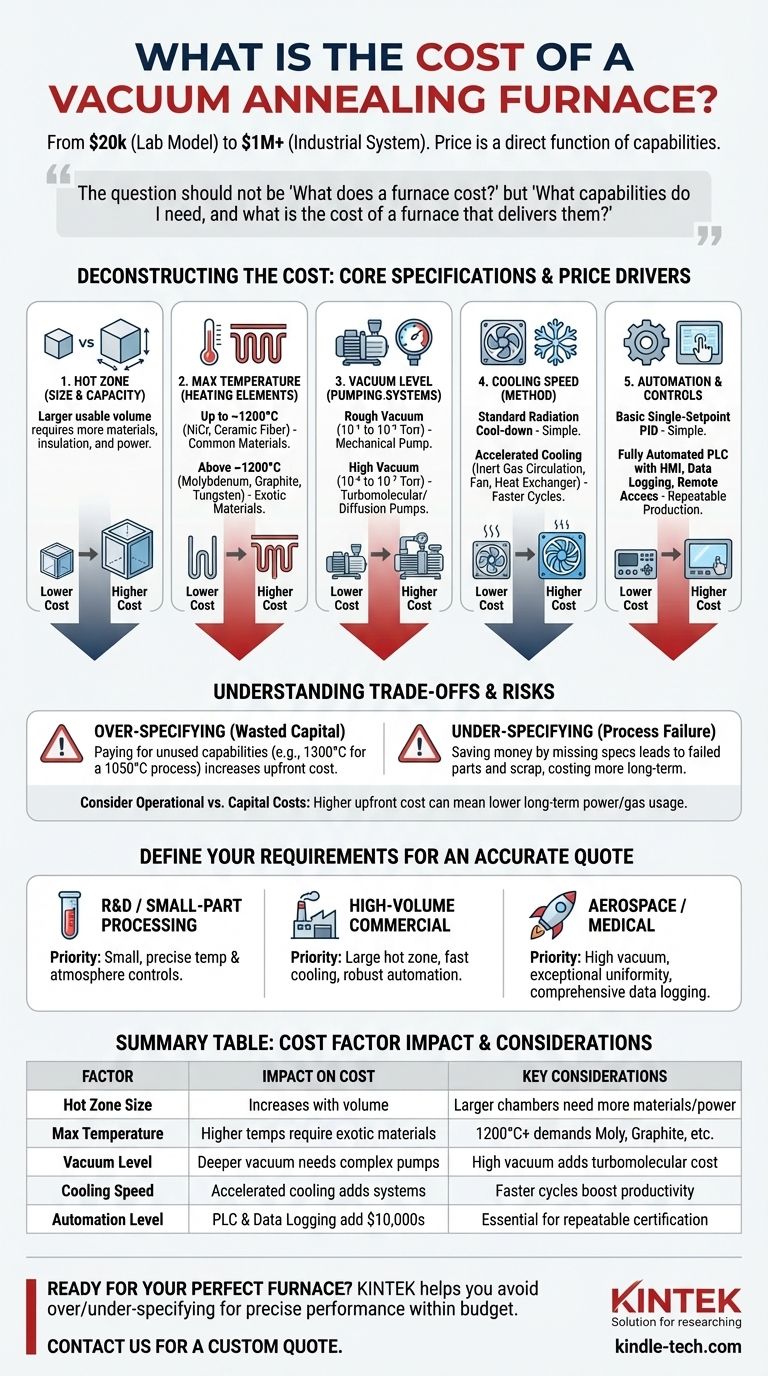
The cost of a vacuum annealing furnace varies dramatically, ranging from as little as $20,000 for a small, basic laboratory model to well over $1,000,000 for a large-scale, highly automated industrial system. The final price is not a simple number but a direct result of specific technical capabilities matched to a specific process requirement.
The question should not be "What does a furnace cost?" but rather, "What capabilities do I need, and what is the cost of a furnace that delivers them?" The price is a direct function of five key factors: size, maximum temperature, vacuum level, cooling speed, and level of automation.
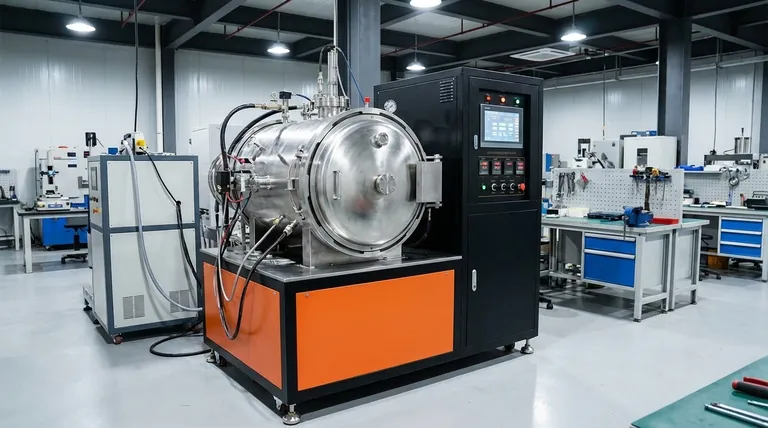

Deconstructing the Cost: The Core Specifications
To understand the price, you must understand the engineering behind the furnace. Each component and performance metric has a direct and significant impact on the final cost.
Factor 1: The Hot Zone (Size and Capacity)
The hot zone is the usable internal volume of the furnace where your parts are heated. It is the single most intuitive cost driver.
A larger hot zone requires more raw materials for the chamber, more extensive insulation, and a more powerful heating and pumping system to achieve the desired conditions throughout the larger volume.
Factor 2: Maximum Temperature and Heating Elements
The required operating temperature dictates the materials used for the heating elements and insulation, which is a primary cost factor.
- Up to ~1200°C: Furnaces in this range can often use nickel-chromium (NiCr) heating elements and ceramic fiber insulation. These are relatively common and less expensive materials.
- Above ~1200°C: This range requires more exotic and expensive materials. Molybdenum (Moly) or graphite elements become necessary, along with specialized graphite board or felt insulation. Furnaces capable of reaching 2000°C or higher may require tungsten elements, which are even more costly.
Factor 3: Vacuum Level and Pumping Systems
The "deepness" of the vacuum you need is a critical cost driver. A lower pressure (a higher vacuum) requires more sophisticated and expensive pump configurations.
- Rough Vacuum (10⁻¹ to 10⁻³ Torr): This can be achieved with a relatively simple mechanical "roughing" pump. This is the least expensive option.
- High Vacuum (10⁻⁴ to 10⁻⁷ Torr): Achieving this level requires a two-stage system. In addition to a mechanical pump, a turbomolecular pump or a diffusion pump is added, significantly increasing complexity and cost. The chamber construction and seals must also be of a much higher quality to prevent leaks.
Factor 4: Cooling Speed and Method
How quickly the furnace can cool your workload (quench) directly impacts your production cycle time and metallurgical results. Faster cooling adds significant cost.
A simple radiation cool-down is standard and inexpensive. For accelerated cooling, a system must be added to circulate inert gas (like Argon or Nitrogen) through the hot zone using a powerful fan and heat exchanger. This adds a motor, fan, heat exchanger, and complex gas plumbing to the furnace design.
Factor 5: Control Systems and Automation
The "brains" of the furnace can range from simple to highly complex.
A basic, single-setpoint PID controller is the cheapest option. A fully automated PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) with a user-friendly HMI (Human-Machine Interface), recipe management, extensive data logging, remote access, and safety interlocks will add tens of thousands of dollars to the cost but is essential for repeatable, certified production environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Beyond the Sticker Price
The goal is to procure a furnace that meets your process requirements reliably without paying for capability you will never use.
Over-specifying: The Most Common Mistake
It is tempting to request the highest possible temperature and the deepest possible vacuum "just in case." This is a costly error. A furnace rated for 1300°C is fundamentally more expensive than one rated for 1100°C. If your process only requires 1050°C, paying for the higher-rated model is a waste of capital.
Under-specifying: The Risk of Process Failure
Conversely, trying to save money by under-specifying can be disastrous. A furnace that cannot achieve the required temperature uniformity, vacuum level, or cooling rate will produce failed parts, costing far more in scrap and rework than the initial savings on the equipment.
Operational vs. Capital Costs
The initial purchase price is only part of the total cost of ownership. A higher-end furnace with better insulation and more efficient pumps may have a higher upfront cost but consume significantly less power and inert gas, leading to lower operational costs over its lifetime.
Defining Your Requirements to Get an Accurate Quote
To move from a broad price range to a firm quote, you must first define your process. A reputable manufacturer will guide you through this, but you should have a clear answer to these core questions.
- If your primary focus is R&D or small-part processing: Your priority should be a smaller benchtop or lab-scale furnace with precise temperature and atmosphere controls.
- If your primary focus is high-volume commercial heat treating: Prioritize a large hot zone, fast cooling for short cycle times, and robust automation for repeatability and reduced labor.
- If your primary focus is aerospace or medical components: The critical factors are high vacuum capability, exceptional temperature uniformity to meet standards like AMS 2750, and comprehensive data logging for certification.
Matching the furnace's specifications to your true operational need is the only path to a sound investment.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Zone Size | Increases significantly with volume | Larger chambers require more materials and power |
| Max Temperature | Higher temps require exotic materials (e.g., Molybdenum, Graphite) | 1200°C+ demands advanced heating elements |
| Vacuum Level | Deeper vacuum needs complex pump systems (e.g., turbomolecular) | High vacuum (10⁻⁷ Torr) adds substantial cost |
| Cooling Speed | Accelerated cooling adds gas quenching systems | Faster cycle times increase price but boost productivity |
| Automation Level | PLC controls and data logging add $10,000s | Essential for repeatable production and certification |
Ready to find the perfect vacuum annealing furnace for your budget and process?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs from R&D to high-volume production. Our experts will help you avoid over-specifying or under-specifying, ensuring you get a furnace that delivers precise temperature control, reliable vacuum performance, and efficient cooling—without paying for unnecessary features.
Contact us today for a personalized consultation and an accurate quote tailored to your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems



















