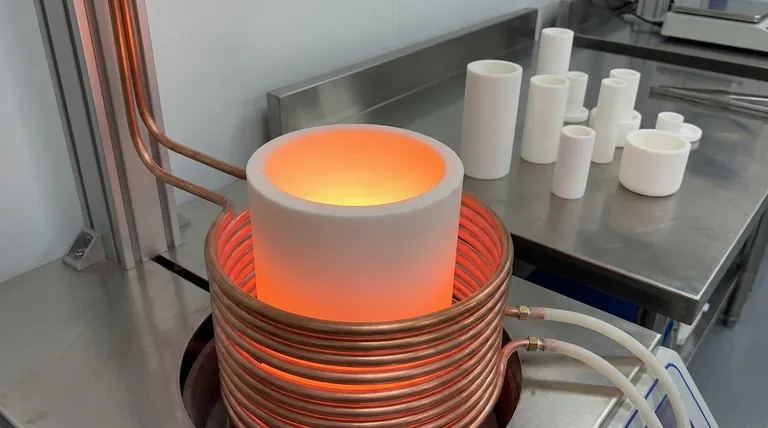
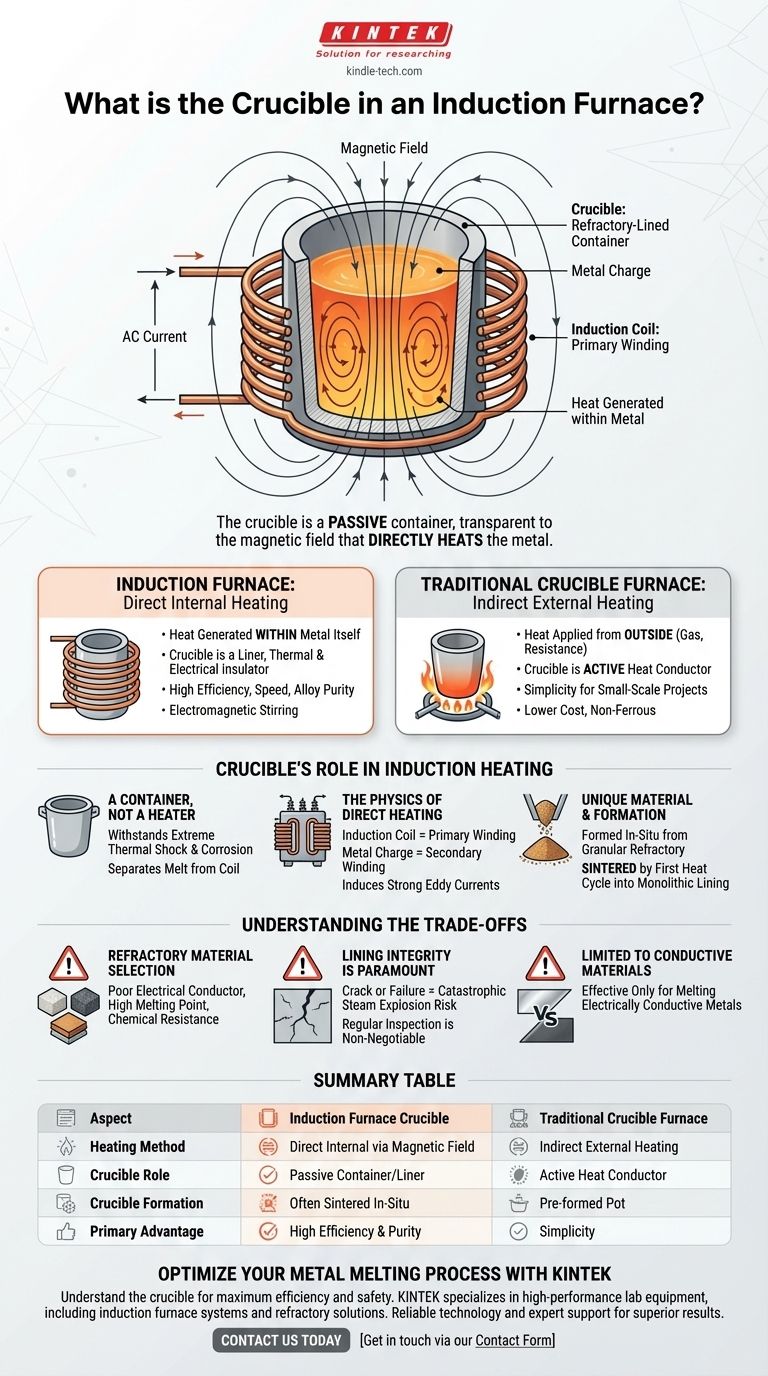
In an induction furnace, the crucible is the refractory-lined container that holds the metal charge to be melted. It is positioned inside the water-cooled induction coil, serving to contain the molten material while remaining transparent to the magnetic field that directly heats the metal.
The critical distinction to understand is that the crucible in an induction furnace is a passive container, not an active heating element. Unlike in a traditional crucible furnace where the pot is heated externally, here the furnace's energy passes through the crucible to heat the metal inside directly.

The Crucible's Role in Induction Heating
The crucible's function is fundamentally different from that of other furnace types. Its design and material are dictated by the physics of induction.
A Container, Not a Heater
The primary job of the crucible is to act as a durable, non-reactive vessel. It must withstand extreme thermal shock and the corrosive action of molten metal while physically separating the melt from the vital induction coil.
The Physics of Direct Heating
An induction furnace operates like a transformer. The main induction coil acts as the primary winding, and the metal charge inside the crucible acts as the secondary winding.
When an AC current flows through the coil, it generates a powerful, alternating magnetic field. This field passes through the crucible and induces strong eddy currents within the metal charge, generating intense heat and causing it to melt.
Unique Material and Formation
Unlike a pre-formed pot, the crucible in many coreless induction furnaces is formed in-situ. A granular refractory material (like silica, alumina, or magnesia) is rammed into the space between the induction coil and an internal template.
During the first heating cycle, this template melts away, and the intense heat sinters the refractory granules into a solid, monolithic lining. This process creates a seamless container perfectly fitted to the furnace.
A Critical Distinction: Induction vs. Crucible Furnaces
A common point of confusion is the difference between an induction furnace and a traditional "crucible furnace." The heating method is the key differentiator.
Induction Furnace: Direct Internal Heating
In an induction furnace, the heat is generated within the metal itself. The crucible is simply a liner that must be a thermal and electrical insulator, allowing the magnetic field to work without being affected.
Crucible Furnace: Indirect External Heating
In a traditional crucible furnace, a pre-made crucible of graphite or ceramic holds the metal. Heat is applied from the outside of this crucible, typically by gas burners or electrical resistance elements. The crucible gets hot first and then transfers its heat to the metal through conduction.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The crucible is a critical component whose properties and maintenance determine the furnace's safety and efficiency.
Refractory Material Selection
The choice of refractory material is crucial. It must be a poor electrical conductor to avoid absorbing energy from the magnetic field. It also needs a high melting point and chemical resistance to the specific alloy being melted.
Lining Integrity is Paramount
The sintered refractory lining is the only thing separating tons of molten metal from the water-cooled copper induction coil. A crack or failure in the lining can lead to a catastrophic steam explosion if the metal reaches the coil. Regular inspection and maintenance are non-negotiable.
Limited to Conductive Materials
Because induction heating relies on generating current within the charge itself, the process is only effective for melting electrically conductive materials, namely metals. The crucible itself is intentionally non-conductive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the crucible's role helps clarify which melting technology suits your application.
- If your primary focus is efficiency, speed, and alloy purity: The induction furnace is superior due to its direct heating, uniform temperature, and electromagnetic stirring action.
- If your primary focus is simplicity for small-scale projects: A traditional gas-fired or resistance-heated crucible furnace can be a viable, lower-cost option for non-ferrous metals.
Ultimately, knowing that the crucible is either a passive liner or an active heat conductor is the key to differentiating modern and traditional melting technologies.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Induction Furnace Crucible | Traditional Crucible Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct internal heating via magnetic field | Indirect external heating |
| Crucible Role | Passive container/liner | Active heat conductor |
| Crucible Formation | Often sintered in-situ from refractory granules | Pre-formed pot (graphite/ceramic) |
| Primary Advantage | High efficiency, purity, and speed | Simplicity for small-scale projects |
Optimize Your Metal Melting Process with KINTEK
Understanding the critical role of the crucible is the first step to maximizing your furnace's efficiency and safety. Whether you are melting ferrous or non-ferrous metals, the right equipment is paramount.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including induction furnace systems and refractory solutions. We provide the reliable technology and expert support your laboratory needs to achieve superior results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your melting operations. Let our experts help you select the perfect equipment for your specific application.
Get in touch via our Contact Form to speak with a specialist!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Tungsten Crucible and Molybdenum Crucible for High Temperature Applications
People Also Ask
- How much heat can a ceramic crucible withstand? A Guide to Material-Specific Temperature Limits
- What is the purpose of using an alumina crucible with a lid for g-C3N4 synthesis? Optimize Your Nanosheet Production
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What precautions should be taken when using a crucible? Essential Steps for Safety and Accuracy



















