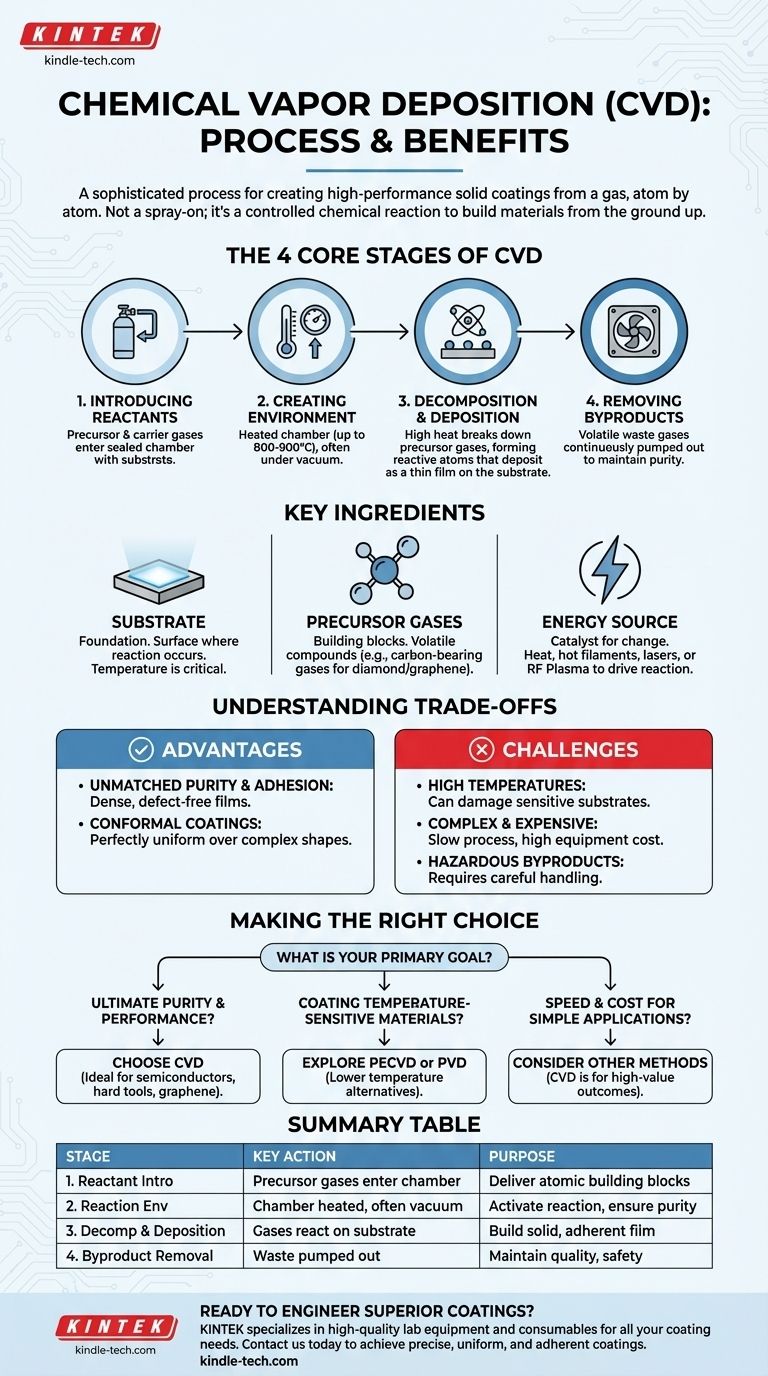
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated process for creating high-performance solid coatings from a gas. It works by introducing volatile precursor gases into a heated chamber containing the object to be coated, known as a substrate. The intense heat triggers a chemical reaction, causing the gases to decompose and deposit a thin, highly pure film of material directly onto the substrate's surface, atom by atom.
CVD is not a simple spray-on application; it is a controlled chemical reaction designed to build a material from the ground up. The process uses a combination of precursor gases, high temperature, and a controlled environment to construct a dense, durable, and highly adherent film on a target surface.
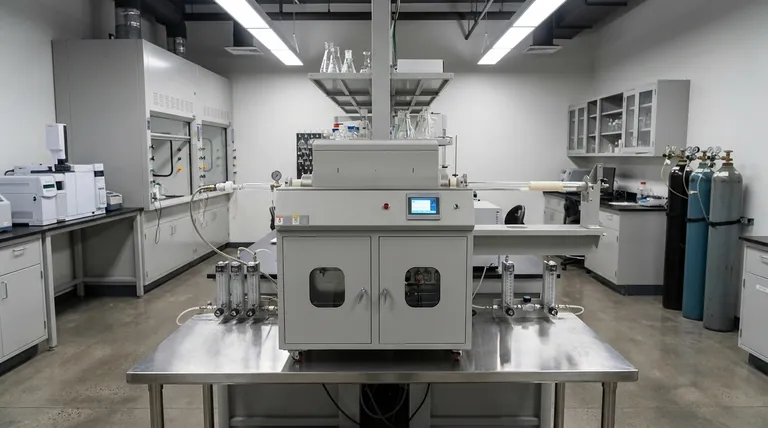

Deconstructing the CVD Process: The Four Core Stages
The CVD process can be understood as a sequence of four fundamental steps, each critical to the formation of a high-quality coating.
Stage 1: Introducing the Reactants
The process begins by placing the substrate—the item to be coated—inside a sealed reaction chamber.
A precise mixture of gases is then introduced. This includes the precursor gases, which contain the atomic building blocks of the final coating, and often an inert carrier gas to help manage the flow and reaction rate.
Stage 2: Creating the Reaction Environment
The chamber is heated to a specific and often very high temperature, sometimes reaching 800-900°C. This temperature is the primary driver of the entire process.
In many cases, the pressure inside the chamber is reduced to create a vacuum. This controlled environment ensures the purity of the reaction and prevents unwanted contaminants from interfering with the coating.
Stage 3: Decomposition and Deposition
The high temperature provides the energy needed to break down, or decompose, the precursor gas molecules into highly reactive atoms, ions, or radicals.
These reactive species then travel to the heated surface of the substrate. A chemical reaction occurs directly on this surface, causing the desired material to form a solid, thin film that bonds strongly to the substrate. The substrate itself often acts as a catalyst for this reaction.
Stage 4: Removing Byproducts
The chemical reactions that form the coating also create unwanted volatile byproducts.
These gaseous waste products are continuously pumped out of the chamber. This step is essential for maintaining the purity of the coating and for safe handling of potentially hazardous exhaust gases.
The Key Ingredients of a Successful CVD Reaction
Three components are absolutely essential for any CVD process: the substrate, the precursor gases, and the energy source that drives the reaction.
The Substrate: The Foundation for the Coating
The substrate is more than just a holder for the new coating; its surface is where the chemical reaction takes place.
The temperature of the substrate is the most critical parameter in the entire process, as it dictates the type of reaction that will occur and the quality of the resulting film.
The Precursor Gases: The Building Blocks
These are volatile chemical compounds that contain the constituent atoms of the material to be deposited.
For example, when creating a diamond film, the chamber is filled with carbon-bearing gases like methane. For graphene, a similar carbon gas is used in the presence of a metal catalyst like copper.
The Energy Source: The Catalyst for Change
Heat is the most common energy source used to activate the chemical reaction. This can be generated using several methods, including hot filaments, lasers, or microwaves.
In some advanced CVD variations, an RF Plasma is used to dissociate the gases at lower temperatures, making it possible to coat materials that cannot withstand extreme heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs of CVD
While powerful, the CVD process involves a series of technical compromises that determine its suitability for a given application.
The Advantage: Unmatched Purity and Adhesion
Because CVD builds a coating atom by atom, the resulting films are exceptionally dense, pure, and highly adherent to the substrate.
The gaseous nature of the process also allows it to create perfectly uniform, or conformal, coatings over complex shapes and geometries, something spray-on methods cannot achieve.
The Challenge: Heat, Complexity, and Cost
The primary limitation of traditional CVD is the extremely high temperature required, which can damage or destroy sensitive substrates like plastics or certain metals.
The equipment is complex and expensive, and the process can be slow, sometimes taking days or weeks to build a sufficiently thick layer. Managing the volatile and often toxic byproduct gases also adds significant safety and environmental overhead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a coating technology depends entirely on balancing the needs of your specific application with the capabilities of the process.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and performance: CVD is the superior choice for creating dense, defect-free films required for semiconductors, hard tool coatings, or advanced materials like graphene.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials: You must explore lower-temperature CVD variations like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) or consider entirely different processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
- If your primary focus is speed and cost for simple applications: Other methods might be more practical, as CVD is a complex and often slow process engineered for high-value, high-performance outcomes.
Ultimately, understanding the CVD process is about recognizing its power to engineer materials from the molecular level, creating coatings with properties unattainable by any other method.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Reactant Introduction | Precursor gases enter the chamber | Deliver the atomic building blocks for the coating |
| 2. Reaction Environment | Chamber is heated, often under vacuum | Activate the chemical reaction and ensure purity |
| 3. Decomposition & Deposition | Gases break down and react on the substrate surface | Build a solid, adherent film atom by atom |
| 4. Byproduct Removal | Gaseous waste is pumped out | Maintain coating quality and handle exhaust safely |
Ready to Engineer Superior Coatings for Your Lab?
The CVD process is the gold standard for creating high-purity, high-performance thin films. If you are developing advanced materials, semiconductor devices, or need durable tool coatings, the right equipment is critical.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your coating needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect system to achieve the precise, uniform, and adherent coatings your research demands.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the challenges of carbon nanotubes? Overcoming Production and Integration Hurdles
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















