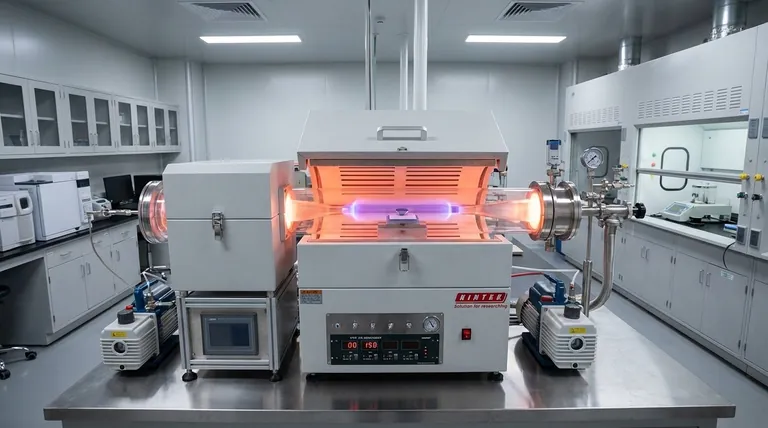
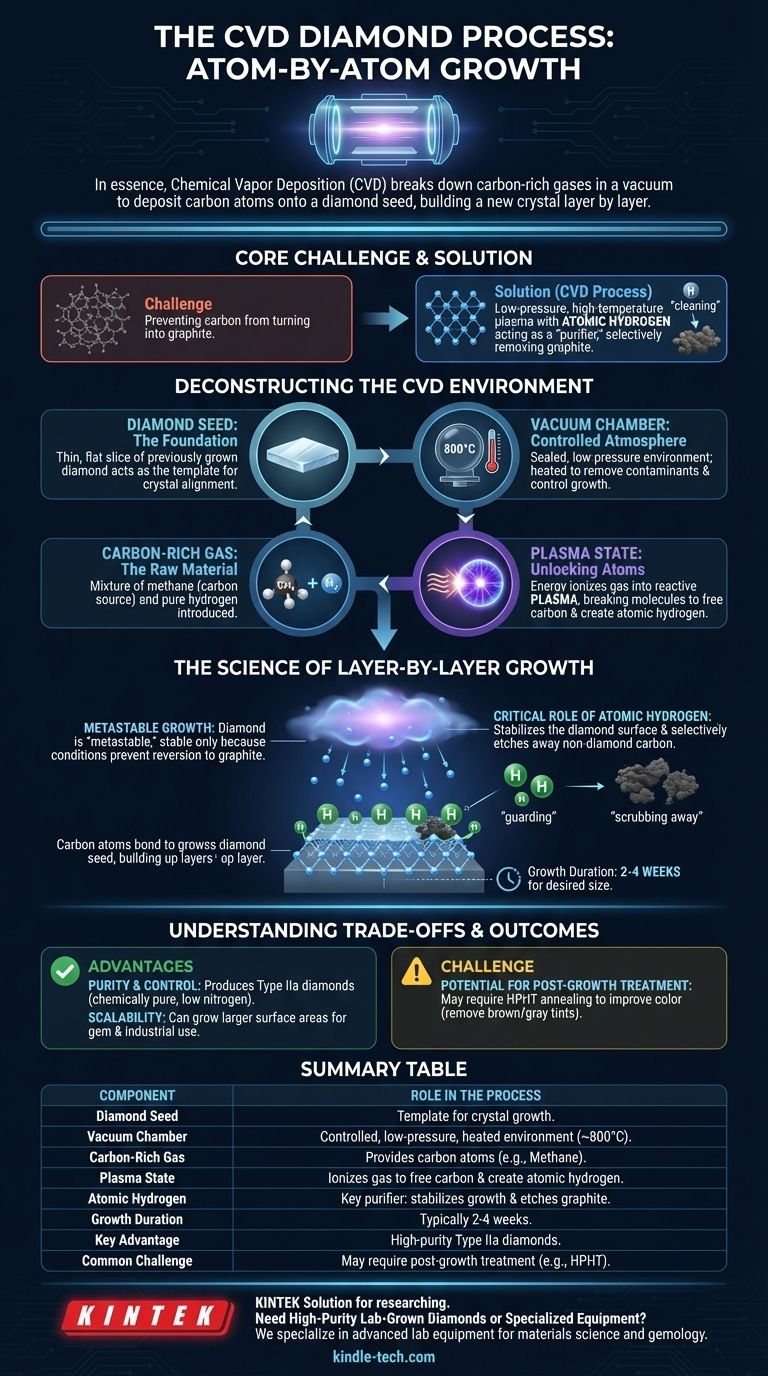
In essence, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process is a method for growing diamonds that involves breaking down carbon-rich gases in a vacuum chamber. Under specific conditions of high heat and low pressure, carbon atoms are released from the gas and deposit onto a diamond "seed," building a new, larger diamond crystal layer by layer over several weeks.
The core challenge of making a diamond is not just sourcing carbon, but preventing it from turning into graphite. The CVD process solves this by using a low-pressure, high-temperature plasma environment where atomic hydrogen acts as a "purifier," selectively removing any graphite and ensuring only the diamond structure can grow.

Deconstructing the CVD Environment
To understand the process, it's best to examine the four critical components that work together to create the diamond.
The Diamond Seed: The Foundation for Growth
The process begins with a diamond seed, which is a very thin, flat slice of a previously grown diamond (either mined or lab-created).
This seed acts as the template. The carbon atoms from the gas will align with the seed's existing crystal lattice, ensuring the new material grows as a diamond.
The Vacuum Chamber: A Controlled Atmosphere
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed, low-pressure vacuum chamber. This chamber is heated to an extremely high temperature, typically around 800°C.
Creating a vacuum is essential to remove any contaminants and to precisely control the atmosphere and pressure required for diamond growth.
The Carbon-Rich Gas: The Raw Material
A mixture of gases, primarily a carbon source like methane (CH₄) and pure hydrogen (H₂), is introduced into the chamber.
Methane provides the carbon atoms that will eventually form the diamond, while the hydrogen plays a a crucial scientific role in the reaction.
The Plasma State: Unlocking Carbon Atoms
Energy, often in the form of microwaves, is used to ionize the gases in the chamber, turning them into a glowing ball of plasma.
In this energized state, the methane and hydrogen molecules break apart. This frees the carbon atoms from the methane and creates reactive atomic hydrogen.
The Science of Layer-by-Layer Growth
The CVD process is a feat of materials science that manipulates carbon at an atomic level. It forces carbon into its diamond structure under conditions where it would normally form graphite.
Metastable Growth: Defying Carbon's Natural State
At the low pressures used in CVD, graphite (the material in pencil lead) is the more stable form of carbon. Diamond growth is therefore metastable, meaning it's stable only because the specific conditions prevent it from reverting to graphite.
The Critical Role of Atomic Hydrogen
This is the key to the entire process. The atomic hydrogen created in the plasma performs two jobs:
- It stabilizes the diamond-growing surface.
- It selectively etches away any non-diamond carbon (graphite) that tries to form.
This continuous "cleaning" action ensures that only the desired diamond crystal structure can build up.
The Deposition Process
The free carbon atoms from the plasma rain down onto the diamond seed. Following the seed's crystal template, they bond to it, slowly building a new diamond, atom by atom and layer by layer. This process continues for two to four weeks until the desired size is reached.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Outcomes
Like any sophisticated technical process, CVD has distinct advantages and challenges that influence the final product.
Advantage: Purity and Control
The CVD process allows for fine control over the growth environment. This makes it particularly effective at producing Type IIa diamonds, which are chemically pure and contain virtually no nitrogen impurities.
Advantage: Scalability
Because it's a deposition process, CVD can be used to grow diamonds over larger surface areas compared to other methods, making it versatile for both gem and industrial applications.
Challenge: Potential for Post-Growth Treatment
While CVD diamonds are very pure, they can sometimes exhibit a brown or gray tint due to structural anomalies during growth. To improve their color, many CVD diamonds undergo a secondary treatment process after they are grown, such as HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature) annealing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the CVD method provides clarity on the origin and properties of the resulting diamond.
- If your primary focus is a distinct technological origin: The CVD process is a marvel of materials science, growing a diamond atom-by-atom from a gas in a way that is fundamentally different from geologic or other lab processes.
- If your primary focus is high chemical purity: CVD is exceptionally good at producing Type IIa diamonds, a category that includes some of the world's most famous and valuable mined diamonds.
- If you are evaluating quality: Know that post-growth treatments are a common and accepted part of the CVD process to enhance a diamond's final color and appearance.
Ultimately, understanding the CVD process reveals that a lab-grown diamond is not a copy, but an achievement of precise chemical engineering.
Summary Table:
| CVD Diamond Growth Component | Role in the Process |
|---|---|
| Diamond Seed | Thin slice of diamond acting as a template for crystal growth. |
| Vacuum Chamber | Sealed, low-pressure environment heated to ~800°C for controlled growth. |
| Carbon-Rich Gas (e.g., Methane) | Provides the carbon atoms that form the diamond structure. |
| Plasma State (via Microwaves) | Ionizes gas to free carbon atoms and create atomic hydrogen for purification. |
| Atomic Hydrogen | Key purifier: stabilizes diamond growth and etches away non-diamond carbon (graphite). |
| Growth Duration | Typically 2-4 weeks for building diamond layers atom by atom. |
| Key Advantage | Produces high-purity Type IIa diamonds with fine control over the growth environment. |
| Common Challenge | May require post-growth treatment (e.g., HPHT annealing) to enhance color. |
Need High-Purity Lab-Grown Diamonds or Specialized Equipment for Your Research?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories in materials science and gemology. Whether you're growing diamonds via CVD or analyzing their properties, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for superior results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's goals with reliable, cutting-edge solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of deposition coatings? Metallic, Ceramic, and Organic Explained
- What is the chemical vapor deposition of parylene? A Guide to Conformal Coating
- What are the methods for preparing graphene? Top-Down vs. Bottom-Up Synthesis Explained
- What is the difference between thick film and thin film? Precision vs. Cost for Your Circuit Design
- What is the vapor phase deposition process? A Guide to CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What is the difference between chemical and physical deposition? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Thin Films
- What are the steps involved in chemical vapour deposition? A Guide to the CVD Process
- What is the effect of temperature on thin film deposition? Master the Key to Film Structure and Performance



















