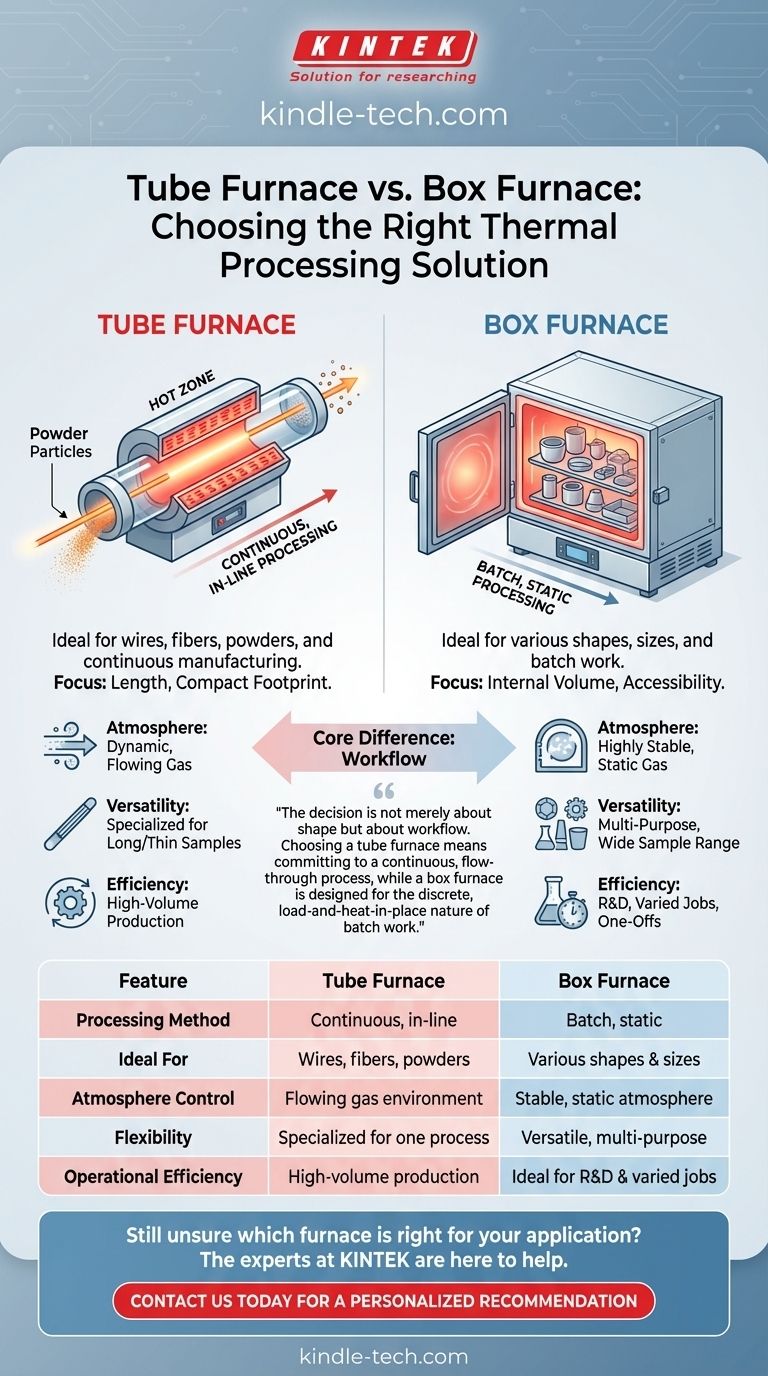
At its core, the difference between a tube furnace and a box furnace comes down to their fundamental design and the type of heating process they enable. A tube furnace heats materials as they pass through a narrow, cylindrical tube, making it ideal for continuous, in-line processes. A box furnace (also known as a chamber or muffle furnace) heats materials placed inside a sealed, static chamber, making it the standard for batch processing.
The decision is not merely about shape but about workflow. Choosing a tube furnace means committing to a continuous, flow-through process, while a box furnace is designed for the discrete, load-and-heat-in-place nature of batch work.

The Fundamental Difference: Processing Method
The most critical distinction lies in how the material is handled during the heating cycle. This single factor influences every other aspect of the furnace's design and application.
Tube Furnaces: Continuous Processing
A tube furnace is built around a central, often ceramic or metal, tube. The heating elements are positioned around the exterior of this tube.
Materials, such as wires, fibers, or powders, are fed through one end of the tube, heated as they travel through the hot zone, and exit the other end. This makes it inherently suited for continuous or in-line manufacturing and analysis.
Box Furnaces: Batch Processing
A box furnace operates like a high-temperature oven. The entire chamber is the heating zone, with elements typically arranged around the interior walls.
Samples are placed inside the chamber on racks or trays, the door is sealed, and the entire batch is heated together in a static environment. Once the process is complete, the chamber is cooled and the batch is removed.
Comparing Key Design and Performance Attributes
Understanding the core processing difference helps clarify the trade-offs in their physical design, atmospheric control, and overall versatility.
Physical Shape and Footprint
Tube furnaces are characteristically long and cylindrical, resulting in a more compact and narrow footprint. They are designed for length, not volume.
Box furnaces are rectangular and require more floor space to accommodate their larger internal chamber and insulated door. Their design prioritizes internal volume and accessibility.
Atmosphere Control and Stability
In a tube furnace, a specific atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) can be flowed through the tube along with the sample. This is excellent for processes that require a dynamic, flowing gas environment.
A box furnace, being a sealed chamber, excels at creating a highly stable and uniform static atmosphere. Once purged and sealed, the internal environment remains consistent throughout the heating cycle, which is critical for many sensitive treatments.
Heating Uniformity
Box furnaces generally provide superior static temperature uniformity across a large volume, as the sample does not move and is surrounded by heating elements.
In a tube furnace, uniformity is measured along the length of the central "hot zone." There will be a temperature gradient as the material enters and exits the furnace.
Sample Versatility
Tube furnaces are highly specialized. They are best for long, thin, or powdered materials that can be easily passed through a tube, such as shafts, strips, or materials for calcination.
Box furnaces are the versatile "workhorses" of the lab. Their open chamber can accommodate a wide variety of sample sizes and shapes, from small crucibles to large, bulky components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these two designs involves balancing cost, efficiency, and flexibility for your specific application.
Flexibility vs. Specialization
The primary trade-off is versatility. A box furnace can handle countless different jobs, making it a staple in research and development or job shops with varied needs.
A tube furnace is a specialist's tool, optimized for one type of continuous process. It performs that one task with exceptional efficiency but lacks the flexibility of a box furnace.
Operational Efficiency
For high-volume production of a single product, a continuous tube furnace is more efficient. It eliminates the need for racks or baskets and reduces energy waste from repeated heating and cooling cycles typical of batch work.
Batch processing in a box furnace requires more hands-on work for loading and unloading. It is less energy-efficient for continuous production but ideal for one-off jobs or process development.
Cost and Complexity
Generally, box furnaces are less complex systems, making them easier to maintain and often less expensive for a given volume.
Continuous tube furnace systems can be more complex, especially when integrated into an automated production line. This can lead to higher initial investment and maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, focus on the nature of your process and material, not just the temperature you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of uniform materials (wires, fibers, powders): A tube furnace is purpose-built for your in-line process.
- If your primary focus is versatile, multi-purpose heat treatment for various sample sizes and shapes: A box furnace offers the essential flexibility you need.
- If your primary focus is a process requiring a highly stable, uniform, and static gas atmosphere: A sealed box furnace provides superior environmental control.
- If your primary focus is research involving long, thin samples or simulating an in-line process on a small scale: A laboratory tube furnace is the ideal choice.
Ultimately, your choice is determined by whether your material needs to take a continuous journey through heat or rest at a discrete, controlled destination.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Box Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Method | Continuous, in-line | Batch, static |
| Ideal For | Wires, fibers, powders | Various shapes & sizes |
| Atmosphere Control | Flowing gas environment | Stable, static atmosphere |
| Flexibility | Specialized for one process | Versatile, multi-purpose |
| Operational Efficiency | High-volume production | Ideal for R&D & varied jobs |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the perfect lab equipment solutions for your specific thermal processing needs, whether you require the continuous flow of a tube furnace or the versatile batch processing of a box furnace.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a personalized recommendation to enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular RTP Heating Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What are the tubes in a furnace called? Understanding the Role of the Working Tube
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















