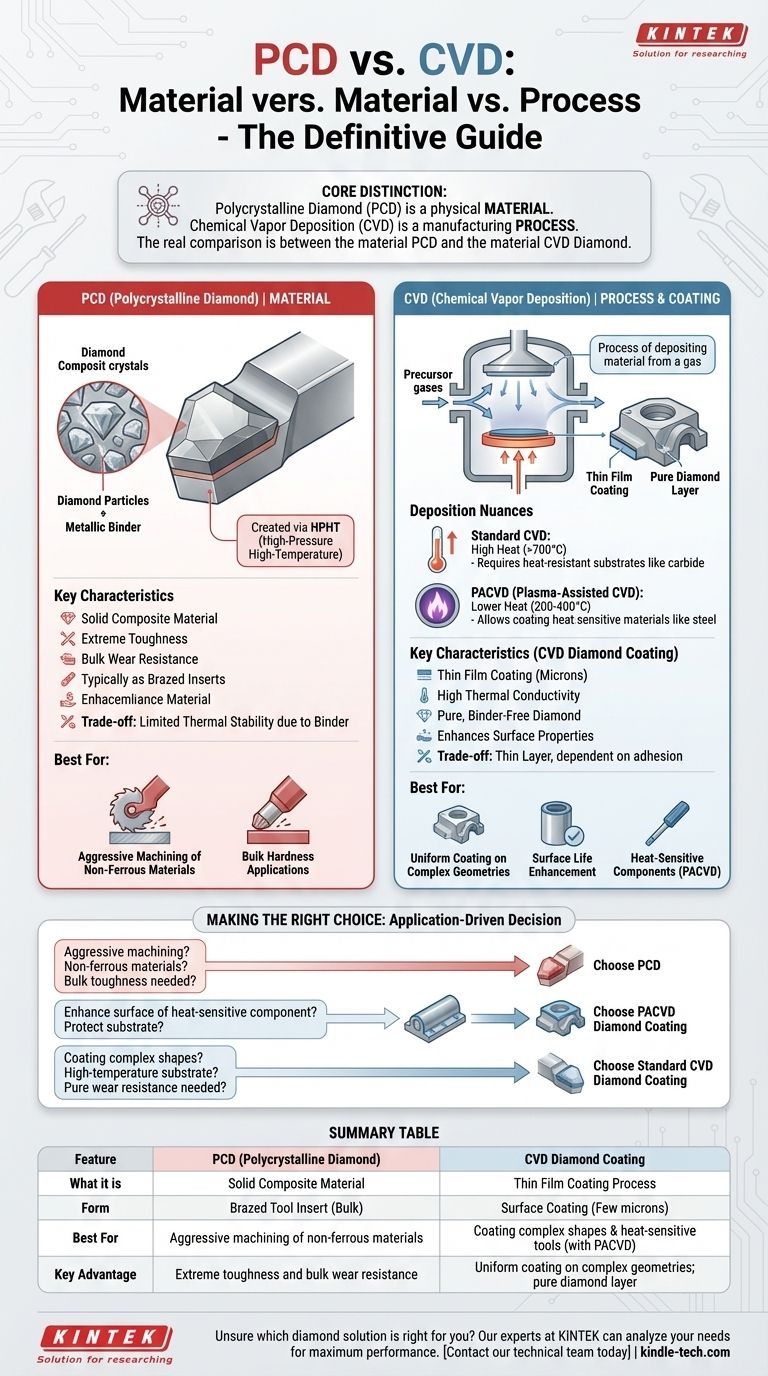
To be clear, the primary difference is that Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) is a physical material, while Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a manufacturing process. PCD is a composite of diamond particles fused together under high pressure and temperature. CVD, on the other hand, is a technique used to grow a thin film of material—which can include diamond—onto a surface from a gas.
The core distinction is not between a material (PCD) and a process (CVD), but between different types of materials and the processes used to create or apply them. Your choice depends entirely on whether you need a solid tool insert or a thin, hard coating on an existing component.

Defining the Core Concepts
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the fundamental nature of both PCD and CVD. They are not direct alternatives but represent different solutions to different engineering problems.
What is PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond)?
PCD is a composite material. It consists of microscopic, man-made diamond crystals that are sintered and bonded together, typically with a metallic binder like cobalt.
This process, known as High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT), creates an extremely hard and wear-resistant solid material. PCD is most often produced in the form of blanks or discs, which are then cut and brazed onto tool bodies for applications like cutting, machining, and grinding non-ferrous materials.
What is CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition)?
CVD is a process, not a material. It involves introducing precursor gases into a vacuum chamber containing the part to be coated (the substrate).
High heat causes these gases to react or decompose, depositing a thin, highly adherent solid film onto the substrate. This technique can be used to deposit many materials, including silicon nitride, tungsten carbide, and even a very pure form of diamond known as CVD Diamond.
The Real Comparison: PCD vs. CVD Diamond
The more accurate comparison is between the material PCD and the material CVD Diamond. PCD is a composite with a metallic binder, making it very tough but limiting its thermal stability. CVD Diamond is a pure, binder-free diamond film, giving it higher thermal conductivity and wear resistance in certain applications, but it exists only as a coating.
How the Deposition Process Impacts Your Choice
Understanding the nuances of the deposition process itself is critical, as it dictates what materials can be coated. This is where process variations like PACVD become important.
The Role of Heat in Standard CVD
Traditional thermal CVD processes require very high temperatures (often >700°C) to provide the energy needed to break down the precursor gases and initiate the coating reaction on the substrate's surface.
This high heat requirement means standard CVD can only be used on substrates that can withstand these temperatures without deforming, melting, or losing their structural properties, such as carbide tools or ceramics.
The PACVD Advantage: Lower Temperatures
Plasma-Assisted CVD (PACVD) is a variation of the CVD process. Instead of relying solely on heat, it uses an electric field to generate a plasma within the chamber.
This plasma energizes the precursor gases, creating reactive radicals that can form a coating at much lower temperatures (typically 200-400°C). As the provided reference correctly notes, this allows for coating heat-sensitive materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a solid PCD tool and a CVD-coated tool involves significant trade-offs in application, cost, and performance.
Solid Material vs. Thin Coating
The most fundamental trade-off is form. PCD is typically used as a solid, brazed insert or tool tip, often several millimeters thick. It provides bulk hardness and is suitable for aggressive material removal.
A CVD diamond film is a coating, usually only a few microns thick. It enhances the surface properties of an existing tool but does not change its bulk characteristics. The tool's performance is dependent on the coating's adhesion to the substrate.
Substrate Limitations
With PCD, the primary concern is brazing the insert onto the tool body without damaging either component. The tool itself is the PCD.
With CVD, the process is defined by the substrate. The high heat of standard CVD limits its use to materials like tungsten carbide. The lower heat of PACVD expands the possibilities to include steels and other alloys that would be damaged by higher temperatures.
Application Geometry
CVD processes excel at applying a uniform, thin coating over complex shapes and geometries, something that is impossible to achieve by brazing a solid PCD insert.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is aggressive machining of non-ferrous materials: A solid PCD tool insert is the industry standard, offering exceptional toughness and wear resistance in a bulk form.
- If your primary focus is applying a hard, wear-resistant diamond layer to a heat-sensitive component: A low-temperature PACVD process is the only viable option to deposit the coating without damaging the underlying substrate.
- If your primary focus is enhancing the surface life of a complex-shaped tool made from a high-temperature material: A standard thermal CVD diamond coating will provide a pure, highly wear-resistant surface.
Ultimately, your success hinges on correctly identifying whether your problem requires a new bulk material or an enhanced surface.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PCD (Polycrystalline Diamond) | CVD Diamond Coating |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | A solid composite material | A thin film coating process |
| Form | Brazed tool insert (bulk) | Surface coating (few microns) |
| Best For | Aggressive machining of non-ferrous materials | Coating complex shapes & heat-sensitive tools (with PACVD) |
| Key Advantage | Extreme toughness and bulk wear resistance | Uniform coating on complex geometries; pure diamond layer |
Unsure whether your application needs a solid PCD tool or a CVD diamond coating?
Our experts at KINTEK specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced tooling solutions. We can help you analyze your specific needs—whether it's aggressive machining or surface enhancement—and recommend the optimal diamond solution for maximum performance and cost-efficiency.
Contact our technical team today to discuss your project and discover how our expertise can improve your tool life and productivity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- How do nanotubes affect the environment? Balancing Low Carbon Footprint with Ecological Risks
- What are nanotubes drawbacks? The 4 Major Hurdles Limiting Their Real-World Use
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















