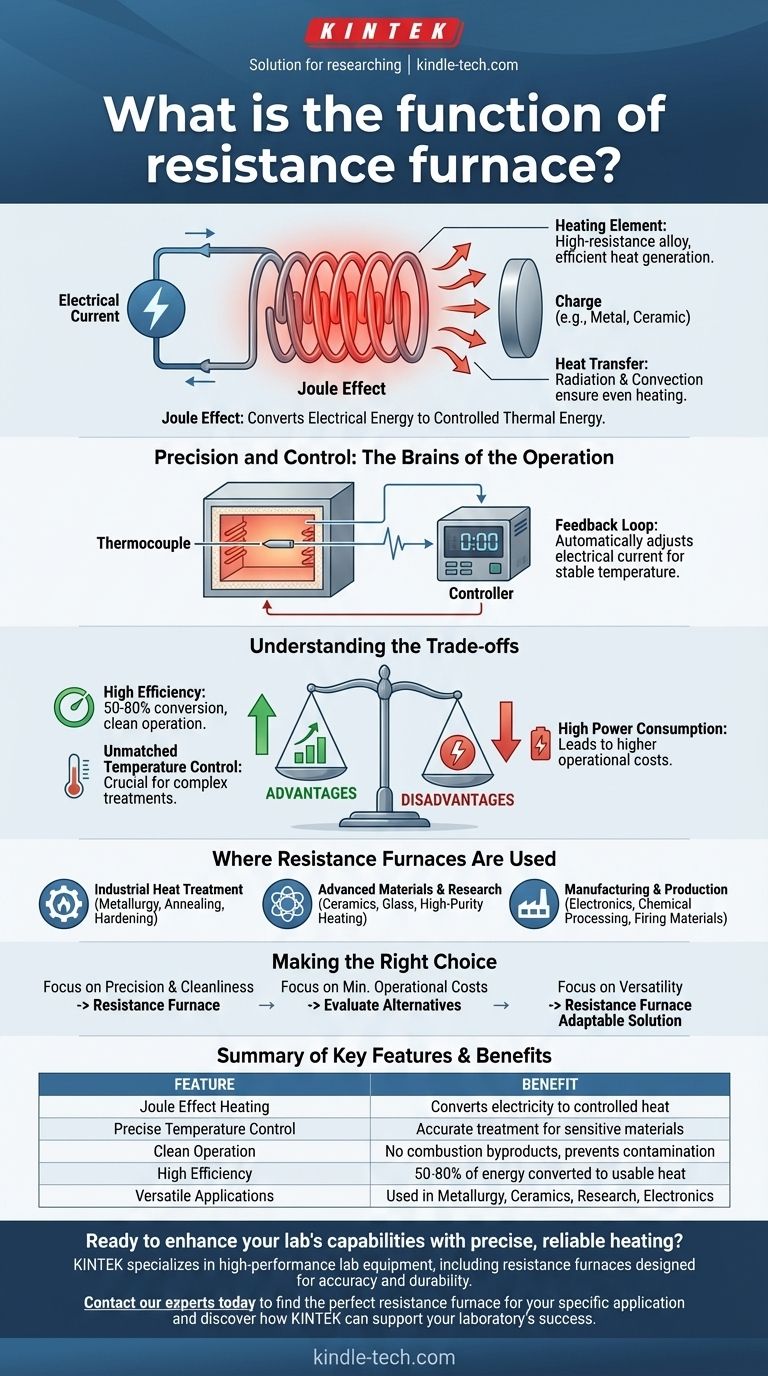
At its core, the function of a resistance furnace is to generate heat by passing an electric current through a material with high electrical resistance. This principle, known as the Joule effect, converts electrical energy into controlled thermal energy. This heat is then transferred to a workpiece to perform industrial processes like heat treatment, material testing, or manufacturing.
A resistance furnace is more than a simple oven; it is a precision instrument designed to create a clean, highly controllable heating environment. Its primary function is to deliver precise thermal energy for applications where temperature accuracy and consistency are critical.

The Fundamental Principle: How a Resistance Furnace Works
A resistance furnace operates on a simple yet powerful electrical principle. Understanding this mechanism is key to appreciating its role in modern industry.
The Joule Effect: Converting Electricity to Heat
The entire function is based on Joule heating. When an electric current flows through a conductor, it encounters resistance. This opposition to the flow of electricity forces the electrical energy to convert into heat energy.
The Heating Element
The furnace uses specialized components called heating elements, or resistors. These are typically made from high-temperature-resistant alloys designed to efficiently generate heat without degrading.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms
Once the heating elements are hot, they transfer their thermal energy to the material inside the furnace (the "charge"). This happens primarily through two methods: radiation and convection, ensuring the workpiece is heated evenly.
Precision and Control: The Brains of the Operation
The defining feature of a modern resistance furnace is its ability to precisely manage temperature. This control is what makes it suitable for demanding applications.
Sensing the Temperature
A thermocouple acts as the furnace's nerve ending. It is a sensor that accurately measures the temperature inside the furnace chamber and sends this information as an electrical signal.
The Controller's Role
This signal is sent to a controller, which compares the actual temperature to the desired setpoint or temperature curve.
Achieving Automatic Adjustment
If the temperature deviates from the setpoint, the controller automatically adjusts the amount of electrical current flowing to the heating elements. This feedback loop allows for incredibly stable and precise temperature management.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technology, resistance furnaces have distinct advantages and limitations that determine their suitability for a given task.
The Advantage: High Efficiency and Clean Operation
Resistance furnaces are highly efficient, converting between 50% and 80% of the electrical energy directly into usable heat. They produce no combustion byproducts, resulting in a clean working environment and preventing contamination of the heated material.
The Advantage: Unmatched Temperature Control
The sophisticated control system allows for exceptional accuracy. This is crucial for complex heat treatments or when working with sensitive materials that have narrow processing windows.
The Disadvantage: High Power Consumption
The primary drawback is their reliance on electricity, which can lead to high operational costs. Their significant power consumption is a critical factor to consider in large-scale industrial applications.
Where Resistance Furnaces Are Used
The combination of precision, cleanliness, and versatility makes resistance furnaces essential tools across a wide range of industries.
Industrial Heat Treatment
They are widely used in metallurgy for processes like annealing, hardening, and tempering metals, where precise temperature profiles are required to achieve specific material properties.
Advanced Materials and Research
In laboratories and specialized manufacturing, they are used for developing and processing ceramics, glass, refractories, and other advanced materials that require high-purity heating.
Manufacturing and Production
Resistance furnaces are integral to the production of electronic components, chemical processing, and the firing of building materials where consistent quality is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your process priorities.
- If your primary focus is precision and process cleanliness: A resistance furnace is the ideal choice due to its superior temperature control and the absence of combustion byproducts.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational energy costs: The high power consumption is a key consideration, and you may need to evaluate alternatives if process precision is less critical.
- If your primary focus is versatility: The wide applicability of resistance furnaces across metallurgy, ceramics, and research makes them a highly adaptable solution for diverse heating needs.
Ultimately, a resistance furnace provides a powerful combination of control and efficiency for any process that demands precise thermal energy.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Joule Effect Heating | Converts electricity directly into controlled thermal energy. |
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables accurate heat treatment for sensitive materials. |
| Clean Operation | No combustion byproducts, preventing material contamination. |
| High Efficiency | 50-80% of electrical energy is converted to usable heat. |
| Versatile Applications | Used in metallurgy, ceramics, research, and electronics manufacturing. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precise, reliable heating?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including resistance furnaces designed for accuracy and durability. Whether you're in materials science, quality control, or R&D, our solutions ensure your thermal processes are efficient and contamination-free.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect resistance furnace for your specific application and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















