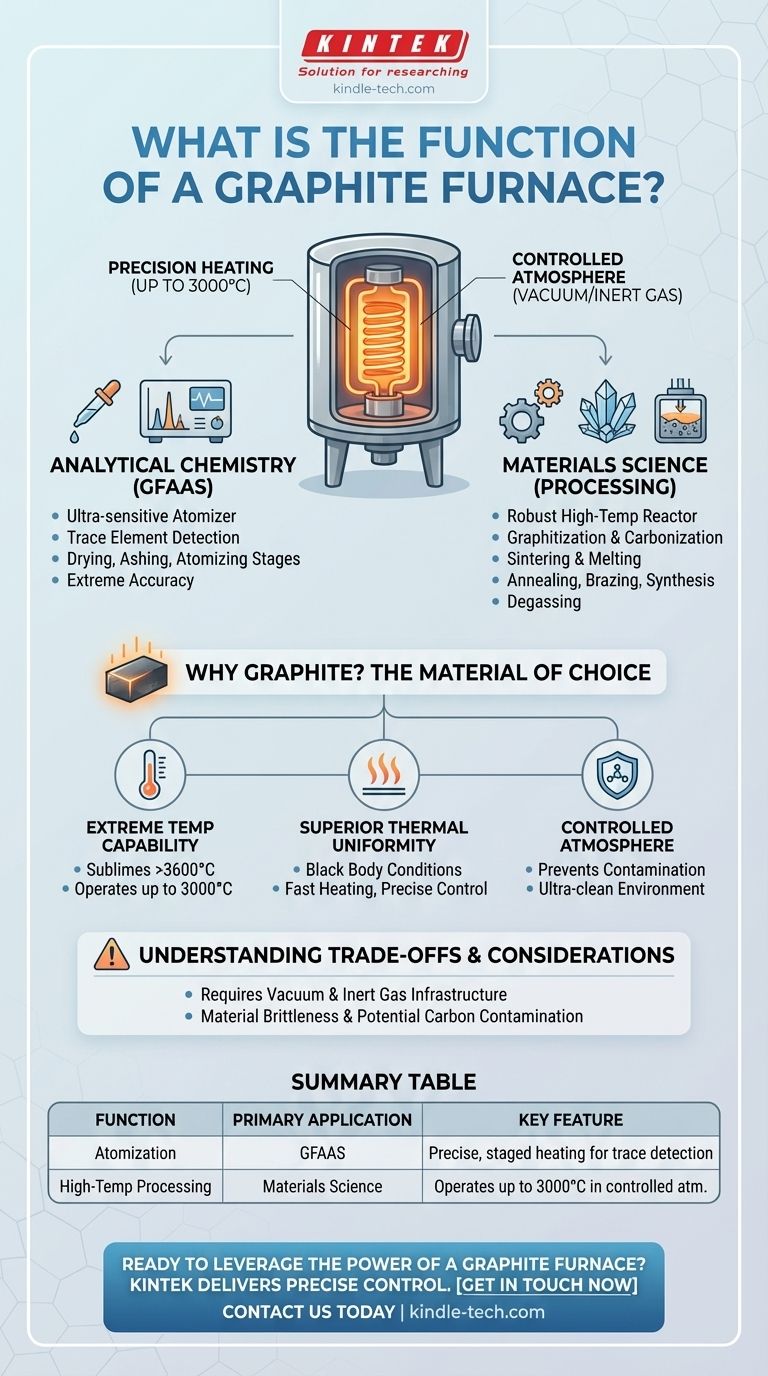
The primary function of a graphite furnace is to serve two distinct but equally critical roles: it is an ultra-sensitive atomizer for chemical analysis and a robust, high-temperature reactor for advanced materials processing. In both applications, it leverages the unique thermal and physical properties of graphite to create a precisely controlled environment that can reach extreme temperatures, often up to 3000°C.
The core value of a graphite furnace lies in its ability to achieve superior temperature uniformity and control within a vacuum or inert atmosphere. This combination is essential for tasks that are highly sensitive to thermal variation and atmospheric contamination, from measuring trace elements to synthesizing next-generation materials.

The Two Core Applications
A graphite furnace is not a single-purpose tool. Its function is best understood through its two primary fields of use: analytical chemistry and materials science.
Elemental Analysis (GFAAS)
The furnace is a key component in Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS), a technique used to measure the concentration of specific elements in a sample.
In this role, the furnace's function is to receive a tiny liquid sample and heat it in a series of controlled stages to dry, ash, and finally atomize it. This process converts the elements into a cloud of free atoms, which can then be measured with extreme accuracy.
High-Temperature Materials Processing
The furnace also functions as a self-contained reactor for creating and treating materials at temperatures far beyond the capability of conventional furnaces.
Common applications include:
- Graphitization & Carbonization: Converting precursors into crystalline graphite or carbon materials.
- Sintering & Melting: Fusing powders into a solid mass or melting metals and ceramics.
- Annealing & Brazing: Heat-treating materials to alter their properties or joining components.
- Growth & Synthesis: Creating novel materials like graphene, carbon nanotubes, and specific carbides.
- Degassing: Removing trapped gases from components, a critical step in creating vacuum-tight parts.
Why Graphite is the Material of Choice
The design of these furnaces centers entirely on the properties of graphite, which serves as the heating elements, the insulation shielding, and the chamber itself.
Extreme Temperature Capability
Graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure; it sublimes at over 3600°C. This allows furnaces built from it to operate reliably at temperatures up to 3000°C, a range needed for processing refractory metals and advanced ceramics.
Superior Thermal Uniformity
Graphite creates near-perfect black body conditions (emissivity of ~1.0) inside the heating chamber. This means heat is radiated and absorbed with exceptional uniformity, eliminating hot spots and ensuring the entire workload is heated evenly.
This property, combined with its low thermal mass, enables fast heating speeds and precise temperature control.
Controlled Atmosphere Operation
Graphite readily oxidizes (burns) in air at high temperatures. Therefore, these furnaces are designed to operate under a vacuum or a protective inert gas like argon.
While this is a technical necessity, it is also a major advantage, as it creates an ultra-clean environment that prevents contamination and unwanted chemical reactions in the processed material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a graphite furnace has specific operational requirements that must be considered.
The Absolute Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Operating a graphite furnace is not as simple as plugging it in. It requires a robust vacuum system and a reliable supply of high-purity inert gas. This adds complexity and cost compared to furnaces that can operate in ambient air.
Material Brittleness
While strong at high temperatures, graphite components can be brittle and susceptible to mechanical shock at room temperature. Careful handling during loading, unloading, and maintenance is essential to prevent cracking.
Potential for Carbon Contamination
For certain highly sensitive applications, the furnace's all-graphite hot zone can be a source of carbon contamination. While often negligible, this is a critical consideration for processing materials where carbon is an undesirable impurity. Sacrificial layers are sometimes used to mitigate this.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a graphite furnace depends entirely on your specific technical objective.
- If your primary focus is quantifying trace elements: The graphite furnace is your tool for achieving the lowest possible detection limits in Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy.
- If your primary focus is creating or treating high-performance materials: A graphite furnace provides the unmatched temperature and atmospheric control required for sintering, graphitizing, and synthesizing advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose high-temperature research: The graphite furnace is a versatile workhorse, provided you can manage its mandatory vacuum and inert gas infrastructure.
Understanding these core functions and properties allows you to leverage the graphite furnace for the most demanding thermal applications.
Summary Table:
| Function | Primary Application | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Atomization | Graphite Furnace AAS (GFAAS) | Precise, staged heating for trace element detection |
| High-Temp Processing | Materials Science (Sintering, Graphitization) | Operates up to 3000°C in a controlled atmosphere |
Ready to leverage the power of a graphite furnace in your lab?
Whether your goal is achieving the lowest detection limits in elemental analysis or pushing the boundaries of materials synthesis, KINTEK's graphite furnaces deliver the precise temperature control and uniform heating you need. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get a solution tailored for high-performance applications like GFAAS, sintering, and graphitization.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK graphite furnace can enhance your research and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why graphite is used in furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Treatment & Energy Efficiency
- What are the applications of graphite material? Leveraging Extreme Heat and Precision for Industrial Processes
- What temperature can graphite withstand? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- What are the advantages of graphite? Unlock Superior Performance in High-Temperature Processes
- Does graphite have a melting point? Unlocking the Extreme Heat Resistance of Graphite



















