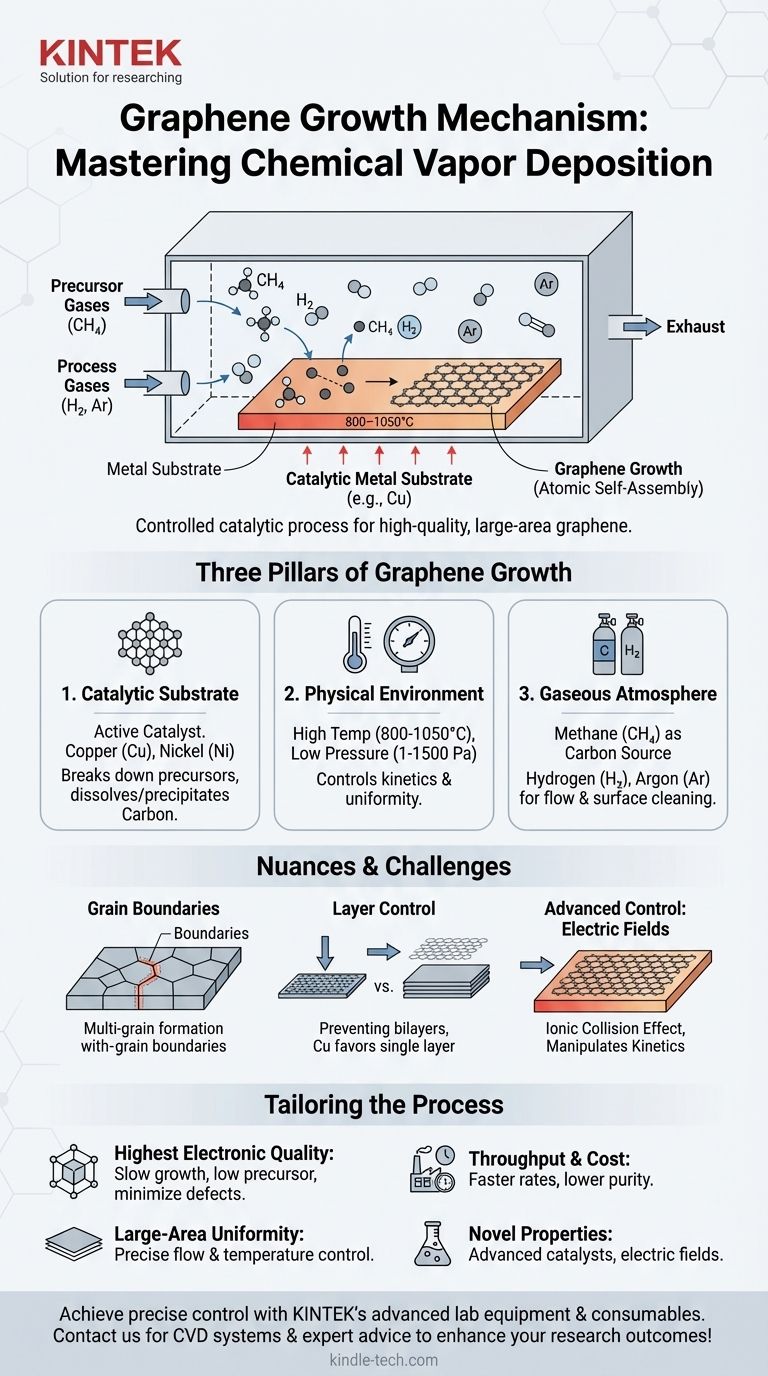
At its core, the most common growth mechanism for high-quality, large-area graphene is a process called Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This method involves exposing a heated catalytic metal substrate, typically copper, to a carbon-containing gas, which decomposes on the hot surface and allows carbon atoms to self-assemble into a single atomic layer.
The growth of graphene is not a simple deposition, but a controlled catalytic process. Success depends on the precise orchestration of a metal catalyst, specific physical conditions like temperature and pressure, and a carefully managed gas atmosphere.

The Foundation: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a cornerstone technique for producing high-purity, high-performance thin films. Think of it as a highly controlled "spray painting" process, but at the atomic level.
In this process, reactive gases (precursors) are passed over a heated substrate. The heat provides the energy for chemical reactions to occur, causing a solid material to deposit onto the substrate surface, forming a film.
The Three Pillars of Graphene Growth
For graphene CVD, this process is refined into a delicate balance of three critical components. The quality, number of layers, and uniformity of the resulting graphene sheet are all direct functions of how these variables are controlled.
The Catalytic Substrate: The Template for Growth
The substrate is not merely a surface to grow on; it is an active catalyst in the reaction. Transition metals like copper (Cu) and nickel (Ni) are widely used.
These metals are effective because they can efficiently break down carbon-containing precursor gases (like methane, CH₄) at high temperatures. The carbon atoms then adsorb onto or dissolve into the metal surface.
Upon cooling, the solubility of carbon in the metal decreases, forcing the carbon atoms to precipitate out onto the surface, where they arrange themselves into the stable, hexagonal lattice structure of graphene.
The Physical Environment: Temperature and Pressure
The conditions inside the CVD chamber are paramount. Even small deviations can dramatically alter the outcome.
High temperatures, typically between 800°C and 1050°C, are required. This thermal energy is necessary to decompose the precursor gas and give the carbon atoms enough mobility on the metal surface to find their ideal positions in the graphene lattice.
Most systems use low-pressure environments (LPCVD), ranging from 1 to 1500 Pa. Low pressure increases the mean free path of gas molecules, preventing them from clumping together in the gas phase and ensuring they deposit more uniformly onto the substrate. This is key to achieving a continuous, single-layer film.
The Gaseous Atmosphere: Precursors and Carrier Gases
The atmosphere inside the chamber consists of two main types of gas.
First is the carbon precursor, most commonly methane (CH₄). Its concentration is kept very low to control the growth rate and prevent the formation of multiple graphene layers.
Second are the carrier and process gases, such as Argon (Ar) and Hydrogen (H₂). Argon acts as an inert gas to maintain pressure and control the flow dynamics. Hydrogen plays a dual role: it helps keep the catalyst surface clean by reducing any native metal oxides and can also etch away weakly bonded or poorly formed carbon, improving the overall quality of the graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While powerful, the CVD process is not without its challenges. The final quality is extremely sensitive to the interplay of all variables.
Grain Boundaries and Defects
Graphene growth doesn't start as one single sheet. It begins at multiple nucleation sites across the copper foil and grows outwards in "islands" or "grains." Where these grains meet, imperfections known as grain boundaries are formed. These boundaries can degrade the electrical and mechanical properties of the sheet.
Controlling Layer Number
Preventing the growth of bilayer or multilayer patches is a constant challenge. If the carbon precursor concentration is too high or the cooling rate is too fast, excess carbon can precipitate, forming undesirable extra layers. Copper is favored for single-layer growth due to the very low solubility of carbon in it.
Advanced Control: The Role of Electric Fields
To gain finer control over the growth process, researchers sometimes apply an external electric field inside the CVD chamber. This advanced technique can influence the plasma environment, accelerating ions toward the substrate.
This "ionic collision effect" can alter the surface chemistry and nucleation density, providing another lever to manipulate the growth rate and potentially the final grain structure of the graphene film.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the growth mechanism allows you to tailor the process to your specific objective. The ideal parameters are not universal; they depend on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is the highest electronic quality: Prioritize slow growth rates and low carbon precursor concentrations to minimize defects and grain boundaries.
- If your primary focus is large-area uniformity: Invest in a CVD system with precise control over gas flow dynamics, pressure stability, and temperature homogeneity across the entire substrate.
- If your primary focus is throughput and cost-effectiveness: You may need to accept a trade-off in quality, using faster growth rates and potentially lower-purity precursors.
- If your primary focus is exploring novel properties: Consider advanced techniques like using different metal alloys as catalysts or applying electric fields to manipulate the growth kinetics.
Ultimately, mastering graphene growth is an exercise in precisely controlling a complex, multiphysics system to guide atomic self-assembly.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in Graphene Growth | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Catalytic Substrate | Template for carbon atom arrangement | Copper (Cu), Nickel (Ni) |
| Physical Environment | Controls reaction kinetics and uniformity | Temperature (800-1050°C), Low Pressure (1-1500 Pa) |
| Gaseous Atmosphere | Provides carbon source and surface conditioning | Methane (CH₄), Hydrogen (H₂), Argon (Ar) |
Ready to achieve precise control over your graphene synthesis? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for materials science research. Whether you need a reliable CVD system for high-quality graphene or expert advice on optimizing growth parameters for your specific application, our team is here to support your laboratory's innovation. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- How is PECVD different from CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the precursor gas in PECVD? The Key to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD over CVD? Achieve High-Quality Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- Why is PECVD better than CVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
















