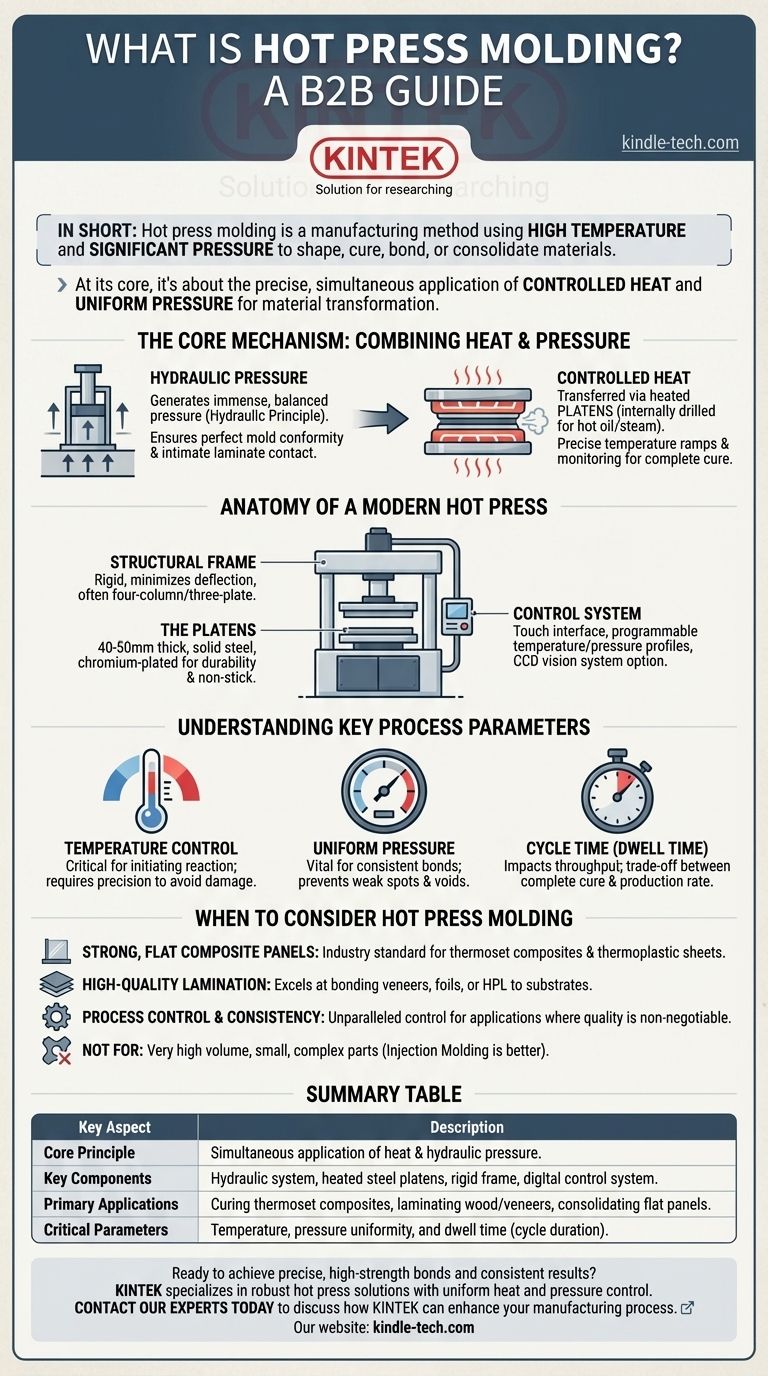
In short, hot press molding is a manufacturing method that uses a combination of high temperature and significant pressure to shape, cure, bond, or consolidate materials. The process involves placing a material into a press, where heated plates, known as platens, close and apply hydraulic force for a set duration to achieve the desired material transformation.
At its core, hot press molding is about the precise, simultaneous application of controlled heat and uniform pressure. This combination is what activates chemical reactions (like curing thermoset resins) or physically consolidates materials (like laminating wood or creating composite panels).

The Core Mechanism: Combining Heat and Pressure
The effectiveness of hot press molding hinges on the interplay between its two fundamental forces: thermal energy and mechanical pressure.
The Role of Hydraulic Pressure
A hot press machine utilizes the hydraulic principle to generate immense and, critically, balanced pressure. This is typically achieved with one or more hydraulic cylinders housed in the base of the machine.
This high pressure ensures that materials conform perfectly to a mold or that layers in a laminate achieve intimate contact, eliminating voids and ensuring a strong, uniform bond. Modern systems can actively monitor and replenish pressure, compensating for any losses during the cycle.
The Role of Controlled Heat
Heat is transferred to the material through large, thick steel plates called platens. These platens are internally drilled with channels that allow a heating medium, such as hot oil or steam, to circulate.
Modern presses employ sophisticated pulse heating technology and multi-stage temperature controls. This allows for precise temperature ramps and real-time monitoring, which is essential for preventing material degradation and ensuring a complete cure or bond.
Anatomy of a Modern Hot Press
While the principle is straightforward, modern hot press machines are precision instruments designed for repeatability and quality control.
The Structural Frame
The machine's rigidity is paramount for applying uniform pressure. A common design is the four-column and three-plate structure, which connects the machine's head to its base. This robust frame minimizes deflection under load, ensuring the platens remain parallel and the pressure is distributed evenly across the part.
The Platens: The Heart of the Press
The platens do more than just get hot. They are typically 40-50 mm thick and made of solid steel to resist warping.
After being ground perfectly flat, their surfaces are often chromium-plated. This serves two purposes: it creates a hard, durable surface and prevents materials like glue or resin from sticking, which simplifies part removal and cleanup.
The Control System
The "brains" of a modern press are found in its control system. A touch-operated interface allows operators to select pre-stored programs or create new ones.
Key programmable parameters include multi-stage temperature profiles, pressure levels, and cycle duration (dwell time). For high-precision applications, a CCD vision system may be integrated to ensure perfect alignment of materials before the press cycle begins.
Understanding the Key Process Parameters
Success with hot press molding requires managing the trade-offs between temperature, pressure, and time. Getting one of these wrong can compromise the final part.
Temperature Control is Critical
The temperature must be high enough to initiate the desired reaction (e.g., curing a resin) but not so high that it damages the material. An uneven temperature across the platen can lead to inconsistent curing and internal stresses in the part.
Pressure Must Be Uniform
The primary goal of the hydraulic system is to deliver uniform pressure. If pressure is higher in the center than at the edges, for example, a laminated panel may have weak bonds or voids near its perimeter.
Cycle Time Impacts Throughput
The amount of time the material spends under heat and pressure, known as dwell time, is a critical variable. While a longer cycle may ensure a more complete cure, it directly reduces the production rate. This trade-off between quality and throughput is a central consideration in manufacturing.
When to Consider Hot Press Molding
Choosing the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your material, part geometry, and production goals.
- If your primary focus is producing strong, flat composite panels: Hot pressing is the industry standard for curing thermoset composites and consolidating thermoplastic sheets.
- If your primary focus is high-quality lamination: The process excels at bonding decorative veneers, foils, or high-pressure laminates to substrates like MDF or particleboard.
- If your primary focus is part complexity and very high volume: Hot pressing is generally best for simpler, often flatter geometries; for small, complex parts in the millions, injection molding is typically a better fit.
- If your primary focus is process control and consistency: Modern hot presses offer unparalleled control over temperature and pressure, making them ideal for applications where quality and repeatability are non-negotiable.
Ultimately, hot press molding is a powerful and reliable process for creating robust parts and bonded structures through the controlled application of heat and force.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Simultaneous application of heat and hydraulic pressure to shape or bond materials. |
| Key Components | Hydraulic system, heated steel platens, rigid frame (e.g., four-column structure), and a digital control system. |
| Primary Applications | Curing thermoset composites, laminating wood/veneers, and consolidating flat panels. |
| Critical Parameters | Temperature, pressure uniformity, and dwell time (cycle duration). |
Ready to achieve precise, high-strength bonds and consistent results in your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing robust hot press solutions that deliver the uniform heat and pressure control essential for your material processing needs. Our expertise ensures your applications—from composite curing to high-quality lamination—are a success.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hot press can enhance your manufacturing process and deliver reliable, repeatable quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- How is conventional heating different from induction heating? Direct vs. Indirect Heat Explained
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts



















