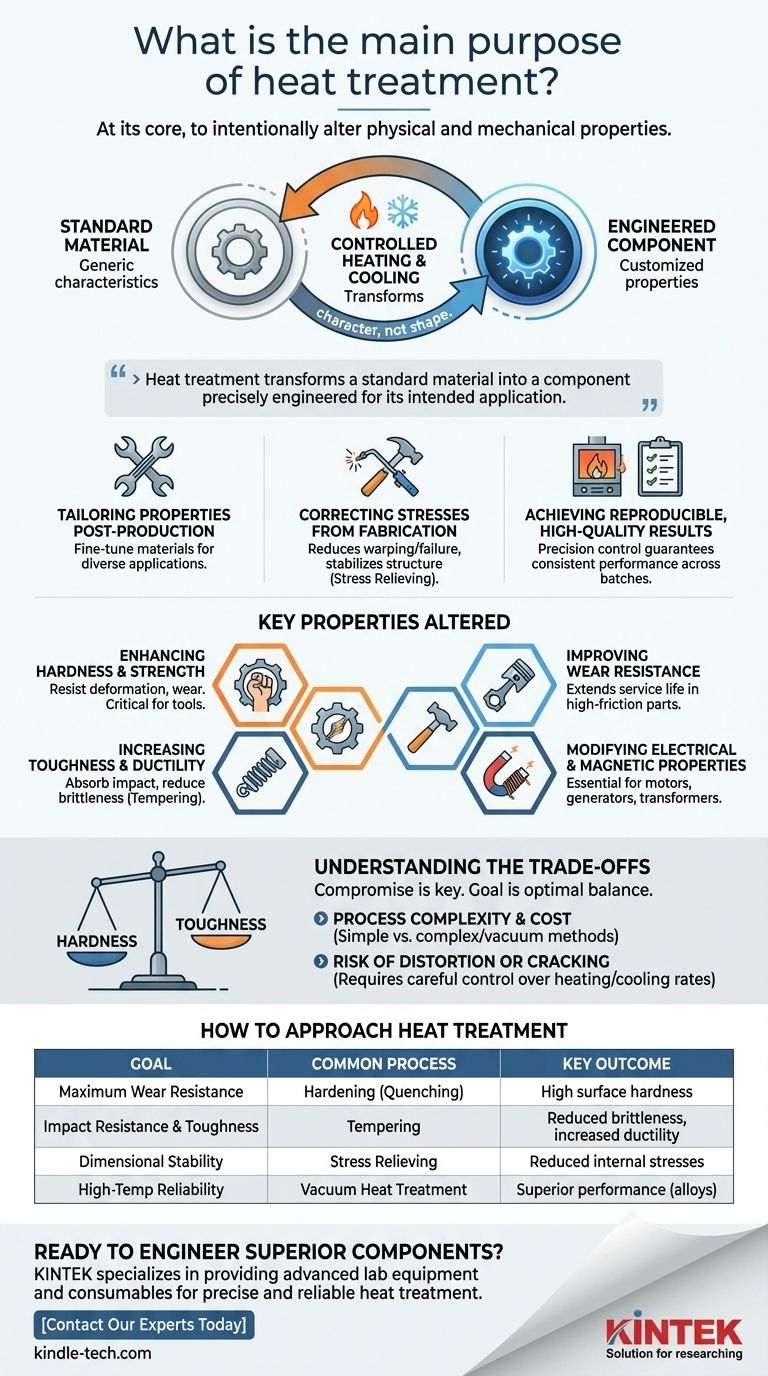
At its core, the main purpose of heat treatment is to intentionally alter the physical and mechanical properties of a material. It is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling metals to change their internal microscopic structure, allowing engineers to customize characteristics like hardness, strength, and ductility to meet specific performance demands.
Heat treatment is not about changing a metal's shape, but about fundamentally changing its character. It transforms a standard material into a component precisely engineered for its intended application, whether that requires extreme hardness, flexibility, or resistance to stress.

Why Heat Treatment is a Critical Manufacturing Step
Heat treatment is a foundational process in metallurgy because it allows for a level of material customization that is otherwise impossible. It enables the creation of parts that can withstand demanding operational environments.
Tailoring Material Properties Post-Production
A single type of steel can be made suitable for vastly different applications through heat treatment. The process allows you to take a metal part that has already been formed and fine-tune its properties to achieve a desired balance of strength, toughness, and durability.
Correcting Stresses from Fabrication
Manufacturing processes like welding, machining, or hot forming introduce significant internal stresses into a material. These stresses can lead to warping or premature failure. Heat treatment, specifically stress relieving, makes the internal structure more stable, reducing these risks.
Achieving Reproducible, High-Quality Results
Modern heat treatment is performed in precisely controlled furnaces that regulate temperature and cooling rates. This precision ensures that every component in a batch achieves the exact same properties, guaranteeing reproducible and reliable performance for critical parts in sectors like aerospace and automotive.
The Key Properties Altered by Heat Treatment
The goal of any heat treatment process is to modify one or more key material properties. The most common objectives fall into a few key categories.
Enhancing Hardness and Strength
One of the most frequent uses of heat treatment is to make a material harder and stronger. This increases a component's ability to resist deformation, scratching, and wear, which is critical for tools, bearings, and gears.
Increasing Toughness and Ductility
While hardness is important, it can sometimes lead to brittleness. Processes like tempering are used after a hardening treatment to increase a material's toughness—its ability to absorb impact without fracturing—and its ductility.
Improving Wear Resistance
For components that experience constant friction, heat treatment can be used to create a very hard, wear-resistant surface. This dramatically extends the service life of parts used in engines and other machinery.
Modifying Electrical and Magnetic Properties
Beyond mechanical characteristics, heat treatment can also be used to enhance a material's electrical conductivity or magnetic properties. This is essential for components used in electric motors, generators, and transformers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it involves balancing competing properties. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for making effective engineering decisions.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Compromise
The most fundamental trade-off in metallurgy is between hardness and toughness. As you increase a metal's hardness, you almost always decrease its toughness, making it more brittle. The goal is often not to maximize one property, but to find the optimal balance for the application.
Process Complexity and Cost
Simple heat treatments are routine and cost-effective. However, achieving superior performance for demanding applications—like engine components in aerospace—requires complex processes like vacuum heat treatment. This adds significant cost and complexity to manufacturing.
Risk of Distortion or Cracking
The very act of heating and cooling a material can cause it to warp or even crack if not done correctly. The process requires careful control over heating rates, hold times, and cooling methods to avoid damaging the component it's meant to improve.
How to Approach Heat Treatment for Your Goal
The right heat treatment strategy is entirely dependent on the final performance requirement of the component.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: A hardening process, such as quenching, will be your starting point to achieve high surface hardness.
- If your primary focus is preventing fracture under impact: A process like tempering is critical to enhance toughness, even if it slightly reduces peak hardness.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability after welding or machining: Stress relieving is essential to remove internal stresses that could cause warping over time.
- If your primary focus is reliability in extreme environments: Specialized methods like vacuum heat treatment for high-performance alloys are necessary to withstand high heat and stress.
Ultimately, heat treatment transforms a generic material into a high-performance component engineered for its specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Common Heat Treatment Process | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Wear Resistance | Hardening (Quenching) | High surface hardness |
| Impact Resistance & Toughness | Tempering | Reduced brittleness, increased ductility |
| Dimensional Stability | Stress Relieving | Reduced internal stresses from fabrication |
| High-Temperature/Extreme Environment Reliability | Vacuum Heat Treatment | Superior performance for aerospace/automotive alloys |
Ready to Engineer Superior Components?
Heat treatment is the key to unlocking the full potential of your materials, transforming standard parts into high-performance components tailored for your specific application. Whether you need to enhance wear resistance, improve toughness, or ensure dimensional stability, the right process is critical.
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise and reliable heat treatment. Our solutions help you achieve reproducible, high-quality results for demanding sectors like aerospace and automotive.
Let's discuss how we can support your material science goals. Contact our experts today to find the perfect heat treatment solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are the requisites of refractories? The Four Pillars for High-Temperature Success
- What is the concept of muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the design and construction of a muffle furnace? A Guide to Its Isolated Heating Chamber
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace work? Achieve Contaminant-Free, Uniform Heating
- What are the precautions for heat in the laboratory? Essential Safety Rules to Prevent Burns and Fires



















