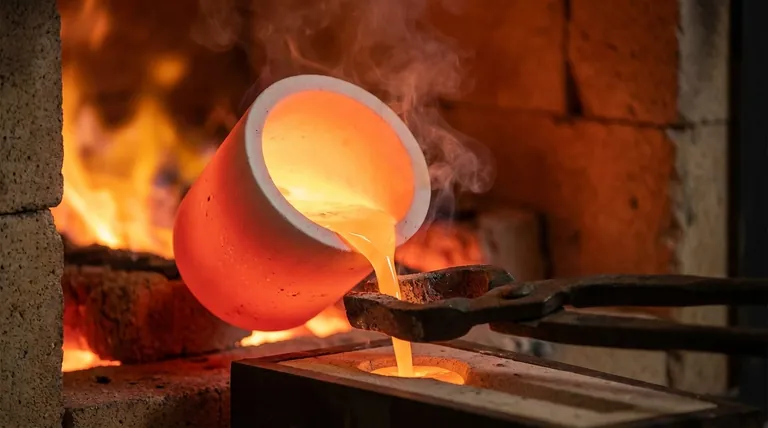
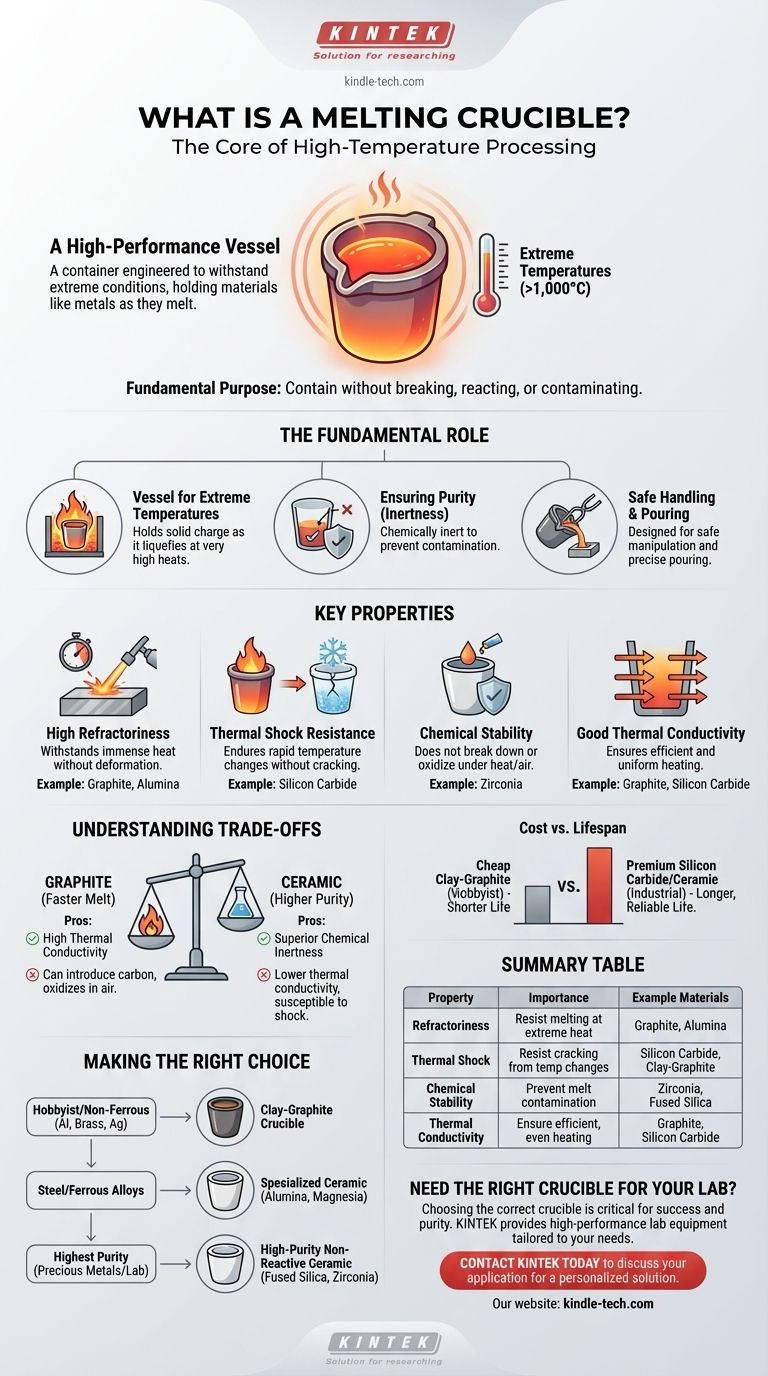
At its core, a melting crucible is a high-performance container designed to withstand extreme temperatures. It serves as a specialized vessel for holding materials—most commonly metals—as they are heated to their melting point. Think of it as a highly durable pot engineered to endure conditions that would destroy any ordinary container.
A crucible's fundamental purpose is to contain a substance during melting without breaking, reacting with it, or contaminating it. Its value lies not just in holding the material, but in ensuring the purity and integrity of the final molten product.

The Fundamental Role of a Crucible
A crucible is more than just a bucket for hot liquid. It is a critical tool in metallurgy, chemistry, and material science, enabling processes that would otherwise be impossible.
A Vessel for Extreme Temperatures
The primary function of a crucible is to hold a solid charge (like scrap metal or pure elements) and contain it safely as it liquefies. This often involves temperatures exceeding 1,000°C (1,832°F) for metals like aluminum and copper, and much higher for iron or platinum.
Ensuring Purity Through Inertness
A crucible must be chemically inert, meaning it does not react with the molten material it holds. This prevents impurities from leaching into the melt, which could ruin the properties of the final cast object, whether it's a gold ring or a high-performance alloy.
Facilitating Safe Handling and Pouring
Crucibles are designed to be manipulated safely at extreme temperatures. Their shapes often incorporate a pouring spout and a profile that can be securely gripped by specialized tongs, allowing a metallurgist to pour the molten material precisely into a mold.
Key Properties of an Effective Crucible
The material a crucible is made from is its most important feature. The choice of material is dictated by the extreme demands of the high-temperature environment.
High Refractoriness
Refractoriness is the ability of a material to withstand immense heat without deforming or melting. A crucible's melting point must be significantly higher than the melting point of the substance it is intended to hold.
Thermal Shock Resistance
The material must be able to endure rapid temperature changes without cracking or shattering. This property, known as thermal shock resistance, is critical, as crucibles are moved from a furnace to a cooler environment for pouring.
Chemical Stability
Beyond being inert, the crucible material must not break down or oxidize when exposed to high heat and air. Materials like graphite, for instance, are highly refractory but can be consumed by oxygen at high temperatures if not protected or used in a controlled atmosphere.
Good Thermal Conductivity
Efficient and even heating is crucial for a consistent melt. Materials with good thermal conductivity, like graphite and silicon carbide, allow heat from the furnace to transfer quickly and uniformly through the crucible walls to the material inside.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single crucible material is perfect for every application. The choice always involves balancing performance, lifespan, and cost.
Graphite vs. Ceramic
Graphite crucibles excel at thermal conductivity, leading to faster and more efficient melts. However, they can introduce carbon into certain alloys and will oxidize in the presence of air at high temperatures.
Ceramic crucibles (made of materials like alumina, zirconia, or clay) offer superior chemical inertness and are better for melting reactive metals or high-purity materials. Their downside is often lower thermal conductivity and a greater susceptibility to cracking from thermal shock.
Cost vs. Lifespan
A cheap clay-graphite crucible might be sufficient for a hobbyist melting aluminum a few times. However, an industrial foundry melting aggressive alloys 24/7 will invest in a premium silicon carbide or pure ceramic crucible that, while expensive, offers a much longer and more reliable service life.
The Hidden Cost of Contamination
Using the wrong crucible is a common and costly mistake. For example, melting platinum in a graphite crucible can introduce carbon impurities, making the final product brittle. A failed or contaminated melt wastes not only the material but also the significant time and energy invested in the heating process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct crucible depends entirely on the material you are melting and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is hobbyist or small-scale casting of non-ferrous metals (like aluminum, brass, or silver): A clay-graphite crucible provides the best combination of cost, durability, and thermal performance.
- If your primary focus is melting steel or ferrous alloys: You need a specialized ceramic crucible, such as alumina or magnesia, that can withstand the higher temperatures and chemical reactions.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest purity for precious metals or lab-grade alloys: A high-purity, non-reactive ceramic crucible (like fused silica, alumina, or zirconia) is the only acceptable choice.
Ultimately, the crucible is the unsung hero of any high-temperature process, providing the stable and inert environment required for transformation.
Summary Table:
| Property | Importance | Example Materials |
|---|---|---|
| High Refractoriness | Withstands extreme heat without melting | Graphite, Alumina |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Resists cracking from rapid temperature changes | Silicon Carbide, Clay-Graphite |
| Chemical Stability | Prevents contamination of the melt | Zirconia, Fused Silica |
| Thermal Conductivity | Ensures efficient, even heating | Graphite, Silicon Carbide |
Need the Right Crucible for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct crucible is critical to the success and purity of your melting process. Whether you're working with precious metals, industrial alloys, or research materials, KINTEK provides high-performance lab equipment tailored to your specific needs.
Our experts can help you select the ideal crucible—be it graphite, ceramic, or silicon carbide—to ensure durability, efficiency, and contamination-free results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution that maximizes your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer with PTFE Crucible and Lid
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of using alumina crucibles as liners in autoclaves? Ensure Purity in High-Pressure Static Tests
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What is the temperature range of alumina crucibles? Key Factors for Safe High-Temp Use
- What are the advantages of using alumina crucibles for the TGA of modified alkyd resins? Ensure Accurate Results
- Why are High-purity Alumina Crucibles selected for corrosion testing? Ensure Data Fidelity in Molten Salt Experiments



















