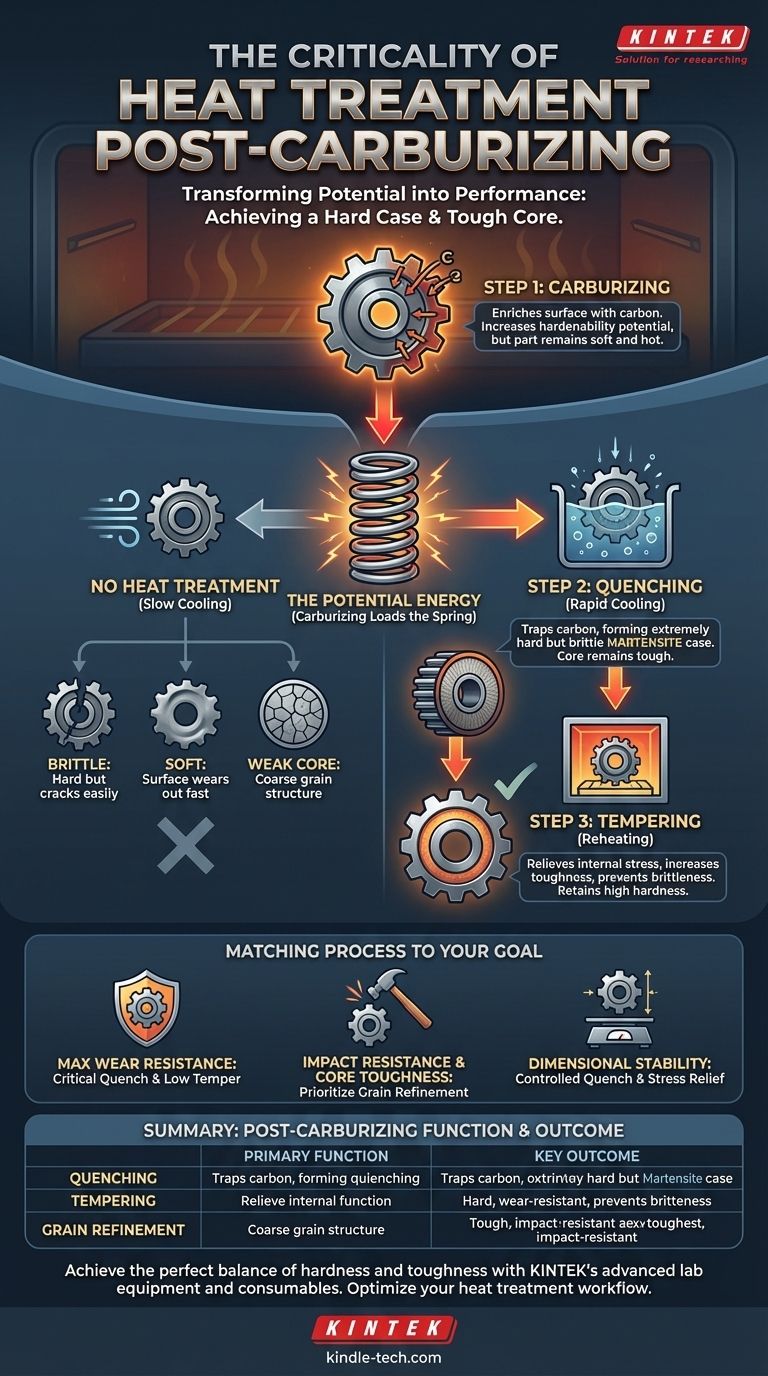
Heat treatment after carburizing is not optional; it is the essential step that achieves the desired material properties. Carburizing itself only enriches the steel's surface with carbon, which increases its hardenability—its potential to become hard. The subsequent quenching and tempering cycles are what actually transform that potential into a hard, wear-resistant surface layer while ensuring the component's core remains tough and ductile.
Think of carburizing as loading a spring. The process adds potential energy (carbon) to the steel's surface, but it's the subsequent quenching and tempering (the release and control) that transforms that potential into the desired outcome: a hard case and a tough core.

The Goal: A Hard Case with a Tough Core
The entire purpose of case hardening is to create a component with two distinct, optimized zones. You need an extremely hard, wear-resistant exterior (the case) to handle friction and abrasion, supported by a softer, more ductile interior (the core) to absorb shock and resist fracture.
What Carburizing Actually Accomplishes
Carburizing is a diffusion process. By heating low-carbon steel in a carbon-rich atmosphere, carbon atoms soak into the surface, creating a high-carbon steel "case" over the original low-carbon core.
This step does not, by itself, make the part significantly harder. At the end of the carburizing cycle, the component is still hot and relatively soft.
The Problem with Stopping After Carburizing
If you were to simply let the component cool slowly in the air after carburizing, the high-carbon case would form a soft microstructure (like pearlite). The part would have a high-carbon surface, but it would lack the hardness needed for virtually any engineering application.
Furthermore, the high temperatures and long duration of the carburizing process cause the steel's crystalline grains to grow large, which reduces the material's overall toughness and strength.
The Critical Role of Post-Carburizing Heat Treatment
The subsequent heat treatment is a carefully controlled two-part process designed to solve these problems and unlock the properties created during carburizing.
Step 1: Quenching for Hardness
After carburizing (and often after a brief temperature adjustment to refine the grain structure), the component is cooled rapidly, or quenched, typically in oil, water, or polymer.
This rapid cooling traps the carbon atoms within the iron crystal lattice of the high-carbon case, forcing the formation of a microstructure called martensite. Martensite is extremely hard and brittle, providing the necessary wear resistance.
Simultaneously, the low-carbon core, which has much lower hardenability, does not transform into brittle martensite. It forms a much softer, tougher microstructure, retaining its ability to absorb impact.
Step 2: Tempering for Toughness
Quenching leaves the martensitic case in a state of high internal stress, making it too brittle for most applications. A minor impact could cause it to shatter.
Tempering is the final, crucial step. The part is reheated to a relatively low temperature (e.g., 150-200°C or 300-400°F) and held for a period of time.
This process relieves the internal stresses from quenching and slightly rearranges the microstructure, drastically increasing the toughness and fracture resistance of the case with only a minor reduction in its peak hardness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Skipping or improperly executing these steps negates the entire purpose of the carburizing process and leads to component failure.
The Brittle Part
A component that is quenched but not tempered will have a hard but dangerously brittle surface. It will likely fail prematurely by cracking or chipping under operational loads.
The Soft Part
A component that is not quenched after carburizing will never form martensite. Its surface will remain soft and will wear out almost immediately in its intended application.
The Weak Core
Improper heat treatment cycles can fail to refine the coarse grain structure that forms during carburizing. This leaves the core weak and susceptible to fracture, even if the surface is hard.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The post-carburizing heat treatment is precisely controlled to achieve specific engineering requirements for the final part.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface wear resistance: The quench is critical to ensure a fully martensitic case, followed by a low-temperature temper to relieve stress without significantly sacrificing hardness.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance and core toughness: The grain refinement cycle before the final quench is paramount, ensuring the low-carbon core has a fine, tough microstructure to absorb shock.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability: Controlled quenching and proper stress relief during tempering are essential to minimize distortion and prevent cracking in complex geometries.
Ultimately, post-carburizing heat treatment is the non-negotiable process that converts the chemical potential of the carbon-rich surface into the superior mechanical performance of the final component.
Summary Table:
| Post-Carburizing Step | Primary Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Quenching | Rapidly cools the steel to form martensite in the high-carbon case. | Creates an extremely hard, wear-resistant surface. |
| Tempering | Reheats the steel to a low temperature to relieve internal stresses. | Increases toughness and fracture resistance, reducing brittleness. |
| Grain Refinement | (Optional) Adjusts temperature before quenching to refine coarse grains. | Enhances core strength and overall material toughness. |
Achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for your components. The precise control of post-carburizing heat treatment is critical to your component's performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for reliable and repeatable heat treatment processes. Let our experts help you optimize your workflow—contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of phased heating and holding protocols in high-temperature furnaces? Enhance Glass Purity
- What is the operating temperature of a furnace? From Home Heating to Industrial Processing
- What function does a vacuum annealing furnace perform for tungsten-diamond coatings? Achieve Strong Metallurgical Bonds
- Can you temper any metal? No, and here’s why the process is exclusive to certain steels.
- Can heat transfer occur in a vacuum? Yes, through radiation, the only way heat travels in space.
- Why is a vacuum oven necessary for drying conductive polymer powders like PEDOT and PANI? Preserve Your Material Purity
- Can you determine the temperature of a vacuum? Unpacking the Physics of 'Empty' Space
- What gas does pyrolysis produce? A Fuel Gas Mixture for Energy & Sustainability



















