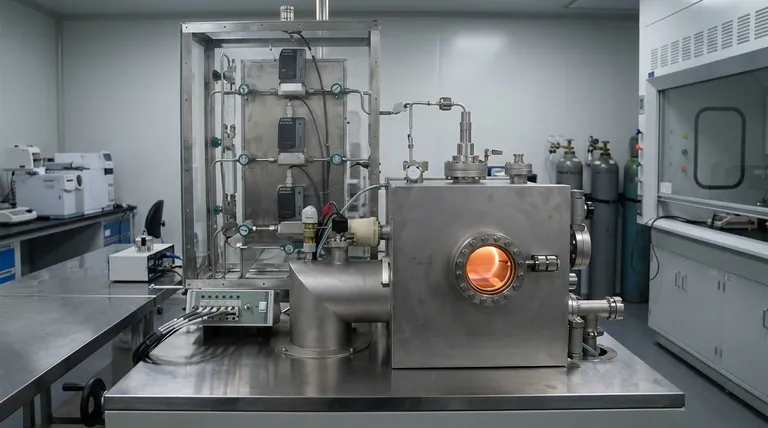
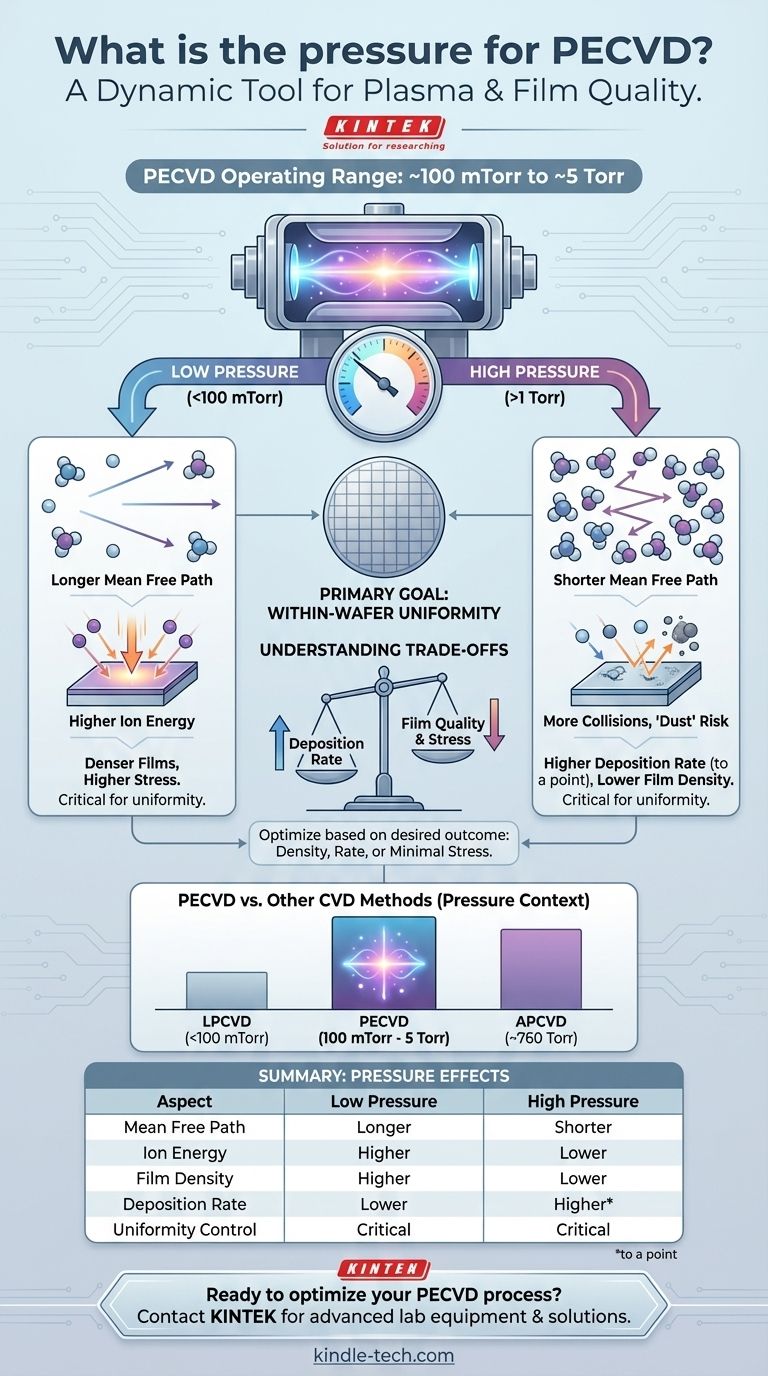
There is no single pressure for PECVD; instead, it operates within a specific low-vacuum range, typically from around 100 millitorr to a few Torr. The exact pressure is a critical process parameter that is carefully optimized for the specific material being deposited. Its primary function is to control the plasma environment to ensure the resulting thin film has excellent uniformity across the entire substrate.
While often called a "low-pressure" process, the pressure in Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a dynamic tool. It's carefully balanced to control the energy and travel path of reactive species, directly influencing the final film's quality, deposition rate, and uniformity.

The Role of Pressure in the PECVD Process
To understand PECVD, you must see pressure not as a static setting, but as a primary lever for controlling the deposition environment. Because PECVD uses plasma instead of high heat to drive the reaction, the pressure inside the chamber dictates the behavior of that plasma.
Defining the Operating Range
PECVD is fundamentally a vacuum deposition process. It operates in a pressure regime that is low compared to atmospheric pressure but often higher than other vacuum techniques like LPCVD (Low-Pressure CVD).
This range, typically 100 mTorr to about 5 Torr, is crucial for creating and sustaining a stable plasma from the reactant gases.
Impact on Mean Free Path
The most important physical concept pressure controls is the mean free path—the average distance a gas molecule or ion travels before colliding with another.
At lower pressures, there are fewer gas molecules, so the mean free path is longer. At higher pressures, the chamber is more crowded, so the mean free path is shorter.
Influence on Plasma and Deposition
The length of the mean free path directly impacts the film's properties. A shorter path (higher pressure) leads to more collisions in the gas phase. This can increase the creation of reactive chemical precursors, but it also reduces the energy of ions hitting the substrate.
A longer path (lower pressure) means ions and radicals are more likely to travel directly to the substrate without collision, striking it with higher energy.
The Goal: Within-Wafer Uniformity
As the references state, the primary goal of pressure optimization is achieving good within-wafer uniformity.
If the pressure is not correct, the reactive species may be depleted before they reach the edges of the wafer, resulting in a film that is thicker in the center. Adjusting pressure, along with gas flow and reactor geometry, ensures all parts of the substrate are coated evenly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pressure for a PECVD process involves balancing competing factors. Changing the pressure to improve one film property will almost certainly affect another.
Pressure vs. Deposition Rate
Generally, increasing pressure can increase the deposition rate up to a certain point by providing more reactant molecules.
However, if the pressure is too high, it can lead to undesirable gas-phase reactions, forming particles ("dust") that fall onto the substrate and create defects in the film.
Pressure vs. Film Quality and Stress
Lower pressures often result in films with higher density. The higher kinetic energy of arriving ions (due to the longer mean free path) can "compact" the growing film, reducing voids.
This ion bombardment, however, can also increase the compressive stress within the film. For some applications, particularly in optics or MEMS, controlling this stress is critical.
PECVD vs. Other CVD Methods
It's helpful to place PECVD in context. Its operating pressure is generally higher than Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD), which can operate in the sub-100 mTorr range.
Compared to Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD), which operates at ~760 Torr, PECVD is a significantly lower-pressure process. The use of plasma is what enables PECVD to achieve high-quality films at lower temperatures than these other methods.
Optimizing Pressure for Your Deposition Goal
The ideal pressure is determined by the desired outcome. There is no universal "best" setting; it must be co-optimized with RF power, temperature, and gas flows for your specific recipe.
- If your primary focus is a dense, high-quality film: Start with a lower pressure to increase ion energy, but monitor film stress carefully.
- If your primary focus is a high deposition rate: Experiment with a higher pressure, but watch for the onset of particle formation and decreased uniformity.
- If your primary focus is minimal film stress: A mid-range or higher pressure may be desirable to reduce ion bombardment and promote a more "chemical" deposition.
Ultimately, mastering the PECVD process means treating pressure as a precise tool to dictate the physics of the plasma and the chemistry of the deposition.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Low Pressure Effect | High Pressure Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Free Path | Longer | Shorter |
| Ion Energy | Higher | Lower |
| Film Density | Higher | Lower |
| Deposition Rate | Lower | Higher (to a point) |
| Uniformity Control | Critical | Critical |
Ready to optimize your PECVD process for superior thin films?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique deposition challenges. Our expertise in plasma-enhanced processes can help you achieve the perfect balance of pressure, power, and gas chemistry for exceptional film uniformity, density, and quality.
Whether you're developing new materials or refining an existing recipe, our team is here to support your success. Contact us today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your PECVD capabilities and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- What materials are deposited in PECVD? Discover the Versatile Thin-Film Materials for Your Application
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is meant by vapor deposition? A Guide to Atomic-Level Coating Technology
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films



















