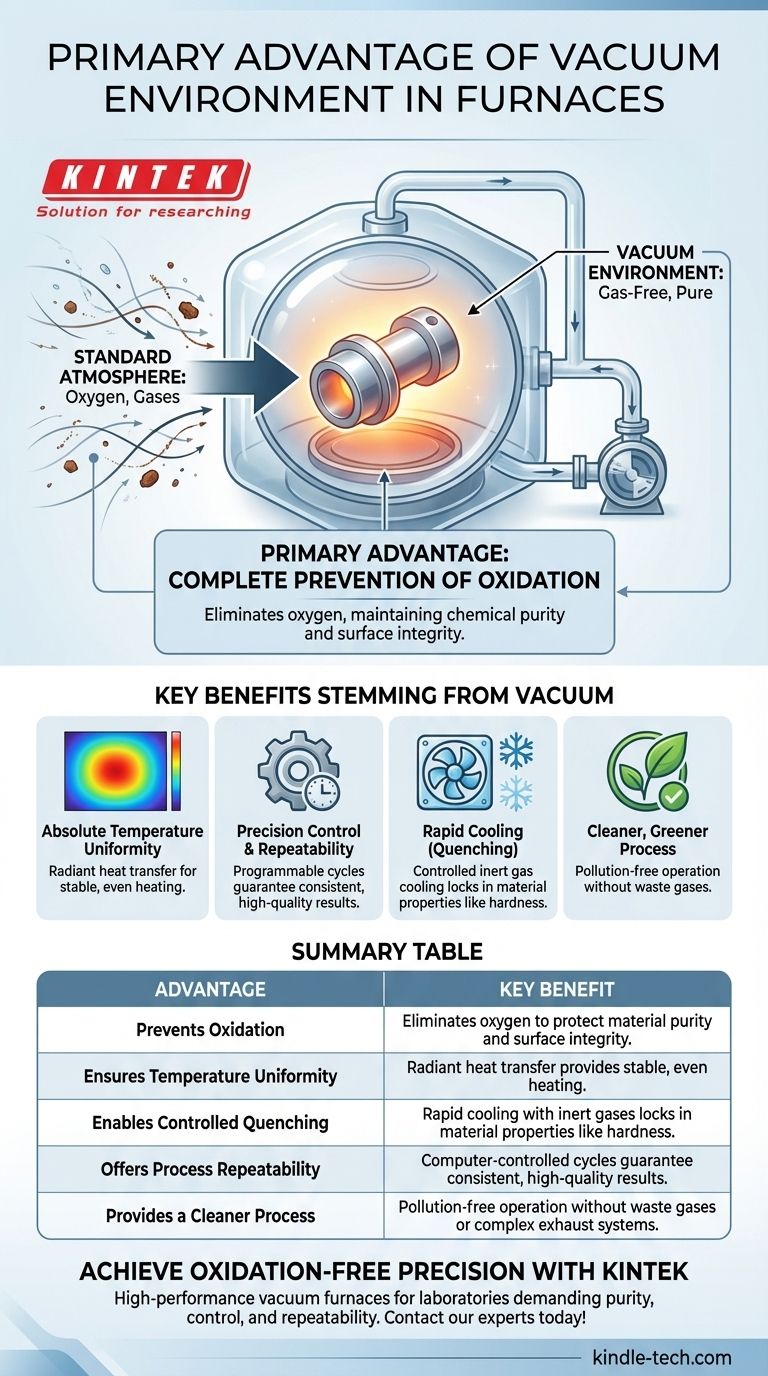
The primary advantage of the vacuum environment in a furnace is the complete prevention of oxidation. By systematically removing air and other gases from the heating chamber, the process eliminates the oxygen that would otherwise react with the material at high temperatures. This ensures the final product maintains its chemical purity and surface integrity.
The core function of the vacuum is not just to create emptiness, but to establish absolute control over the material's environment. This control prevents unwanted chemical reactions, guaranteeing a higher quality and more reliable end product.

Why Preventing Oxidation is Critical
Heating metals in the presence of air triggers a series of undesirable chemical reactions. The vacuum environment is the definitive solution to this fundamental problem in metallurgy.
The Problem with a Standard Atmosphere
When metals are heated to high temperatures in a standard furnace, they react aggressively with the oxygen present in the air.
This rapid chemical reaction is known as oxidation. It forms a brittle, often discolored layer of oxides on the material's surface.
The Impact of Contamination
This oxide layer compromises the quality of the part. It can alter the material's dimensions, weaken its structural integrity, and negatively affect its mechanical or electrical properties.
The vacuum furnace solves this by removing the key reactant—oxygen—before the heating process begins. No oxygen means no oxidation.
Achieving Unmatched Purity
Beyond preventing reactions with air, the vacuum actively pulls unwanted gases and volatile impurities out of the material itself. This process, known as outgassing, results in a final product with a higher purity than could be achieved otherwise.
Key Benefits Stemming from the Vacuum Environment
The controlled, gas-free environment created by the vacuum enables several other significant advantages that define modern heat treatment.
Absolute Temperature Uniformity
In a vacuum, heat transfer occurs primarily through radiation, not convection (which relies on gas movement). This allows for exceptionally uniform and stable temperatures, which is critical for ensuring every part of the component receives the exact same thermal treatment.
Precision Control and Repeatability
Modern vacuum furnaces are computer-controlled. The process is highly programmable, from the pump-down rate to the precise heating temperature and duration. This ensures that every cycle is identical, guaranteeing metallurgical repeatability for high-specification components.
The Power of Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
After the heating cycle, the furnace can be rapidly backfilled with a high-purity inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon. This allows for controlled, rapid cooling, a process known as quenching, which is essential for locking in specific material properties like hardness.
A Cleaner, Greener Process
Vacuum furnaces do not produce waste gases or fumes during operation. This makes them a pollution-free technology that meets stringent environmental standards without requiring complex and costly exhaust treatment systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the vacuum furnace is a specialized piece of equipment with specific considerations.
Increased System Complexity
A vacuum furnace requires a system of pumps, seals, and sophisticated controls to create and maintain the vacuum. This makes it inherently more complex than a conventional atmospheric furnace.
Longer Cycle Times
The step of pumping all the air out of the chamber takes time, which can extend the total process cycle compared to simply heating a part in an atmospheric furnace.
Higher Initial Cost
The precision engineering and complex systems involved mean that vacuum furnaces typically represent a higher initial investment and can have higher maintenance costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vacuum furnace hinges on the required quality and properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is pristine surface finish and material purity: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable, as it is the only way to completely prevent oxidation and scaling.
- If your primary focus is achieving advanced metallurgical properties: The unmatched temperature uniformity and controlled quenching capabilities provide superior results and repeatability.
- If your primary focus is low-cost processing where surface oxidation is acceptable: A conventional atmospheric furnace may be a more economical solution for less critical applications.
Ultimately, choosing a vacuum furnace is a decision to prioritize control and quality above all else.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents Oxidation | Eliminates oxygen to protect material purity and surface integrity. |
| Ensures Temperature Uniformity | Radiant heat transfer provides stable, even heating. |
| Enables Controlled Quenching | Rapid cooling with inert gases locks in material properties like hardness. |
| Offers Process Repeatability | Computer-controlled cycles guarantee consistent, high-quality results. |
| Provides a Cleaner Process | Pollution-free operation without waste gases or complex exhaust systems. |
Ready to achieve oxidation-free precision and superior material quality in your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance vacuum furnaces designed for laboratories that demand the highest standards of purity, control, and repeatability. Our equipment ensures your materials maintain their integrity and properties, batch after batch.
Let us help you enhance your heat treatment processes. Contact our experts today to find the perfect vacuum solution for your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the role of vacuum induction melting in Fe-20Cr-25Ni-Nb steel? Achieve High-Purity Alloy Precision
- What are the two types of induction furnace? Coreless vs. Channel for Your Melting Needs
- What are the parts of induction furnace? A Complete Breakdown of the Core System
- What is the difference between coreless and channel induction furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Melting Job
- What is the highest temperature of an induction furnace? Discover the limits for your materials
- What role does an arc melting furnace play in HEA synthesis? Achieve High-Purity NiCoFeCr and NiCoFeCrMn Alloys
- What is the difference between flame brazing and induction brazing? Precision vs. Flexibility for Your Brazing Needs
- What role does a Vacuum Induction Melting furnace play in 12% Cr martensitic steel? Achieve Ultra-Pure Alloy Control



















