At its core, furnace brazing is a semi-automated metal-joining process where an entire assembly is heated in a controlled furnace. This heat melts a filler metal alloy, which flows into the joints between components via capillary action. As the assembly cools, the filler solidifies, creating a strong, clean, and repeatable metallurgical bond across potentially thousands of joints simultaneously.
The critical distinction of furnace brazing is its use of a controlled atmosphere or vacuum furnace. This isn't simply about heating; it's a precise method that prevents oxidation, enabling the creation of exceptionally clean and strong joints in high volumes, especially for complex designs or reactive metals.

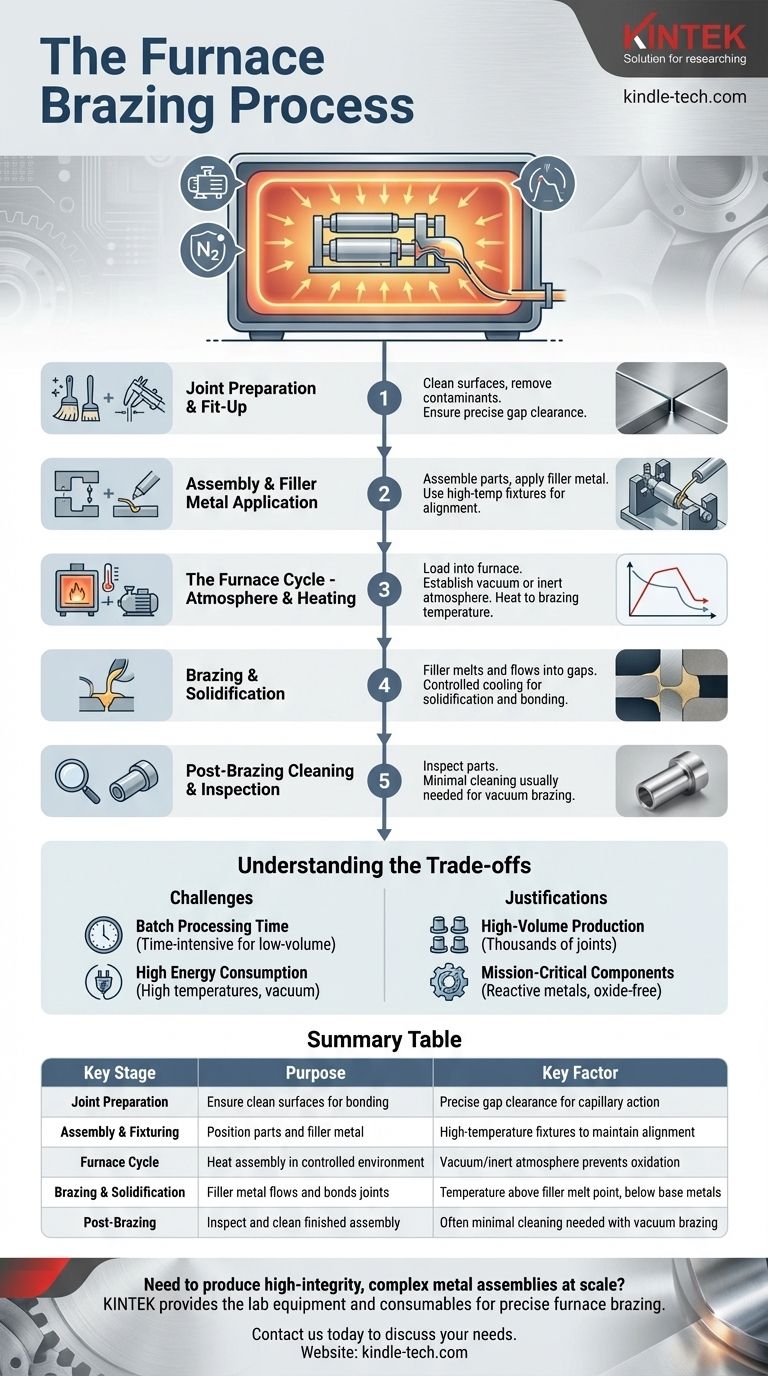
The Furnace Brazing Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Furnace brazing is a systematic, batch-oriented process. Each step is critical for achieving a successful, high-integrity bond.
Step 1: Joint Preparation and Fit-Up
Before any heating occurs, the components must be meticulously prepared. All surfaces to be joined are thoroughly cleaned to remove oils, oxides, and other contaminants that could interfere with the bond.
Equally important is ensuring the correct gap clearance between the parts. The gap must be precise enough to allow the molten filler metal to be drawn in by capillary action but not so large that it fails to fill the joint completely.
Step 2: Assembly and Filler Metal Application
The cleaned parts are assembled into their final configuration. The brazing filler metal, which can be in the form of a paste, wire, or pre-formed shim, is applied at or near the joints.
To maintain precise alignment during the heating cycle, parts are often held in place using specialized fixtures or clamps. These fixtures must be able to withstand the high temperatures of the furnace without distorting.
Step 3: The Furnace Cycle - Atmosphere and Heating
The entire assembly (or a batch of many assemblies) is loaded into the furnace. This is the defining stage of the process.
The furnace is sealed, and all air is pumped out to create a vacuum, or it is filled with a controlled, inert atmosphere. This step is crucial because it eliminates oxygen, which would otherwise cause the base metals to oxidize at high temperatures and prevent a successful braze.
Once the protective environment is established, the furnace begins to heat the batch to the specified brazing temperature, which is above the melting point of the filler alloy but below the melting point of the base metals.
Step 4: Brazing and Solidification
At the brazing temperature, the filler metal melts and flows into the tight gaps of the joints. The controlled atmosphere ensures the metal surfaces remain clean, allowing the molten alloy to "wet" the surfaces and be pulled through the entire joint.
After a predetermined time at temperature, the assembly is cooled in a controlled manner. This might involve slow cooling within the furnace or a more rapid "quench" to achieve desired metallurgical properties in the finished part. As it cools, the filler metal solidifies, creating a permanent bond.
Step 5: Post-Brazing Cleaning and Inspection
Once the batch has cooled and is removed from the furnace, the parts are inspected. In most cases, parts brazed in a vacuum furnace are exceptionally clean and require no further processing. If necessary, any remaining flux or excess filler can be removed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, furnace brazing is not universally applicable. Understanding its operational realities is key to using it effectively.
Batch Processing Time
Furnace brazing is a batch process, not a continuous one. The full cycle of loading, pumping down the vacuum, heating, brazing, cooling, and unloading is time-intensive. This makes it less suitable for low-volume, rapid-turnaround work.
High Energy Consumption
Heating a large furnace chamber to temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F) and maintaining a vacuum requires a significant amount of energy. This contributes to the overall cost of the process.
Justification is Application-Dependent
The time and energy costs are most easily justified in two scenarios: high-volume production, where thousands of joints can be made at once, or for mission-critical components made from materials like titanium or stainless steel that are highly reactive to oxygen and demand a pristine, oxide-free joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's specific goals and constraints.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex assemblies: Furnace brazing is ideal, as it allows for the simultaneous creation of multiple, consistent joints on a massive scale.
- If your primary focus is joining oxygen-reactive materials (e.g., titanium): The vacuum environment of a furnace brazer is non-negotiable for preventing oxide formation and ensuring a robust metallurgical bond.
- If your primary focus is maintaining tight dimensional tolerances: Furnace brazing is superior to welding, as the uniform heating and lack of base metal melting minimize part distortion.
By understanding the complete furnace brazing cycle, you can confidently leverage its unique strengths to produce robust, high-integrity components at scale.
Summary Table:
| Key Stage | Purpose | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Joint Preparation | Ensure clean surfaces for bonding | Precise gap clearance for capillary action |
| Assembly & Fixturing | Position parts and filler metal | High-temperature fixtures to maintain alignment |
| Furnace Cycle | Heat assembly in controlled environment | Vacuum/inert atmosphere prevents oxidation |
| Brazing & Solidification | Filler metal flows and bonds joints | Temperature above filler melt point, below base metals |
| Post-Brazing | Inspect and clean finished assembly | Often minimal cleaning needed with vacuum brazing |
Need to produce high-integrity, complex metal assemblies at scale?
Furnace brazing is the ideal solution for joining reactive materials like titanium or creating thousands of consistent joints simultaneously. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables that make this precise process possible, serving the exacting needs of modern laboratories and manufacturing.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your brazing capabilities and deliver superior results for your mission-critical projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the dangers of pyrolysis? Managing Environmental, Operational, and Chemical Risks
- What is the purpose of using a precision furnace for glass stress relief? Ensure Durability in Molded Glass
- What role does a laboratory vacuum annealing furnace play in HEA treatment? Ensure Purity and Phase Stability
- What is the cost of a vacuum annealing furnace? Find the Right Price for Your Lab or Production Needs
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum annealing furnace play in Zircaloy post-treatment? Enhance Oxide Stability
- Can all metals be annealed? Mastering the Thermal Process for Optimal Material Properties
- What are the factors of pyrolysis? Balancing Technical and Economic Levers for Success
- What are the different design schemes and common mediums used for gas cooling in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process



















